Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCC) from Streptomyces coelicolor catalyses the carboxylation of proprionyl-CoA (and, less efficiently, butyryl-CoA) to provide methylmalonyl-CoA (or ethylmalonyl-CoA). This carboxylation reaction provides key extender units for the biosynthesis of fatty acids and polyketide natural products.
PCC has three units, pccA, pccB and pccE. The alpha subunit (pccA) contains the BCCP (biotin carboxyl carrier protein) and BC (biotin carboxylase) domains. The beta subunit (pccB) contains the carboxyltransferase (CT) function, which transfers the carboxyl group from biotin to propionyl-CoA [PMID:15518551]. BC catalyses carboxylation of the biotin attached to the biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP) in the first half reaction which requires ATP Mg(II) and bicarbonate [PMID:2673009]. CT catalyses the second half reaction, the carboxyl transfer from biotin to propanoyl-CoA [PMID:2673009, PMID:15518551].
pccE may act to associate pccA and pccB. The pccB unit shows sequence and structure homology with other carboxyltransferases from other organisms. They are all dimers or hexamers, with the monomers comprising two domains; two active sites run between each pair of adjacent monomers, with catalytic residues being contributed from the C-terminal domain from one monomer and the N-terminal domain from the next monomer.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9X4K7

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Streptomyces coelicolor (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1xny
- Biotin and propionyl-CoA bound to Acyl-CoA Carboxylase Beta Subunit from S. coelicolor (PccB)
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.226.10
 (see all for 1xny)
(see all for 1xny)
- Cofactors
- Biotinate (1), Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.4.1.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The substrate proprionyl-CoA, and cofactor carboxylbiotin (covalently attached to pccA), both have carbonyl groups which hydrogen bond to backbone amides: Gly 182 and Gly 183 for the substrate, Gly 419' and Ala 420' for the carboxylbiotin. (The primed numbers indicate residues on a different monomer to the unprimed residues.) These amides serve as oxyanion holes whenever the need arises. Carboxylbiotin has a pi orbital spanning the CO2-N1-CO-N atoms. Binding to the enzyme bends this orbital (no specific residues indicated) and induces release of CO2. This moves the negative charge of the carboxylate group to the -CO- carbonyl group (to give a ureido enolate), which is stabilised by its oxyanion hole. The ureido enolate collapses, deprotonating propionyl-CoA to give the enolate and regenerating biotin. The substrate enolate is stabilised by its oxyanion hole. The enolate attacks CO2 through the alpha-carbon, reforming the C=O double bond and attaching a carboxyl group to the substrate to give methylmalonate-CoA.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xny) | ||
| Gly183 (main-N), Gly182 (main-N) | Gly183A (main-N), Gly182A (main-N) | Acts as an oxyanion hole for the substrate enolate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly419 (main-N), Ala420 (main-N) | Gly419B (main-N), Ala420B (main-N) | Acts as an oxyanion hole for the cofactor ureido enolate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, decarboxylation, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), cofactor used, intermediate terminated, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of enzyme is not regenerated, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, native state of cofactor regenerated, bimolecular electrophilic additionReferences
- Diacovich L et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 14027-14036. Crystal Structure of theβ-Subunit of Acyl-CoA Carboxylase: Structure-Based Engineering of Substrate Specificity†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi049065v. PMID:15518551.
- Knowles JR (1989), Annu Rev Biochem, 58, 195-221. The Mechanism of Biotin-Dependent Enzymes. DOI:10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001211. PMID:2673009.
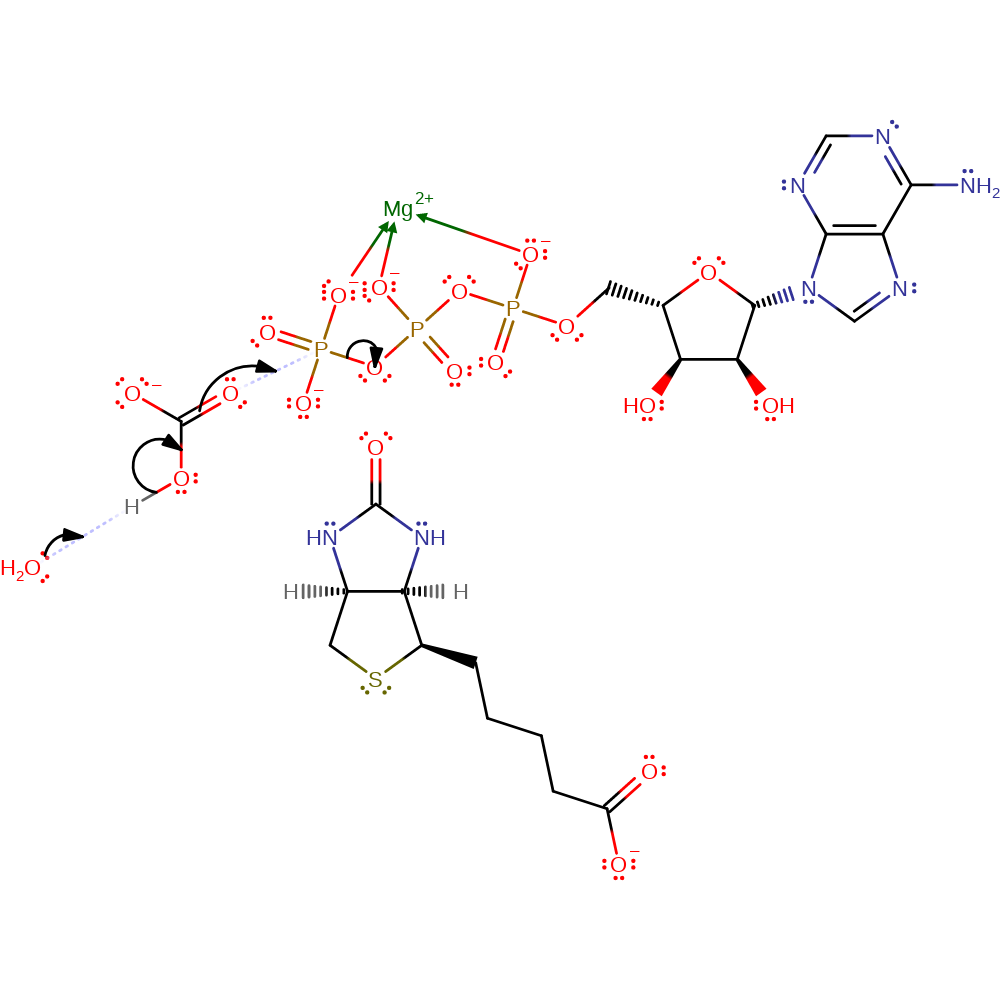
Step 1. Reaction occurs in the alpha-subunit. The bicarbonate is deprotonated by an unidentified base (shown as water here). The activate bicarbonate then acts as a nucleophile and attacks the gamma-phosphate in a substitution reaction, liberating ADP. Mg(II) stabilises/activates the ATP
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed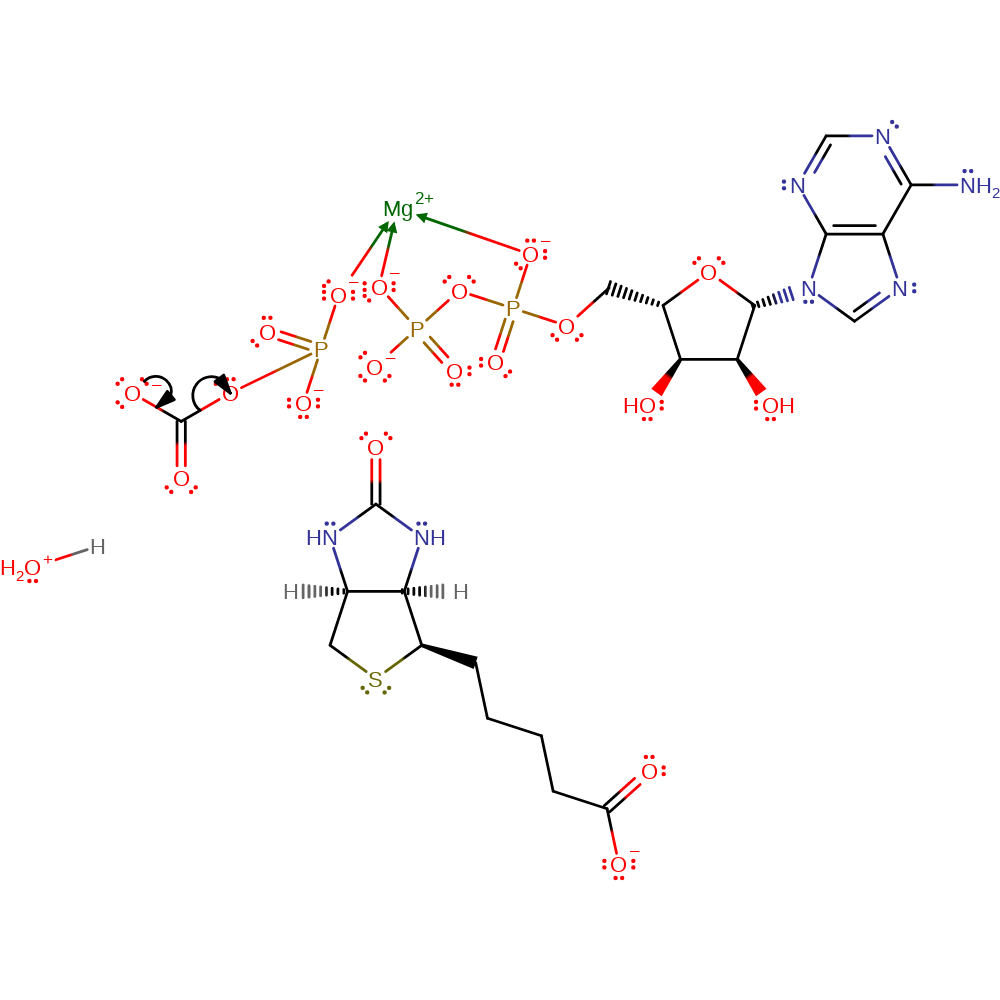
Step 2. Reaction occurs in the alpha-subunit. The phosphorylated bicarbonate undergoes a decarboxylation reaction (E1cb) to liberate carbon dioxide and phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, decarboxylation
Step 3. Reaction occurs in the alpha-subunit. The phosphate deprotonates one of the N-H groups of biotin with concomitant tautomerisation to produce an oxyanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), cofactor used, intermediate formation, intermediate terminated, overall product formed
Step 4. Reaction occurs in the alpha-subunit. The oxyanion re-forms the carbonyl group, causing the C=N bond of the activated biotin to add to the carbon dioxide in a nucleophilic manner.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, native state of enzyme is not regenerated
Step 5. Reaction occurs in the beta-subunit. Once the carboxylated biotin has relocated to the beta-subunit, the biotin undergoes a decarboxylation reaction (E1cb) to liberate carbon dioxide and the activated biotin molecule. the main chain amides of Gly419B and Ala420B stabilise the oxyanion of the activated biotin.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly182A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly183A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly419B (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala420B (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, decarboxylation
Step 6. Reaction occurs in the beta-subunit. The oxyanion re-forms the carbonyl group, causing the C=N bond of the activated biotin to deprotonate the propanoyl-CoA with concomitant tautomerisation. The main chain amides of Gly182 and Gly183 stabilise the activated propanoyl-CoA, the main chain amides of Gly419B and Ala420B stabilise the oxyanion of the activated biotin.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly182A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly183A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly419B (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala420B (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated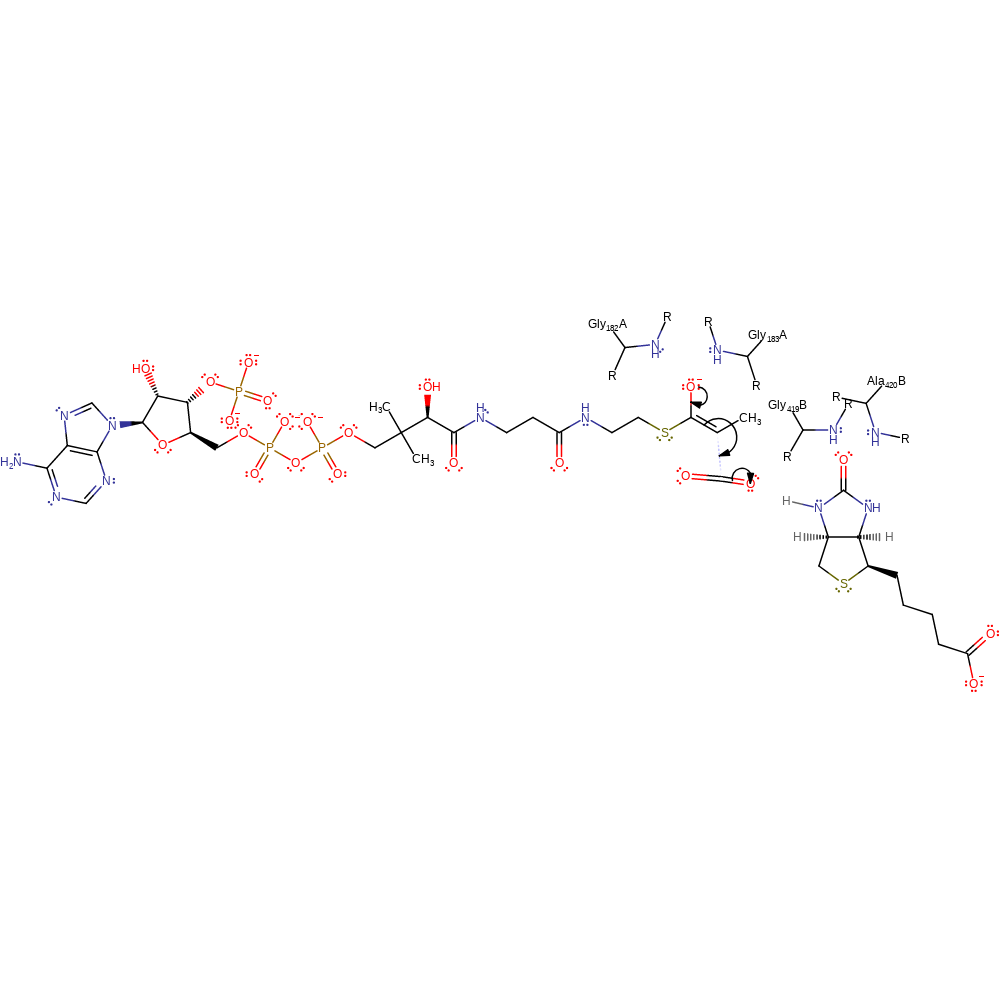
Step 7. Reaction occurs in the beta-subunit. The oxyanion re-forms the carbonyl group causing the C=C bond of the activated propanoyl-CoA to add to the carbon dioxide molecule in an electrophilic manner.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly182A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly183A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly419B (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ala420B (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |







 Download:
Download: