Pantoate-beta-alanine ligase
Pantothenate synthetase (PS), isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, catalyses the ATP-dependent condensation between pantoate and beta-alanine to form pantothenate. This is the last step in the biosynthesis of pantothenate, which is required for CoA synthesis. The reaction proceeds by a Bi Uni Uni Bi Ping Pong kinetic mechanism. PS is a potential drug target for the treatment of tuberculosis.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P9WIL5
 (6.3.2.1)
(6.3.2.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2a84
- Crystal structure of A Pantothenate synthetase complexed with ATP
(1.55 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.620
 3.30.1300.10
3.30.1300.10  (see all for 2a84)
(see all for 2a84)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.3.2.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
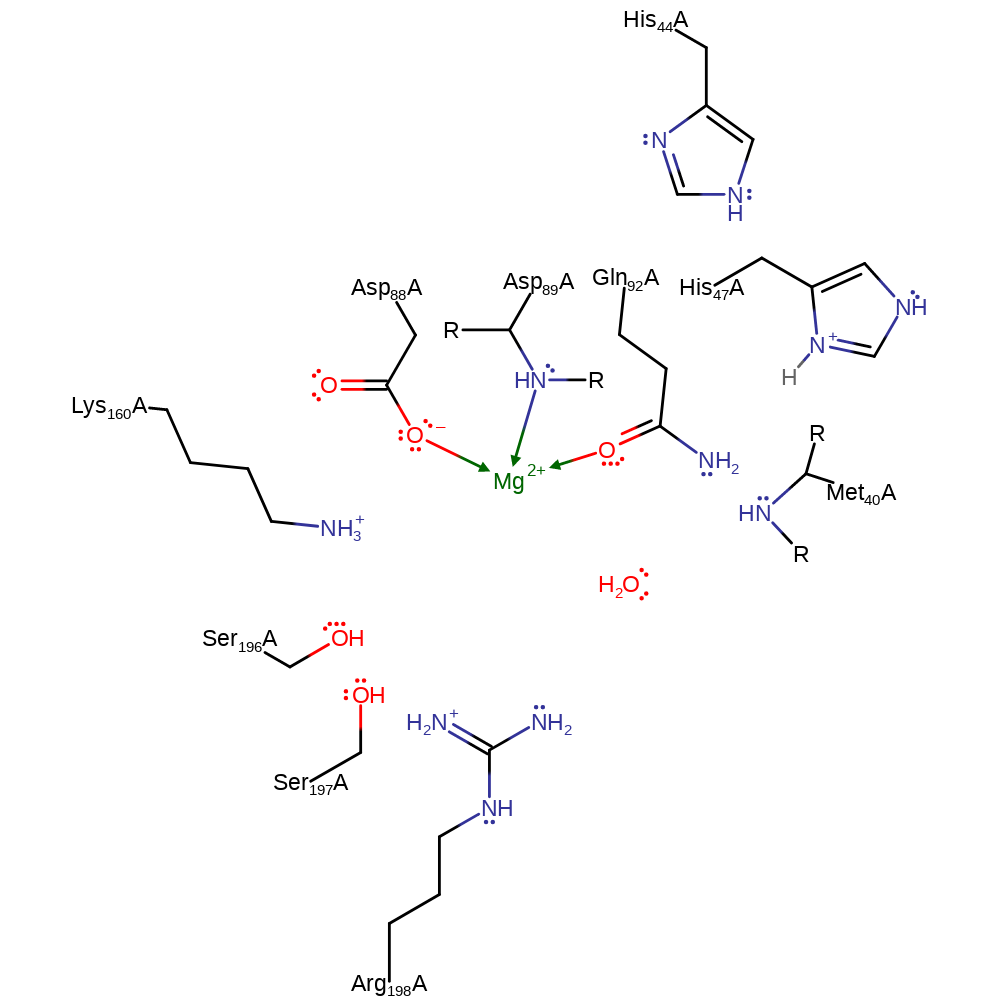
The carboxyl oxygen of pantoate attacks the alpha-phosphate of ATP in an in-line nucleophilic attack to give pantoyl adenylate and pyrophosphate. The transition state is stabilised by a number of interactions with residues and with a magnesium ion bound to the three phosphate groups. His47 donates a proton to the pyrophosphate leaving group. The amino group of beta-alanine is the nucleophile for attack on the carbonyl carbon of pantoyl adenylate to give pantothenate and AMP.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2a84) | ||
| Met40 (main-N) | Met40A (main-N) | Met 40 forms a hydrogen bond to the alpha-phosphate of ATP in the transition state of the adenylation reaction, thus stabilising it. It may also stabilise the transition state of the second reaction in the same way. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His44 | His44A | His44 is hydrogen bonded to the beta-phosphate of ATP and so can stabilise the transition state of the adenylation reaction. It is part of the HIGH motif. | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His47 | His47A | His47 donates a proton to the pyrophosphate leaving group during adenylation. It also stabilises the transition state of this reaction by hydrogen bonding to the beta-phosphate. It is part of the HIGH motif. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg198 | Arg198A | Arg198 interacts with the gamma-phosphate of ATP during the adenylation step and stabilises the transition state. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser196 | Ser196A | Ser196 interacts with the gamma-phosphate of ATP during the adenylation step and stabilises the transition state. It is part of the KSMKS motif. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser197 | Ser197A | Ser197 interacts with the gamma-phosphate of ATP during the adenylation step and stabilises the transition state. It is part of the KSMKS motif. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys160 | Lys160A | Lys160 interacts with the beta-phosphate of ATP during the adenylation step and stabilises the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp89 (main-N), Asp88, Gln92 | Asp89A (main-N), Asp88A, Gln92A | Forms the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Wang S et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 1554-1561. Crystal Structure of the Pantothenate Synthetase fromMycobacterium tuberculosis, Snapshots of the Enzyme in Action†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi051873e. PMID:16460002.
- Xu Z et al. (2014), Bioorg Med Chem, 22, 1726-1735. Reaction intermediate analogues as bisubstrate inhibitors of pantothenate synthetase. DOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2014.01.017. PMID:24507827.
- Satoh A et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 6400-6410. Substrate-Induced Closing of the Active Site Revealed by the Crystal Structure of Pantothenate Synthetase fromStaphylococcus aureus. DOI:10.1021/bi1004206. PMID:20568730.
- Ciulli A et al. (2008), Chembiochem, 9, 2606-2611. Inhibition ofMycobacterium tuberculosisPantothenate Synthetase by Analogues of the Reaction Intermediate. DOI:10.1002/cbic.200800437. PMID:18821554.
- Zheng R et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 7171-7178. Active Site Residues inMycobacterium tuberculosisPantothenate Synthetase Required in the Formation and Stabilization of the Adenylate Intermediate†. DOI:10.1021/bi049676n. PMID:15170354.
- Wang S et al. (2003), Protein Sci, 12, 1097-1108. Crystal structures of a pantothenate synthetase fromM. tuberculosisand its complexes with substrates and a reaction intermediate. DOI:10.1110/ps.0241803. PMID:12717031.
- Saraste M et al. (1990), Trends Biochem Sci, 15, 430-434. The P-loop — a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. DOI:10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. PMID:2126155.
- Leatherbarrow RJ et al. (1987), Biochemistry, 26, 8524-8528. Investigation of transition-state stabilization by residues histidine-45 and threonine-40 in the tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase. DOI:10.1021/bi00400a005. PMID:3126804.

Step 1. The carboxylate oxygen is involved in in-line nucleophilic attack on the alpha-phosphate of ATP to produce pyrophosphate and a pantoyl adenylate intermediate. The pyrophosphate is protonated by His147.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser196A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg198A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His44A | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser197A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His47A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp88A | metal ligand |
| Gln92A | metal ligand |
| Met40A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp89A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Lys160A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His47A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer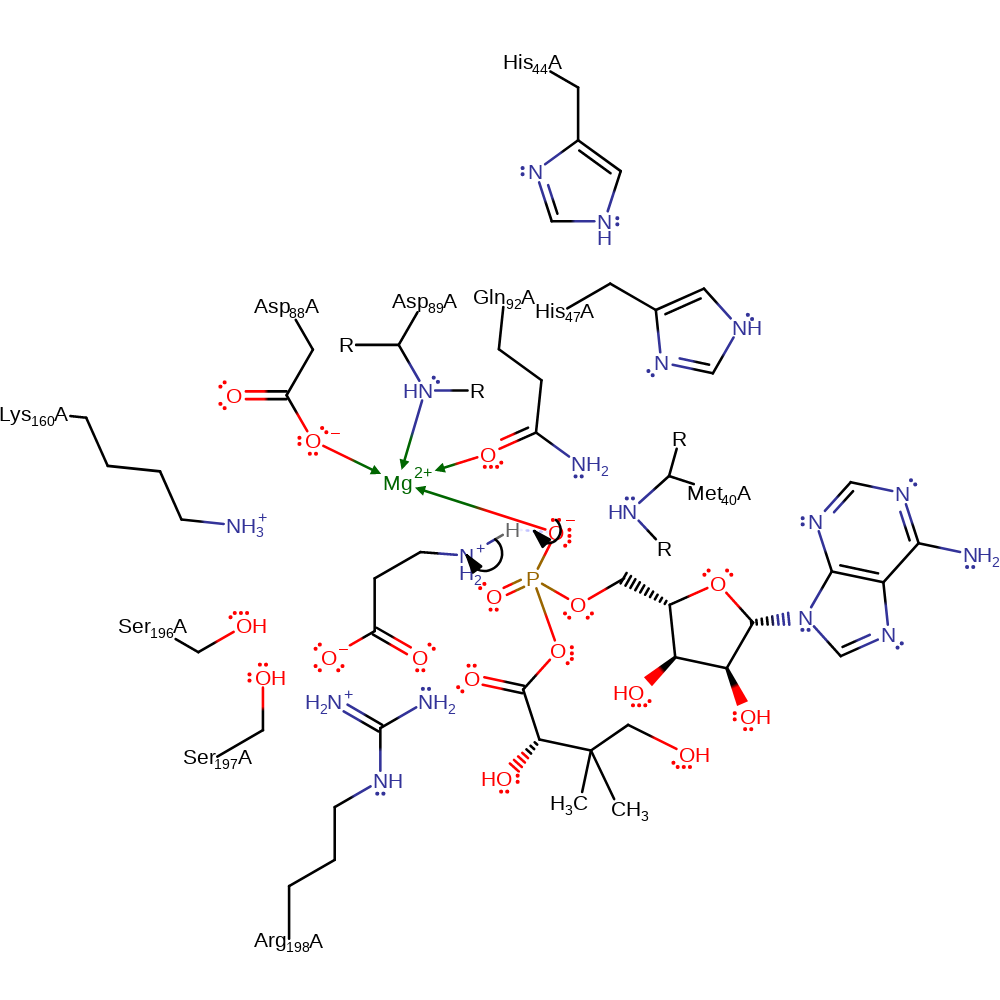
Step 2. The phosphate group of the pantoyl adenylate forms a hydrogen-bond with the amine group of the beta-alanine substrate, deprotonating it to make the beta-alanine a better nucleophile
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser196A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg198A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His44A | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser197A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His47A | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp88A | metal ligand |
| Gln92A | metal ligand |
| Asp89A (main-N) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer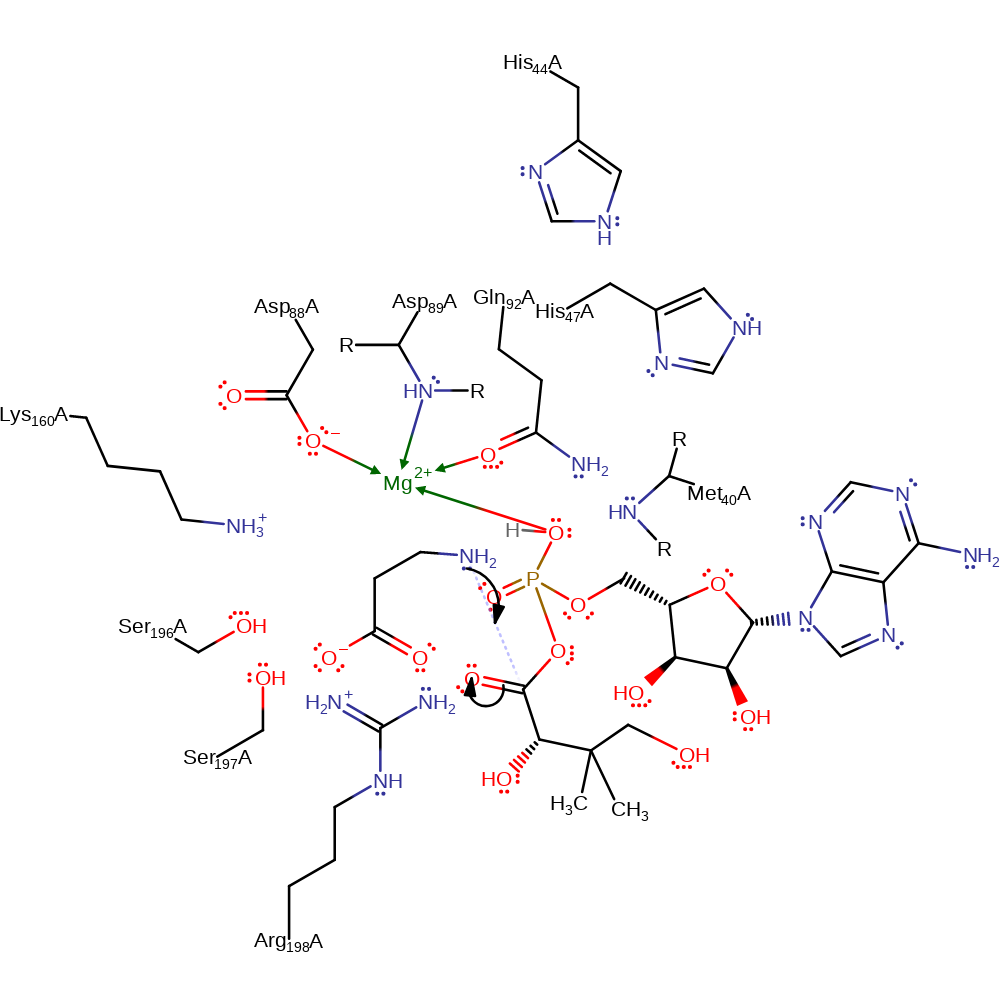
Step 3. Beta-alanine initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl of the pantoyl adenylate intermediate to form a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser196A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg198A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His44A | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser197A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His47A | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp88A | metal ligand |
| Gln92A | metal ligand |
| Asp89A (main-N) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition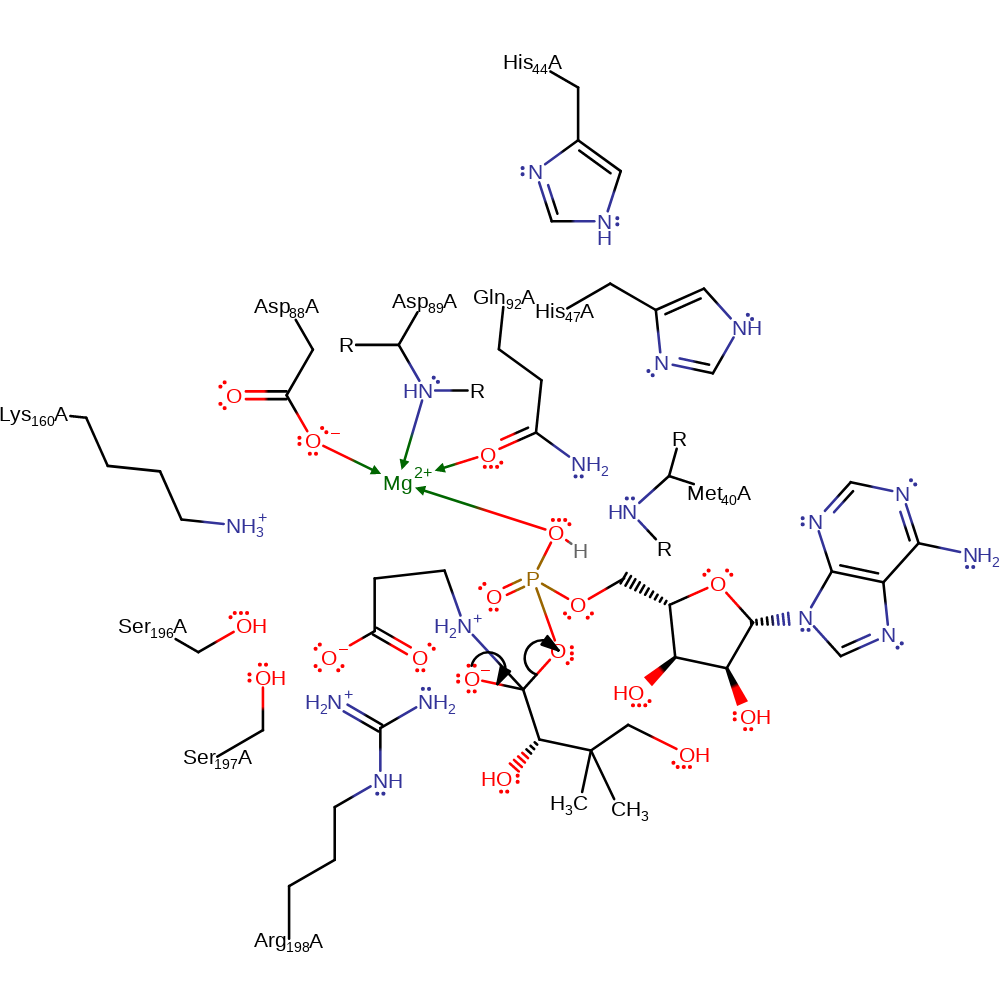
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses to eliminate AMP and the product, pantothenate, which almost immediately dissociates from the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser196A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg198A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His44A | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser197A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His47A | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp89A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Asp88A | metal ligand |
| Gln92A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate baseCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His44A | van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His47A | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp88A | metal ligand |
| Gln92A | metal ligand |
| Asp89A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| His47A | proton acceptor |







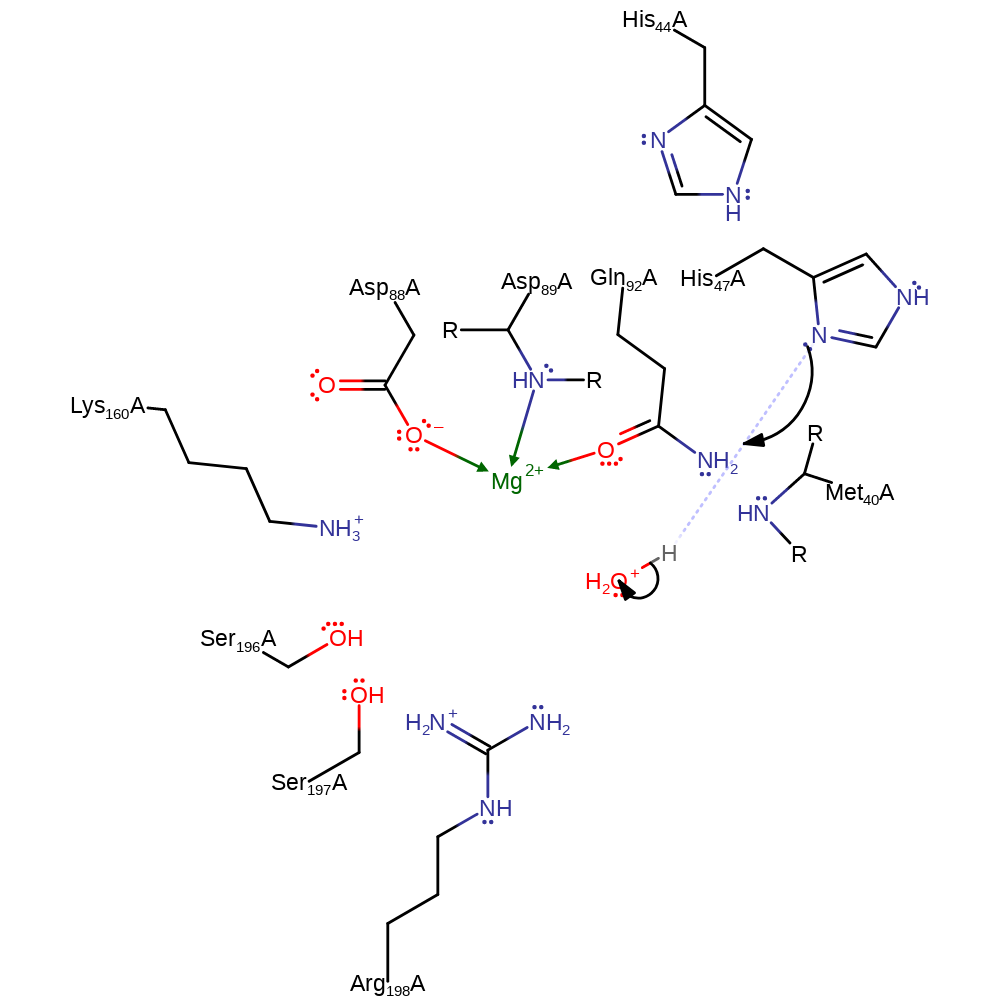
 Download:
Download: