Triacylglycerol lipase (pancreatic)
Pancreatic lipase from Equus caballus catalyses the conversion of triacylglycerol to 2-monoacylglycerol and free fatty acids. This occurs in the intestine and plays a key role in dietary fat digestion. This is important as it is converting an insoluble substrate into soluble products.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P29183
 (3.1.1.3)
(3.1.1.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Equus caballus (Horse)

- PDB
-
1hpl
- HORSE PANCREATIC LIPASE. THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AT 2.3 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1820
 (see all for 1hpl)
(see all for 1hpl)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.1.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The negative charge on Asp 176 acts to affect the pKa of His 263, making it more basic. His 263 acts as a general base, by deprotonating Ser 152, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the ester bond. This forms a negatively charged tetrahedral intermediate which is stabilised by the oxyanion hole formed by the main chain amides of Phe 77 and Leu 153. As the carbonyl is reformed, the ester bond is broken, the leaving group being protonated by His 263. His 263 then acts as a general base again, this time by deprotonating a water molecule, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the substrate carbonyl. Another negatively charged tetrahedral intermediate is formed, and again is stabilised by the oxyanion hole. As the carbonyl is reformed, the substrate-Ser 152 bond is broken, and Ser 152 is then re-protonated by His 263.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hpl) | ||
| Leu166 (main-N) | Leu153(154)A (main-N) | The main chain amide of Leu 153 acts to stabilise the negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser165 | Ser152(153)A | Part of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. Acts as a nucleophile. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp189 | Asp176(177)A | The negatively charged Asp 176 helps to activate His 263 to become more basic. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His276 | His263(264)A | Activates Ser 152 by deprotonating it. Donates a proton to the leaving acylglycerol. Activates a water molecule by deprotonating it. Donates a proton back to the leaving group Ser 152. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Phe90 (main-N) | Phe77(78)A (main-N) | The main chain amide of Phe 77 acts to stabilise the negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Lowe ME (1997), J Nutr, 127, 549-557. Molecular mechanisms of rat and human pancreatic triglyceride lipases. PMID:9109604.
- Eydoux C et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 9553-9564. Structure of human pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 with the lid in an open conformation. DOI:10.1021/bi8005576. PMID:18702514.
- Bourne Y et al. (1994), J Mol Biol, 238, 709-732. Horse Pancreatic Lipase. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1331. PMID:8182745.
- Kazlauskas RJ (1994), Trends Biotechnol, 12, 464-472. Elucidating structure-mechanism relationships in lipases: Prospects for predicting and engineering catalytic properties. DOI:10.1016/0167-7799(94)90022-1. PMID:7765546.
- van Tilbeurgh H et al. (1993), Nature, 362, 814-820. Interfacial activation of the lipase–procolipase complex by mixed micelles revealed by X-ray crystallography. DOI:10.1038/362814a0. PMID:8479519.
- Winkler FK et al. (1990), Nature, 343, 771-774. Structure of human pancreatic lipase. DOI:10.1038/343771a0. PMID:2106079.
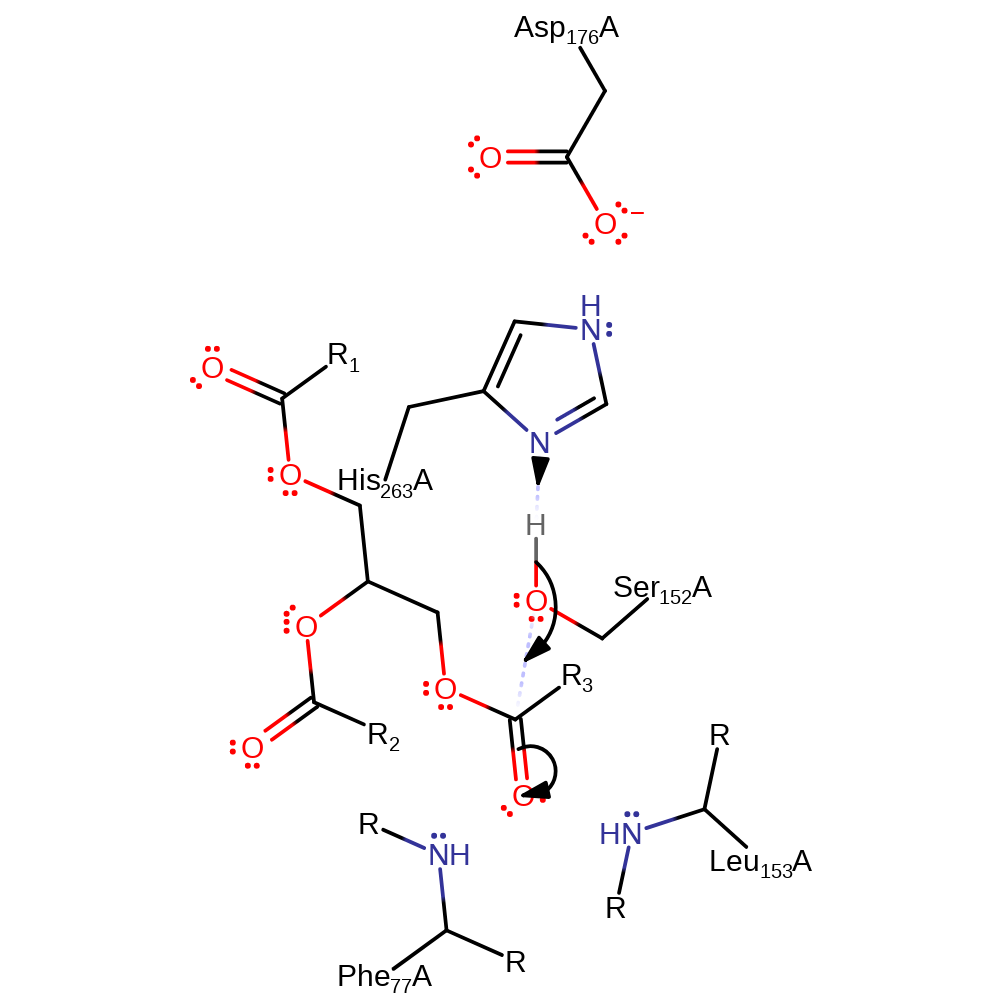
Step 1. His263 (part of a Ser-His-Asp triad) deprotonates Ser152, which attacks the carboxy carbon on the Re face [PMID:7765546] of the triacylglycerol substrate in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu153(154)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser152(153)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe77(78)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His263(264)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp176(177)A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser152(153)A | nucleophile, proton donor |
| His263(264)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses, initiating an elimination of the diacylglycerol product, which deprotonates His263 and acylated Ser152.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu153(154)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser152(153)A | covalently attached |
| Phe77(78)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His263(264)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp176(177)A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His263(264)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, intermediate formation
Step 3. His263 deprotonates water, which attacks the carboxyl carbon of the acylated Ser152 in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu153(154)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser152(153)A | covalently attached |
| Phe77(78)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His263(264)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp176(177)A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His263(264)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 4. The oxyanion collapses, initiating an elimination of the carboxylate product, and Ser152, which deprotonates His263.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu153(154)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser152(153)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe77(78)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His263(264)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp176(177)A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser152(153)A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| His263(264)A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: