Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase (prokaryotic)
S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase (AdoMetDC) isolated from Thermotoga maritima is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet or SAM) to S-adenosyl-5'-(3-methylthiopropylamine) (dcAdoMet). AdoMetDC is regulatory enzyme in the biosynthesis of spermine and spermidine. It is a class 1B AdoMetDC and belongs to a small family of decarboxylating enzymes that act on amino acids using bound pyruvate as an electron sink. AdoMetDC is synthesised as a proenzyme and must undergo self-maturation by nonhydrolytic serinolysis. It is during this process that the pyruvate group is formed at the carboxy terminus of the alpha chain.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9WZC3
 (4.1.1.50)
(4.1.1.50)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Thermotoga maritima MSB8 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1vr7
- Crystal structure of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase proenzyme (TM0655) from THERMOTOGA MARITIMA at 1.2 A resolution
(1.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.90.10
 (see all for 1vr7)
(see all for 1vr7)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.1.50)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Step 13
- Step 14
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
Nonhydrolytic serinolysis: Ser63 acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl of Glu62. The oxyoxazolidine intermediate rearranges into an ester intermediate. His68 removes the C-alpha proton from Ser63 causing beta-elimination to form the C-terminus of the beta-chain and the terminal dehydroalanine residue of the alpha chain. The latter tautomerises into an imine and is hydrolysed to form the terminal pyruvoyl residue of the alpha-chain. AdoMet decarboxylation: the pyruvoyl prosthetic group forms a Schiff base with the alpha-amino group of AdoMet. This prompts the loss of the alpha-carboxylate to form an extended enolate system with the negative charge residing on the amide oxygen of the pyruvoyl group. The carbonyl reforms and the alpha-carbon of the intermediate accepts a proton from Cys83. The Schiff base is then hydrolysed and dcAdoMet is released.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1vr7) | ||
| Cys83 | Cys83(95)A | Cys83 may stabilise the formation of the oxyoxazolidine intermediate in nonhydrolytic serinolysis through a hydrogen bond to the exocyclic oxygen. Cys83 acts a proton donor for the decarboxylated Schiff base during AdoMet decarboxylation. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, polar interaction, proton donor |
| Glu62 (main-C) | Glu62(74)A (main-C) | Involved in the autocatalytic serinolysis that results in the formation of the pyruvyl cofactor and C-terminus carboxylate at Glu62. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, electrophile |
| Ser63 | Ser63(75)A | Ser63 is the nucleophile for the protocleavage reaction and is subsequently converted to a pyruvoyl residue. It forms a Schiff base with the alpha-amino group of SAM, prompting decarboxylation. The Schiff base is then hydrolysed. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, polar interaction, proton donor |
| His68 | His68(80)B | His68 removes the C-alpha proton from Ser63 in the ester intermediate during nonhydrolytic serinolysis. This causes beta-elimination and strand cleavage. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser55 | Ser55(67)B | Ser55 is thought to stabilise the oxyoxazolidine intermediate in nonhydrolytic serinolysis by forming a hydrogen bond to the exocyclic oxygen. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
intramolecular electrophilic addition, proton transfer, cyclisation, intermediate formation, intramolecular rearrangement, decyclisation, bimolecular elimination, tautomerisation (not keto-enol), bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydrolysis, intramolecular elimination, deamination, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, inferred reaction step, bimolecular homolytic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, cofactor used, dehydration, schiff base formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decarboxylation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Ekstrom JL et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 9495-9504. Structure of a human S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase self-processing ester intermediate and mechanism of putrescine stimulation of processing as revealed by the H243A mutant. DOI:10.2210/pdb1jl0/pdb. PMID:11583148.
- Lee BI et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 340, 1-7. Crystal Structure of the Schiff Base Intermediate Prior to Decarboxylation in the Catalytic Cycle of Aspartate α-Decarboxylase. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.04.049. PMID:15184017.
- Toms AV et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 33837-33846. Evolutionary Links as Revealed by the Structure of Thermotoga maritima S-Adenosylmethionine Decarboxylase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m403369200. PMID:15150268.
- Xiong H et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 2462-2470. Role of Cysteine-82 in the Catalytic Mechanism of HumanS-Adenosylmethionine Decarboxylase†. DOI:10.1021/bi9825201. PMID:10029540.

Step 1. First step of the non-hydrolytic serinolysis process. The hydroxyl side chain of Ser63 is involved in nucleophilic attack on the main chain carbonyl of Glu62 to form an oxyoxazolidine intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu62(74)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser55(67)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu62(74)A (main-C) | proton acceptor |
| Ser63(75)A | nucleophile |
| Glu62(74)A (main-C) | electrophile |
| Ser63(75)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, proton transfer, cyclisation, intermediate formation
Step 2. Part of the non-hydrolytic serinolysis process. The oxyoxazolidine intermediate rearranges to form the ester intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser55(67)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu62(74)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond donor, covalently attached |
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, covalently attached |
Chemical Components
intramolecular rearrangement, proton transfer, decyclisation, intermediate formation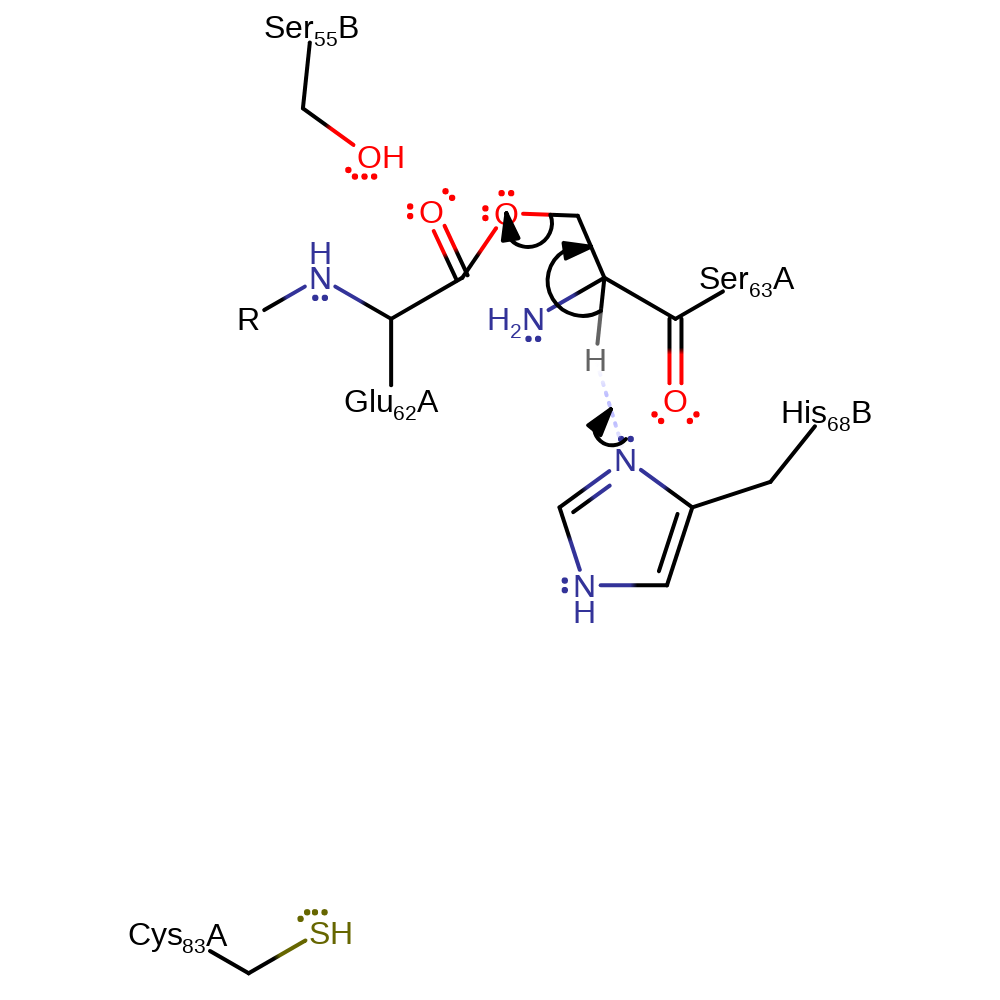
Step 3. Part of the non-hydrolytic serinolysis process. His68 deprotonates the C-alpha of Ser63 causing beta-elimination to form the C-terminus of the beta chain and the terminal dehydroalanine residue of the alpha chain.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser55(67)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu62(74)A (main-C) | covalently attached |
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His68(80)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, intermediate formation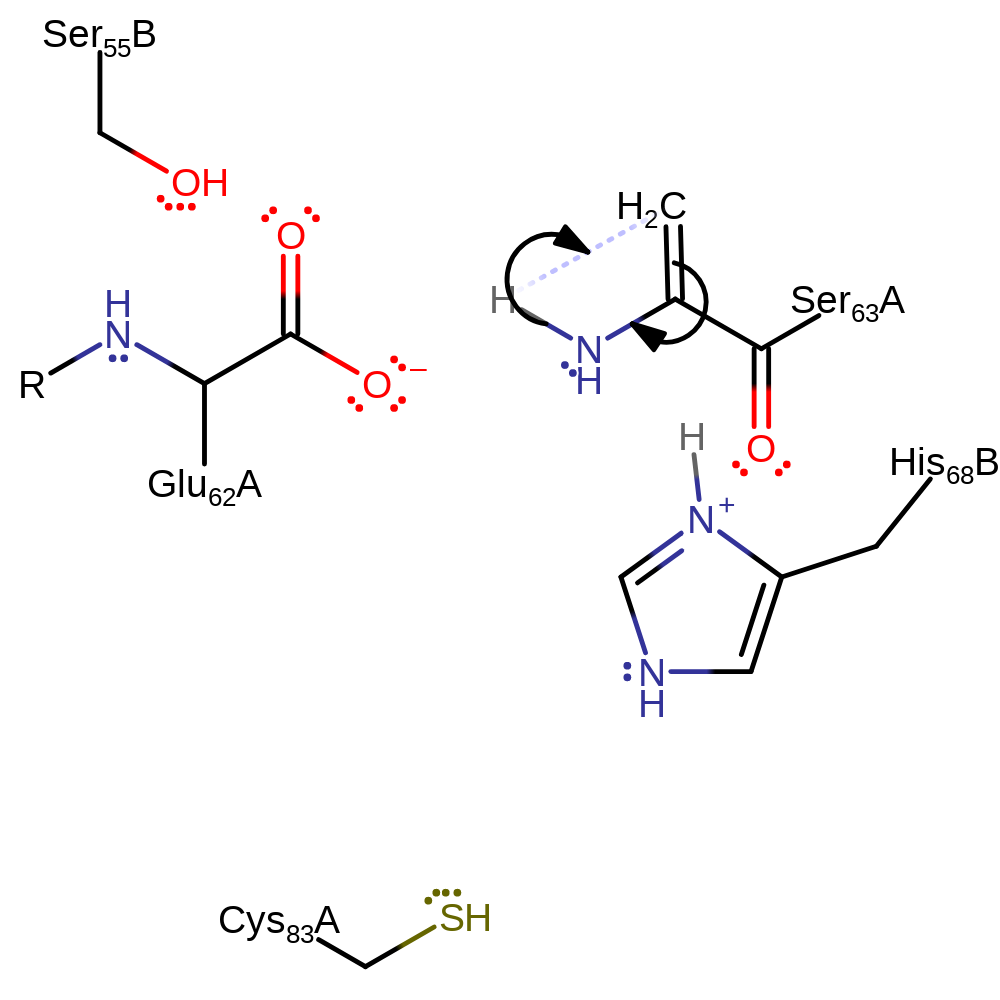
Step 4. Part of the non-hydrolytic serinolysis process. The dehydroalanine residue tautomerises into an imine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His68(80)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate formation
Step 5. Part of the non-hydrolytic serinolysis process. Water is involved in nucleophilic attack on the imine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His68(80)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, hydrolysis, intermediate formation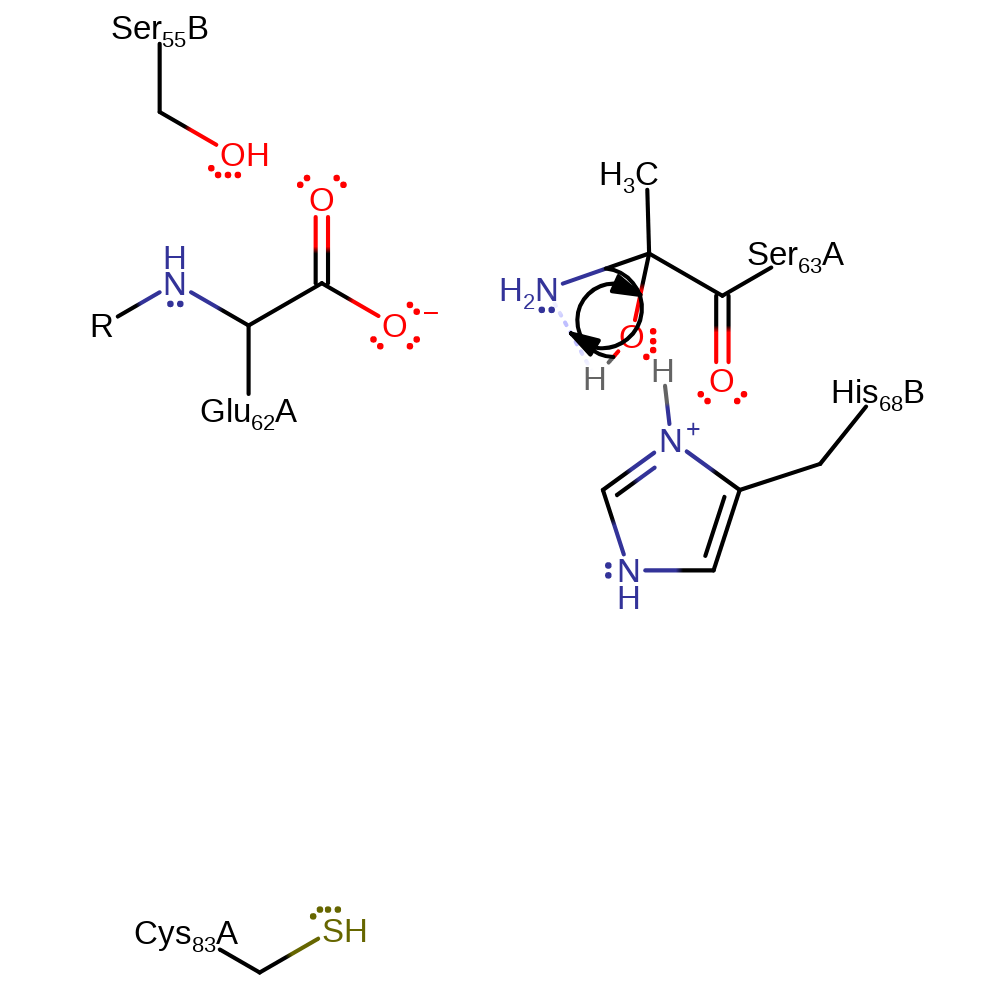
Step 6. Final step of the non-hydrolytic serinolysis process. Intramolecular elimination of ammonia to form the pyruvoyl residue.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His68(80)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, deamination, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated
Step 7. First step of Schiff base formation. The amine group is deprotonated by a base, assumed to be ammonia due to lack of further evidence.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, inferred reaction step
Step 8. Second step of the Schiff base formation. The amine of S-adenosyl-L-methionine is involved in nucleophilic attack on the terminal carbonyl of the pyruvoyl residue.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, cofactor used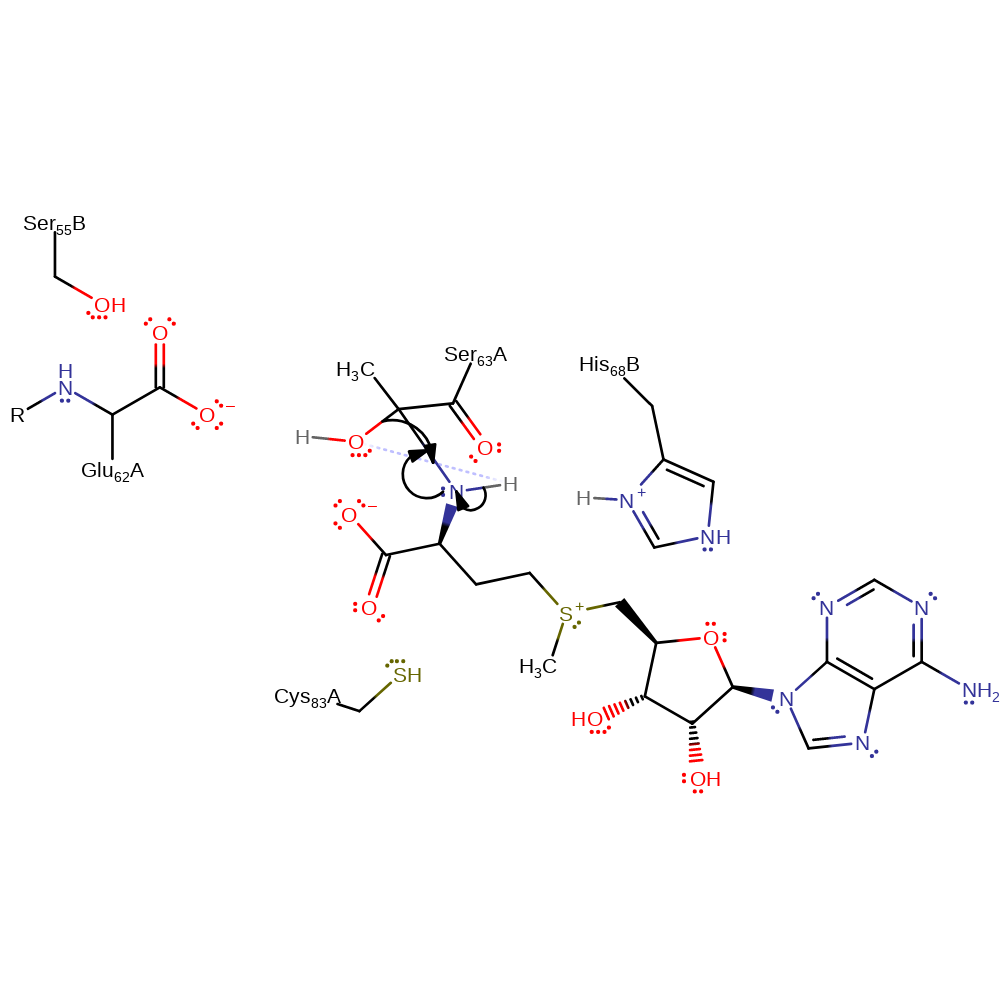
Step 9. Final step of Schiff base formation. The intermediate dehydrates to form the Schiff base.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser63(75)A | covalently attached |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, dehydration, schiff base formed, intermediate formation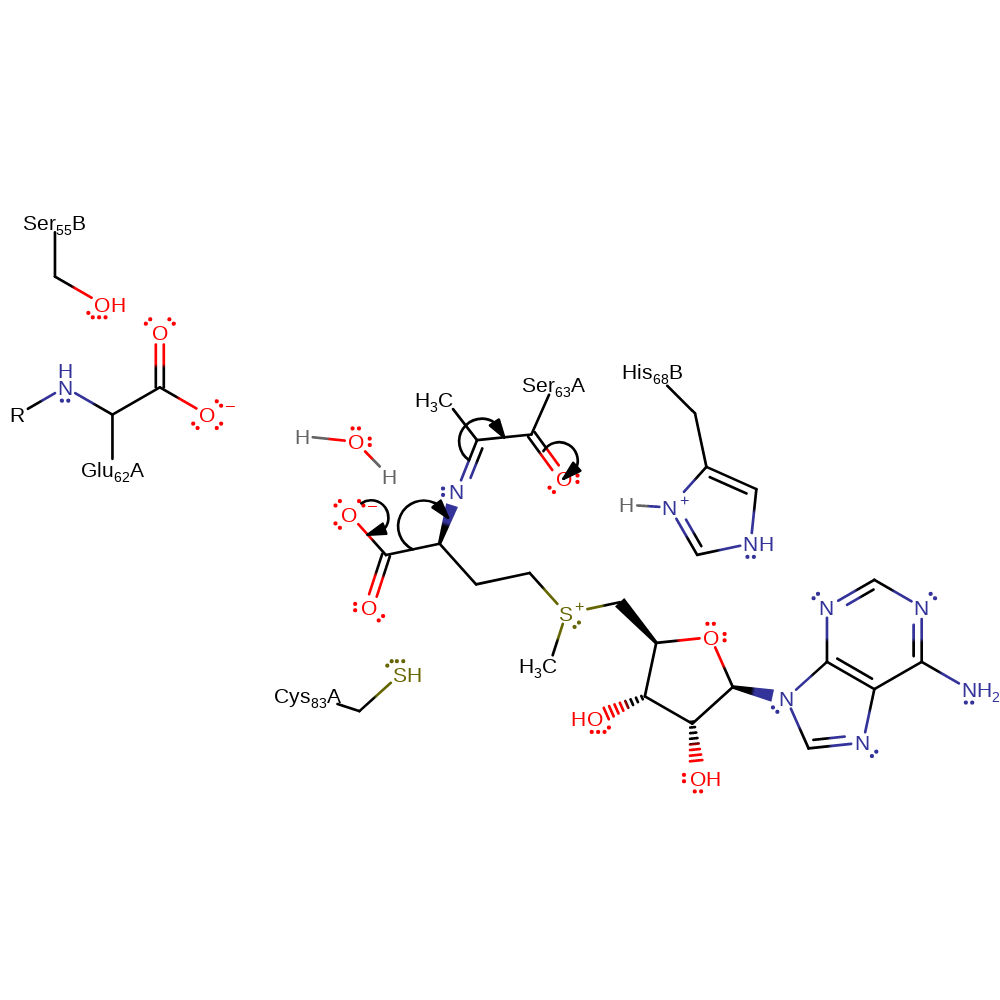
Step 10. The covalently attached intermediate decarboxylates and the post-translationally modified serine acts as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser63(75)A | covalently attached |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decarboxylation, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys83(95)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser63(75)A | covalently attached, polar interaction |
| Cys83(95)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, schiff base formed, intermediate formation
Step 12. First step one of the hydrolysis of the Schiff base. Water is involved in nucleophilic attack on the imine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys83(95)A | polar interaction |
| Ser63(75)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, proton transfer, hydrolysis, intermediate formation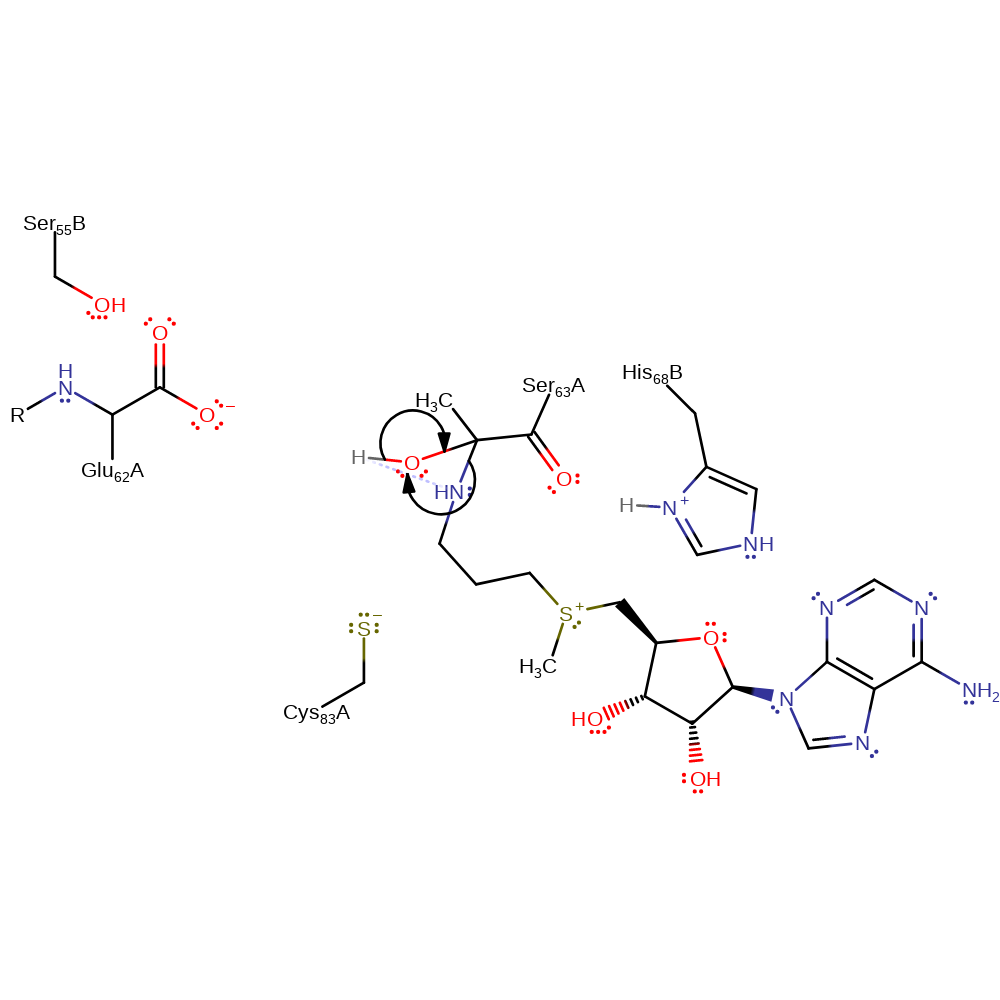
Step 13. Final step the hydrolysis of the Schiff base. S-Adenosylmethioninamine is eliminated from the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser63(75)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, covalently attached |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of cofactor regenerated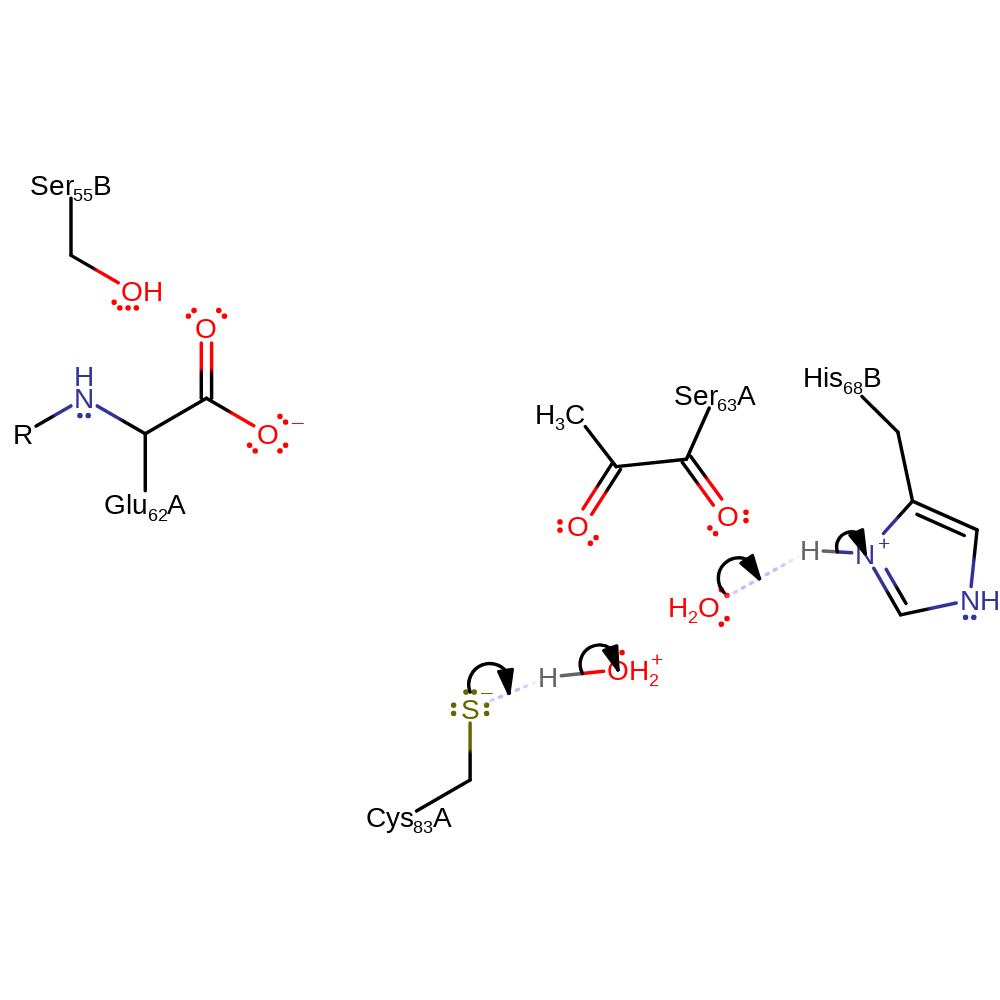
Step 14. His68 is deprotonated by a base, assumed to be water based on the lack of other evidence. Cys83 id re-protonated by another base, again assumed to be water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys83(95)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His68(80)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys83(95)A | proton acceptor |
| His68(80)B | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: