Benzoin aldolase
Thiamine diphosphate dependent benzaldehyde lyase (BAL) from Pseudomonas fluorescens catalyses the cleavage of (R)-benzoin producing two molecules of benzaldehyde. This allows the bacterium to grow on (R)-benzoin as its only carbon and energy source.
The reverse reaction is catalysed by benzoylformate decarboxylase (BFD). The X-ray structure of BAL was compared to that of BFD and pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) in order to determine which residues are likely to have catalytic roles and should be analysed by point mutations.
BAL looses its catalytic activity upon treatment with EDTA but activity can be restored by addition of 1millimolar MgCl2, MnSO4 or CaSO4.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9F4L3

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas fluorescens (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2ag0
- Crystal structure of Benzaldehyde lyase (BAL)- native
(2.58 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.970
 (see all for 2ag0)
(see all for 2ag0)
- Cofactors
- Thiamine(1+) diphosphate(3-) (1), Magnesium(2+) (1), Water (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.2.38)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
(R)-benzoin is cleaved producing two molecules of benzaldehyde. Thiamine diphosphate (ThDP) is activated by the deprotonation of a carbon and the carbanion reacts with (R)-benzoin producing a tetrahedral intermediate. Benzaldehyde is eliminated leaving an enamine. At low benzaldehyde concentration the enamine is protonated via a water molecule attached to His29 and then the other benzaldehyde molecule is released.
Alternatively, at high benzaldehyde concentration carboligation of the enamine with another benzaldehyde molecule generates (R)-benzoin but this does not occur under normal circumstances.
In fact, alteration of a single residue (A28S) converts benzaldehyde lyase into a benzoylformate decarboxylase.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2ag0) | ||
| Gly419 (main-C) | Gly419A (main-C) | Forms a hydrogen bond to the N1' of the ThDP cofactor and is thought to induce the 1',4'-imino tautomer in the pyrimidine ring. (PMID:16302970) Circular dichroism studies of other thiamin diphosphate (ThDP)-dependent enzymes such as the E1 subunit of Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase demonstrate the presence of the 1',4'-imino tautomer of ThDP. (PMID:15157089) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29 | His29B | H29 supposedly deprotonates the hydroxyl group on the tetrahedral intermediate resulting in cleavage of the tetrahedral intermediate with the release of the first benzaldehyde molecule (PMID:16302970). It also hydrogen bonds to a water molecule which is thought to protonate the enamine in the subsequent step leading to the release of the second benzaldehyde molecule (PMID:16302970). | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu50 | Glu50B | Forms a hydrogen bond to the N1' on the pyrimidine of ThDP. (PMID:16302970) Activation of ThDP cofactor by Glu50, has been inferred based upon the other thiamine dependent reactions in MACiE. Glu50 is thought to deprotonate N1' leading to the formation of the ThDP carbanion. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gln113 | Gln113B | Comparisons of X-ray structures of BAL with BFD suggest that Gln113 may have a role in stabilising the transition state. It also forms hydrogen bonds to His29 and water. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), cofactor used, inferred reaction step, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, aldol addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, bimolecular elimination, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Kneen MM et al. (2005), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1753, 263-271. Exploring the active site of benzaldehyde lyase by modeling and mutagenesis. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.08.025. PMID:16226928.
- Brandt GS et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 7734-7743. Probing the active center of benzaldehyde lyase with substitutions and the pseudosubstrate analogue benzoylphosphonic acid methyl ester. DOI:10.1021/bi8004413. PMID:18570438.
- Chakraborty S et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 3800-3809. Mechanism of benzaldehyde lyase studied via thiamin diphosphate-bound intermediates and kinetic isotope effects. DOI:10.1021/bi702302u. PMID:18314961.
- Mosbacher TG et al. (2005), FEBS J, 272, 6067-6076. Structure and mechanism of the ThDP-dependent benzaldehyde lyase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04998.x. PMID:16302970.
- Nemeria N et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 6565-6575. Tetrahedral Intermediates in Thiamin Diphosphate-Dependent Decarboxylations Exist as a 1‘,4‘-Imino Tautomeric Form of the Coenzyme, Unlike the Michaelis Complex or the Free Coenzyme†. DOI:10.1021/bi049549r. PMID:15157089.

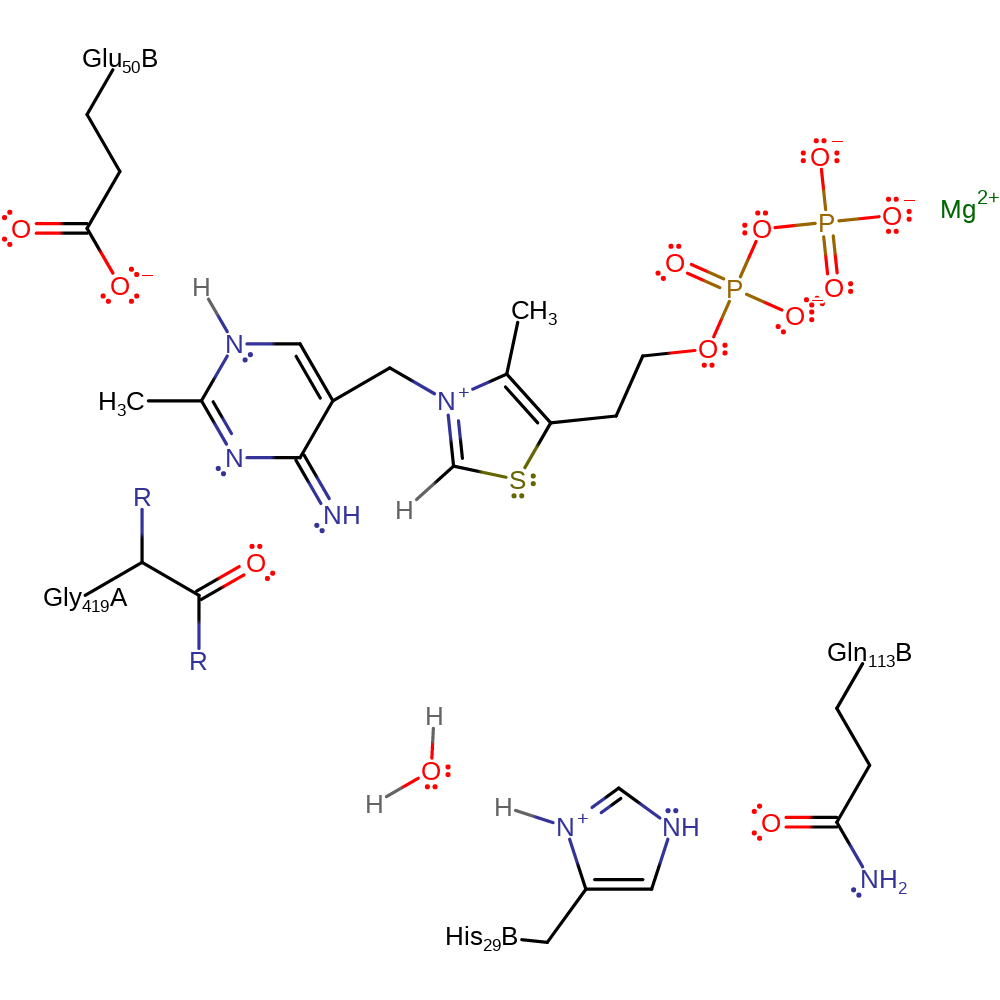
Step 1. Glu50B deprotonates the thiamine diphosphate cofactor, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of the N=CH-S group, activating the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly419A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu50B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), cofactor used, inferred reaction step
Step 2. The carbanion of thiamine diphosphate attacks the carbonyl carbon of benzoin in a nucleophilic addition. Kneen et al. suggest that the protonation event might be mediated through a water molecule and the His29B, with the Gln113B activating the His29B [PMID:16226928].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly419A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, aldol addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay
Step 3. His29B deprotonates one of the hydroxyl groups (again, mediated through a water molecule) of the bound intermediate, initiating an elimination that productes one of the benzaldehyde products. Thiamine diphosphate acts as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly419A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), overall product formed, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse
Step 4. Thiamine diphosphate initiates a double bond rearrangement, which results in the intermediate being protonated by His29B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly419A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate formation
Step 5. His29B deprotonates the second hydroxyl group of the intermediate, initiating an elimination that results in a reformation of the carbanionic activated cofactor and the second benzaldehyde product.)Substrates=(M0221-I3,2ag0-His29B
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly419A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 6. The carbanion of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor deprotonates the adjacent amine, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of Glu50B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu50B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly419A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His29B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln113B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu50B | proton donor |


 Download:
Download: