Alanine racemase
Alanine racemase catalyses the pyridoxal-dependent conversion of L-alanine into D-alanine, a key component of bacterial peptidoglycan.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P10724
 (5.1.1.1)
(5.1.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Geobacillus stearothermophilus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1l6g
- Alanine racemase bound with N-(5'-phosphopyridoxyl)-D-alanine
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.10
 2.40.37.10
2.40.37.10  (see all for 1l6g)
(see all for 1l6g)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The ground state of the enzyme contains a covalent linkage between Lys39 and the PLP cofactor. The reaction proceeds via an initial transldimination in which the substrate alanine eliminates Lys39 from PLP. In the L-Ala to D-Ala direction Tyr265B abstracts a proton from the alpha carbon of the alanine (and Lys39 deprotonates water). Water deprotonates Tyr265B. The carbanionic intermediate deprotonates Lys39. In the final steps, a second transaldimination occurs, eliminating the product and returning the protein to its ground state. In the D-Ala to L-Ala direction, the roles of Tyr265B and Lys39 are reversed. The tyrosine and the lysine residues are on opposite sides of the PLP cofactor.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1l6g) | ||
| Arg219 | Arg219A | Arg219 forms a hydrogen bond with the pyridine nitrogen of the cofactor, which is assumed to influence electron delocalisation in PLP-alanine intermediates | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr265 | Tyr265B | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp313 | Asp313B | Activates and stabilises Lys39. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys311, His166 | Cys311B, His166A | Acts to stabilise the reactive intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39 | Lys39A | The pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) cofactor lies in and above the barrel mouth and is covalently linked via an aldimine linkage to Lys39. Also acts as a general acid/base. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleofuge, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleophile, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Arg136 | Arg136A | Arg136 donates a hydrogen bond to the phenolic oxygen of PLP, and may be involved in substrate binding and stabilisation of intermediates | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, intramolecular elimination, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, schiff base formed, rate-determining step, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- LeMagueres P et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 1471-1481. The 1.9 Å Crystal Structure of Alanine Racemase fromMycobacterium tuberculosisContains a Conserved Entryway into the Active Site†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0486583. PMID:15683232.
- Spies MA et al. (2007), J Am Chem Soc, 129, 10678-10685. Intrinsic Primary and Secondary Hydrogen Kinetic Isotope Effects for Alanine Racemase from Global Analysis of Progress Curves. DOI:10.1021/ja067643k. PMID:17691728.
- Major DT et al. (2006), J Am Chem Soc, 128, 8114-8115. Transition State Stabilization and α-Amino Carbon Acidity in Alanine Racemase. DOI:10.1021/ja062272t. PMID:16787057.
- Major DT et al. (2006), J Am Chem Soc, 128, 16345-16357. A Combined Quantum Mechanical and Molecular Mechanical Study of the Reaction Mechanism and α-Amino Acidity in Alanine Racemase. DOI:10.1021/ja066334r. PMID:17165790.
- Watanabe A et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 19166-19172. Reaction Mechanism of Alanine Racemase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. X-RAY CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC STUDIES OF THE ENZYME BOUND WITH N-(5'-PHOSPHOPYRIDOXYL)ALANINE. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m201615200. PMID:11886871.
- Ondrechen MJ et al. (2001), J Am Chem Soc, 123, 2830-2834. A Model for Enzyme−Substrate Interaction in Alanine Racemase. DOI:10.1021/ja0029679. PMID:11456969.
- Watanabe A et al. (1999), J Biol Chem, 274, 4189-4194. Role of Lysine 39 of Alanine Racemase from Bacillus stearothermophilus That Binds Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate. CHEMICAL RESCUE STUDIES OF Lys39 right-arrow Ala MUTANT. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.7.4189. PMID:9933615.
- Sun S et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 4058-4065. Evidence for a Two-Base Mechanism Involving Tyrosine-265 from Arginine-219 Mutants of Alanine Racemase†. DOI:10.1021/bi982924t. PMID:10194319.
- Watanabe A et al. (1999), J Biochem, 125, 987-990. Role of Tyrosine 265 of Alanine Racemase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022406. PMID:10348897.
- Watanabe A et al. (1999), J Biochem, 126, 781-786. Tyrosine 265 of Alanine Racemase Serves as a Base Abstracting -Hydrogen from L-Alanine: The Counterpart Residue to Lysine 39 Specific to D-Alanine. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022517. PMID:10502689.
- Stamper GF et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 10438-10445. Reaction of Alanine Racemase with 1-Aminoethylphosphonic Acid Forms a Stable External Aldimine†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi980692s. PMID:9671513.
- Shaw JP et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 1329-1342. Determination of the Structure of Alanine Racemase fromBacillus stearothermophilusat 1.9-Å Resolution†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi961856c. PMID:9063881.
Step 1. The amine of the substrate L-alanine attacks the PLP cofactor in a nucleophilic addition and the bound Lys39 deprotonates the newly attached amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His166A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg219A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr265B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg136A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys311B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound lysine, resulting in free PLP and lysine in a neutral state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys39A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His166A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg219A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr265B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp313B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg136A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys311B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular elimination, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, schiff base formed
Step 3.
Tyr265B deprotonates the alpha carbon of the covalently bound intermediate, resulting in a carbanionic intermediate. Lys39 deprotonates water.
The activity of the tyrosine as the base in this step has been confirmed by mutagenesis, kinetic isotope effects and computational studies. On the basis of electrostatic potential calculations [PMID:17165790], it has been found that the lysine is likely to be protonated. However, it is unclear what species performs this protonation, thus water has been used. This step is known to be the RDS [PMID:17165790]. It is known that the PLP of this enzyme is unprotonated and this form is stabilised by the H-bond to Ag219A, this and the fact that the quinoid intermediate has not been experimentally observed support the negative charge remaining on the carbon of the alanine moiety [PMID:17165790].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys39A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His166A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg219A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr265B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp313B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys311B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr265B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, rate-determining step
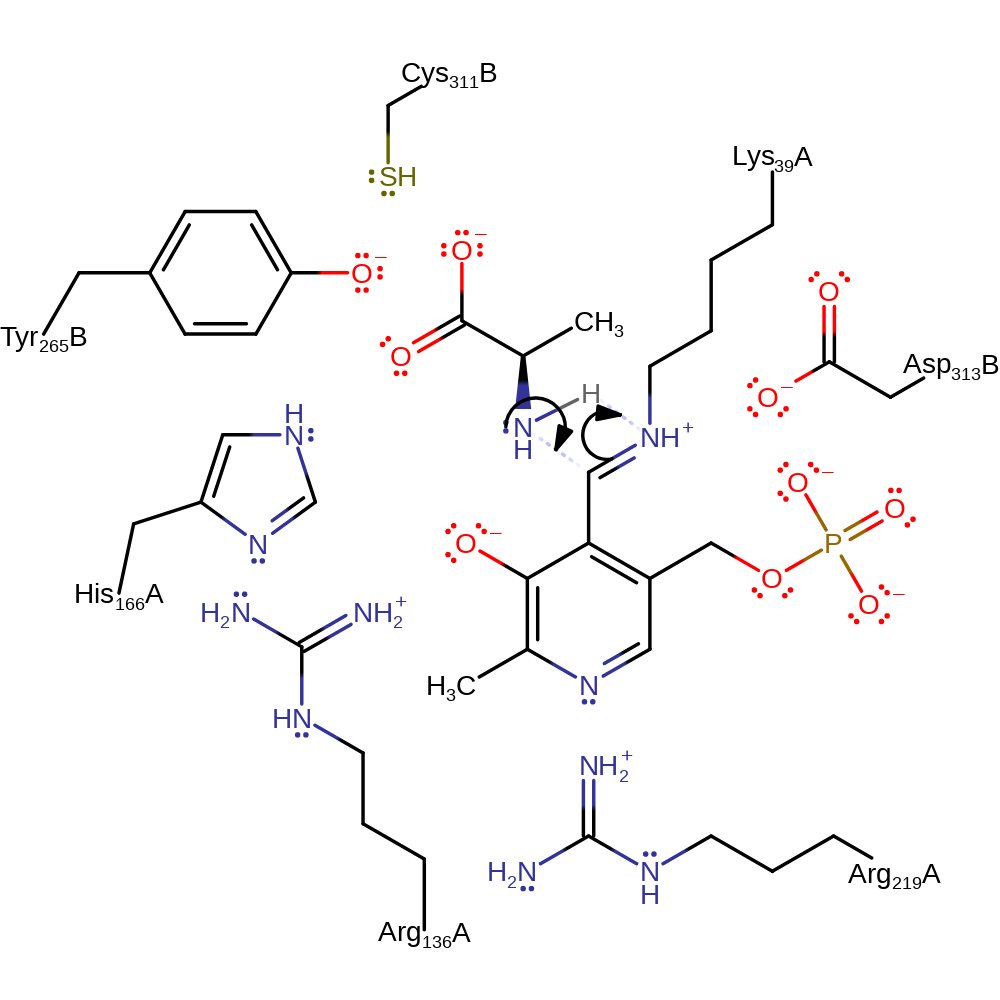
Step 4. Water deprotonates Tyr265B. The carbanionic intermediate deprotonates Lys39.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys39A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His166A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg219A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr265B | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp313B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg136A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys311B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39A | proton donor |
| Tyr265B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation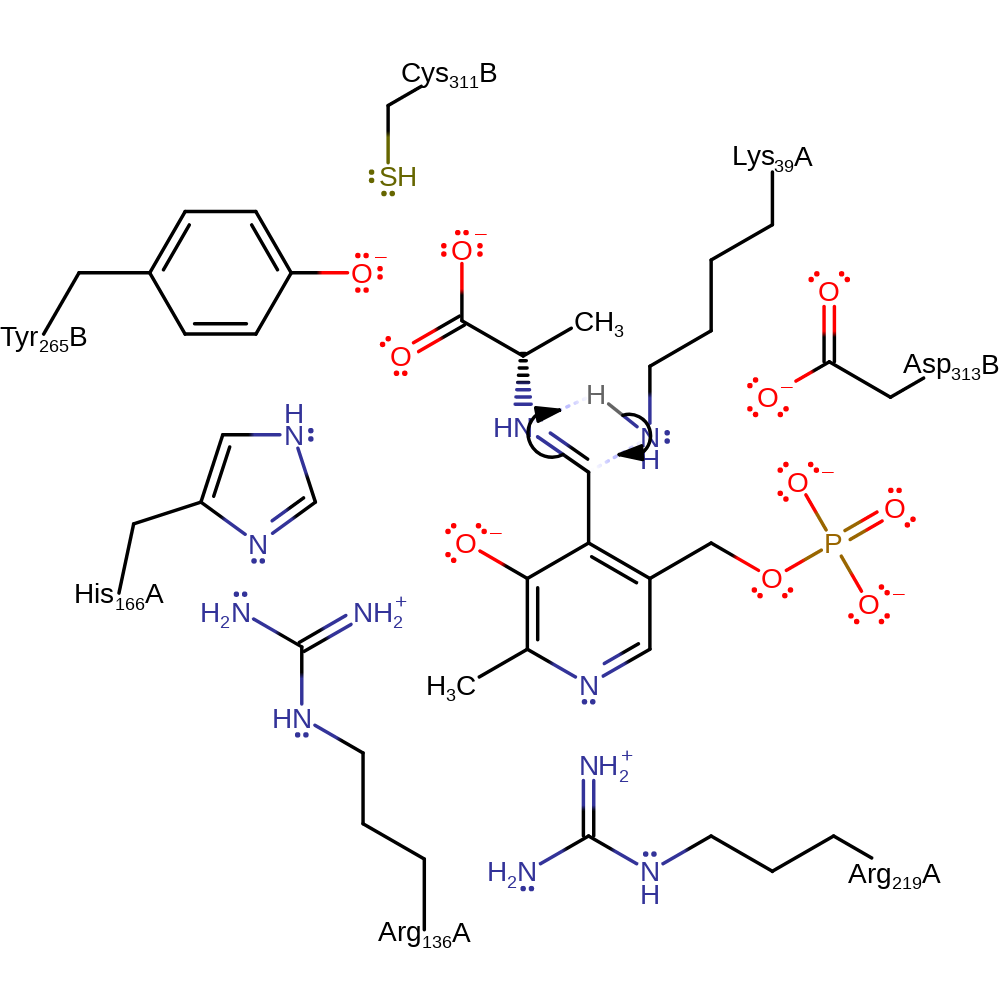
Step 5. The amine of Lys39 attacks the PLP in a nucleophilic addition reaction, the secondary amine of the attached substrate reprotonates from the bound Lys39
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys39A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His166A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg219A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr265B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp313B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg136A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys311B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 6. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound product, resulting in D-alanine and the regenerated PLP cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg136A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys311B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His166A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg219A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr265B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp313B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys39A | electron pair donor |


 Download:
Download: