Glutamate-1-semialdehyde 2,1-aminomutase
Tetrapyrroles are large macrocyclic compounds derived from a common biosynthetic pathway. The end-product, uroporphyrinogen III, is used to synthesise a number of important molecules, including vitamin B12, haem, sirohaem, chlorophyll, coenzyme F430 and phytochromobilin.
This entry represents glutamate-1-semialdehyde (GSA) aminotransferase (EC:5.4.3.8), which catalyses a transamination reaction to produce 5-aminoaevulinic acid during the first stage of tetrapyrrole biosynthesis by the C5 pathway. It is a class III aminotransferase.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P24630
 (5.4.3.8)
(5.4.3.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Synechococcus elongatus PCC 6301 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2gsa
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF GLUTAMATE-1-SEMIALDEHYDE AMINOMUTASE (AMINOTRANSFERASE, WILD-TYPE FORM)
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.640.10
 (see all for 2gsa)
(see all for 2gsa)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
This is a pyridoxal-phosphate (PLP) dependent enzyme. It is possible that the same group of the enzyme is responsible for all the general acid and base steps of the mechanism. By analogy to aspartate aminotransferase this group is assumed to be the Lys273A [PMID:8519748,PMID:1730703].
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2gsa) | ||
| Lys273 | Lys273(272)A | Acts as a catalytic nucleophile (forming a covalent intermediate with the PLP cofactor). Also acts as a general acid/base. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Asp245 | Asp245(244)A | Acts to stabilise the PLP, enabling the cofactor to act as an electron sink. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150 | Tyr150(149)A | Holds the PLP cofactor in place (stops it rotating within the active site) to ensure the correct reaction occurs. | steric role |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, dehydration, schiff base formed, enzyme-substrate complex formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, bimolecular elimination, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Pugh CE et al. (1992), J Biol Chem, 267, 1584-1588. Mechanism of glutamate semialdehyde aminotransferase. Roles of diamino- and dioxo-intermediates in the synthesis of aminolevulinate. PMID:1730703.
- Li S et al. (2018), Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 500, 804-809. Crystal structure of a glutamate-1-semialdehyde-aminomutase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.163. PMID:29684343.
- Hennig M et al. (1997), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 94, 4866-4871. Crystal structure of glutamate-1-semialdehyde aminomutase: An 2-dimeric vitamin B6-dependent enzyme with asymmetry in structure and active site reactivity. DOI:10.1073/pnas.94.10.4866. PMID:9144156.
- Brody S et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 15918-15924. Characterization of the different spectral forms of glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase by mass spectrometry. DOI:10.1021/bi00049a006. PMID:8519748.
- Smith MA et al. (1992), Biochemistry, 31, 11249-11254. Glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase: anomalous enantiomeric reaction and enzyme mechanism. DOI:10.1021/bi00160a041. PMID:1445864.

Step 1. The amine of the PMP cofactor attacks the carbonyl carbon of the (S)-4-amino-5-oxopentanoate substrate in a nucleophilic addition. This results in a the oxyanion formed deprotonating the newly attached amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation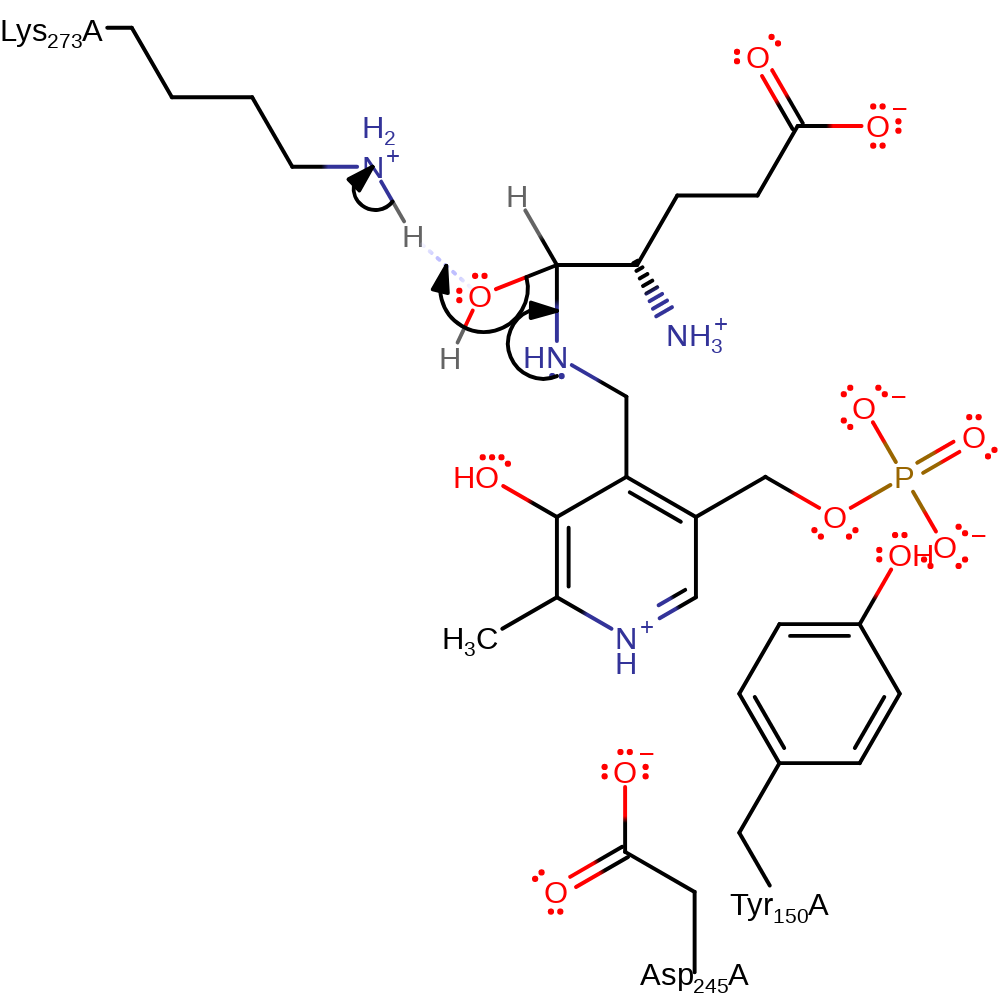
Step 2. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of water, resulting in the substrate being covalently bound as a Schiff base.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys273(272)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, dehydration, schiff base formed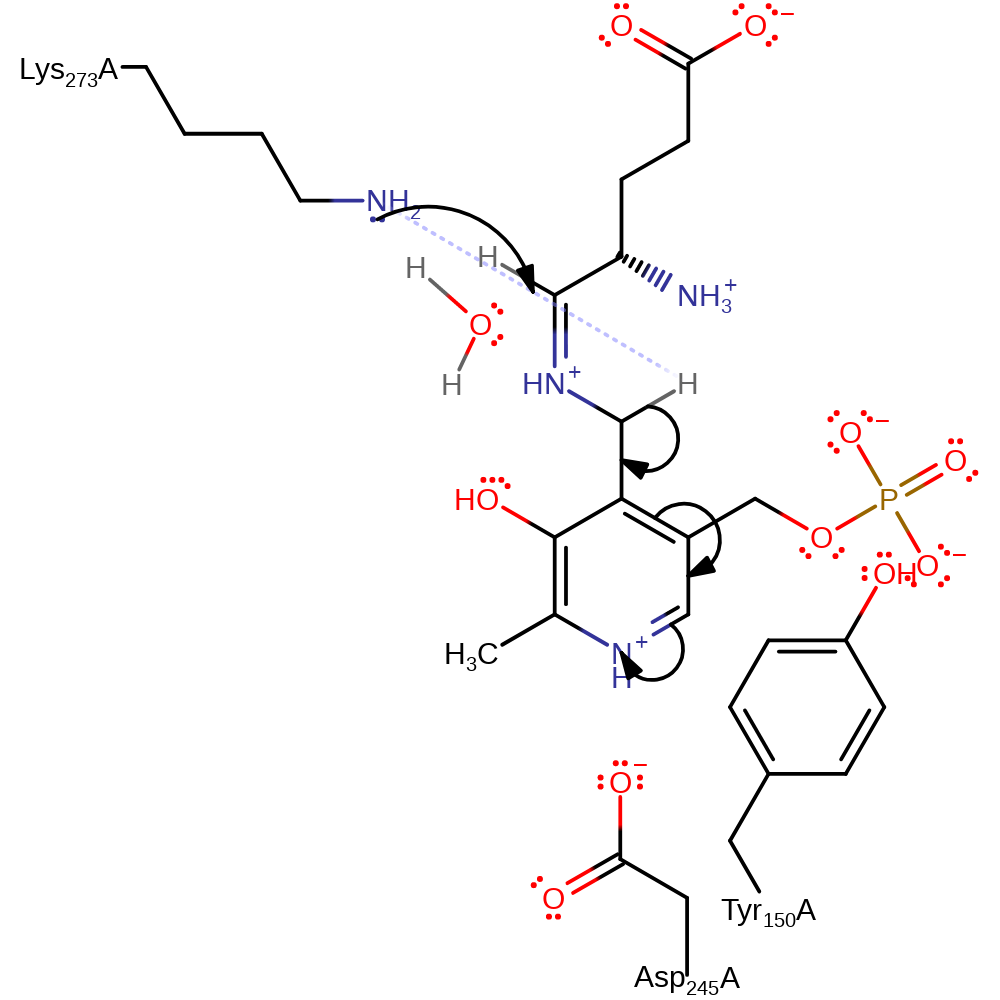
Step 3. The amine of Lys273 deprotonates the C1 of the PMP, which acts as an electron sink and undergoes a double bond rearrangement.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys273(272)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation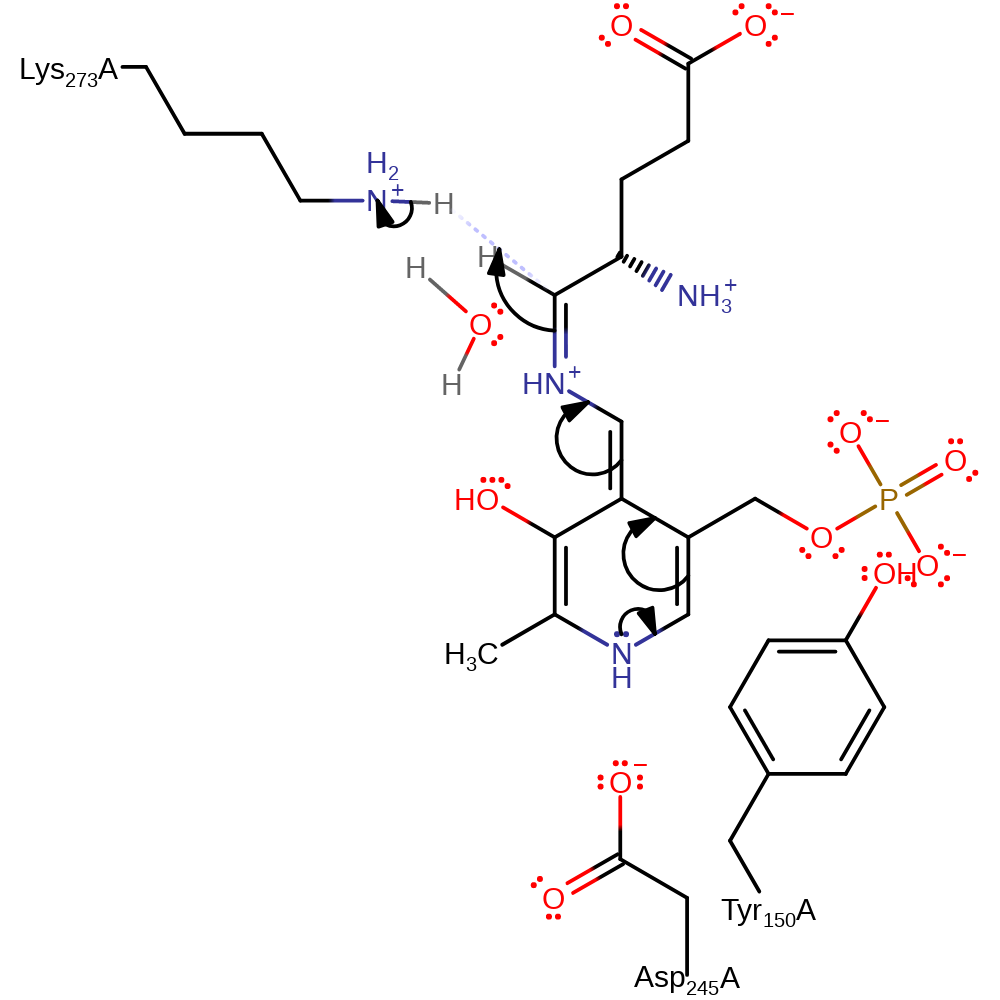
Step 4. The PMP initiates a deprotonation of the Lys273 through its conjugated pi-bond system, resulting in the protonation at the covalently bound carbon of the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys273(272)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys273(272)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 5. The amine of Lys273 attacks the PMP in a nucleophilic addition reaction, the secondary amine of the attached intermediate reprotonates from the bound Lys229
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation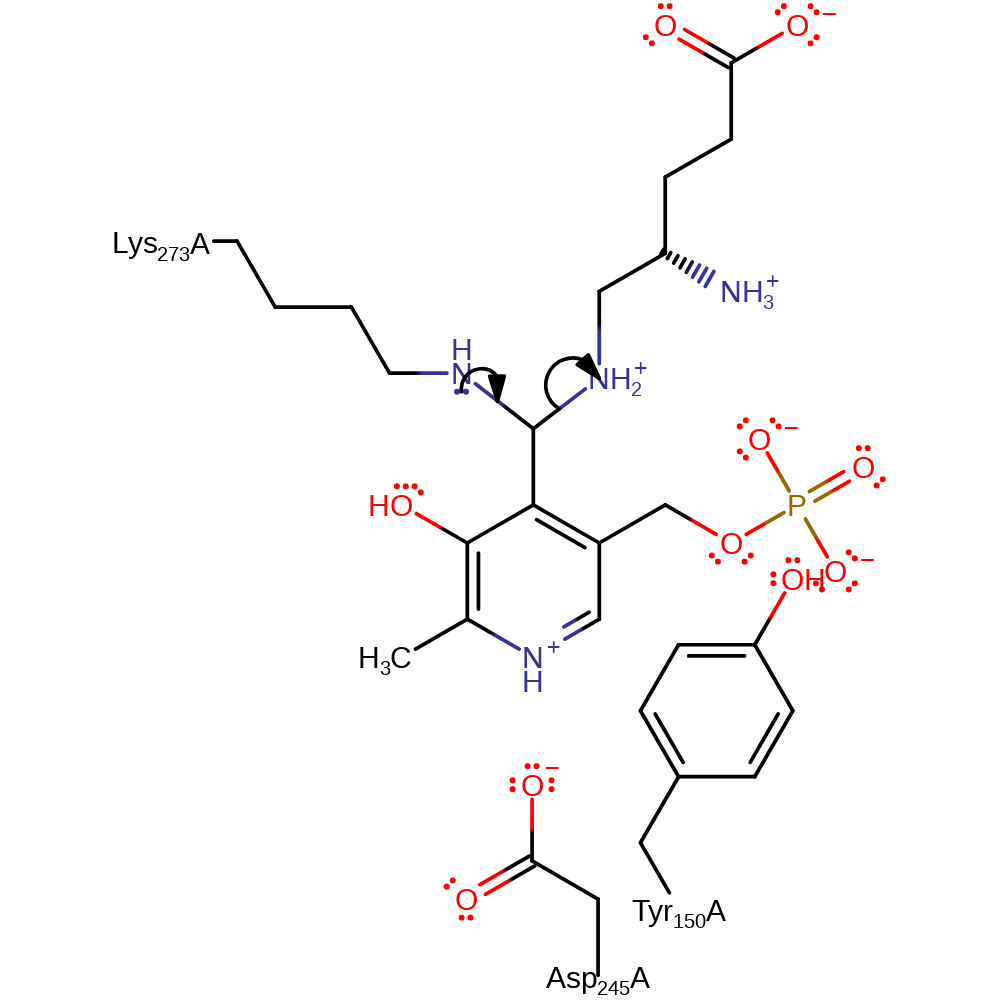
Step 6. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound PMP, and the free diamino intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys273(272)A | covalently attached |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, schiff base formed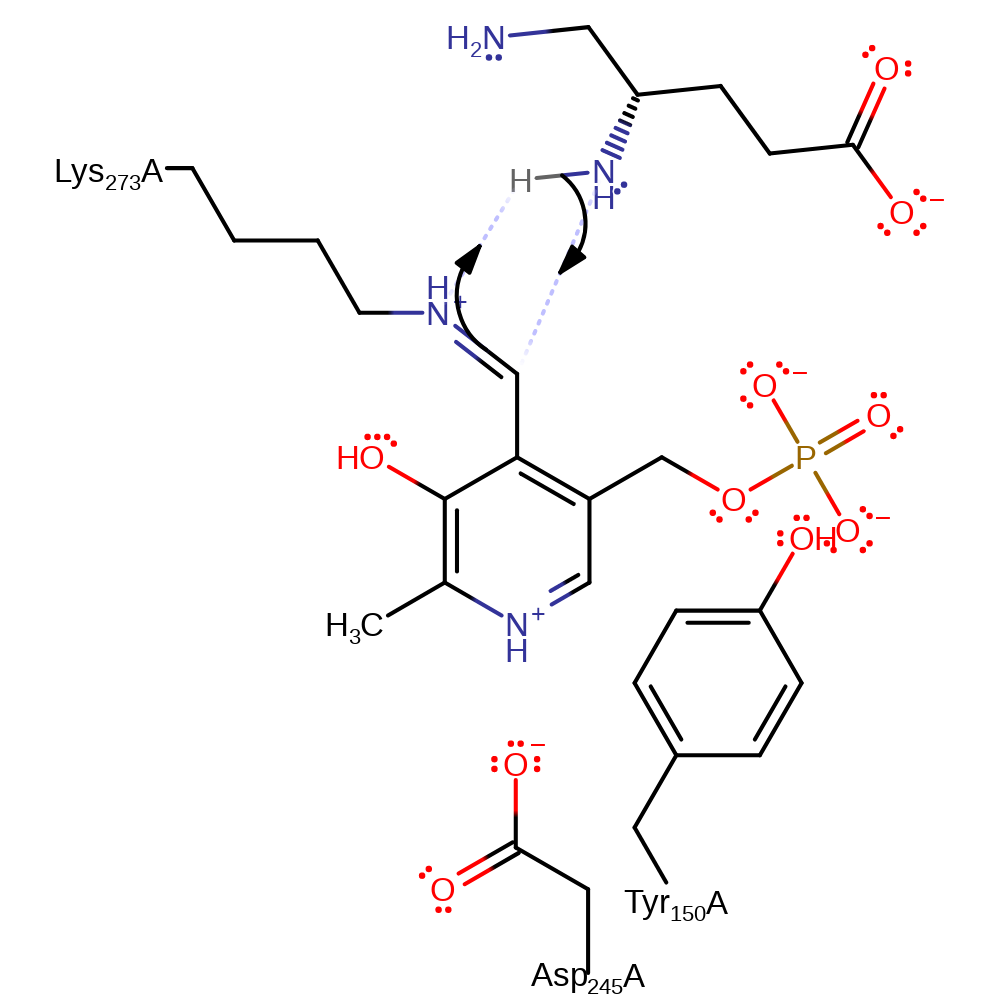
Step 7. The original amine of the intermediate attacks the covalently bound PMP cofactor in a nucleophilic addition and the bound Lys273 deprotonates the newly attached amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys273(272)A | covalently attached |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation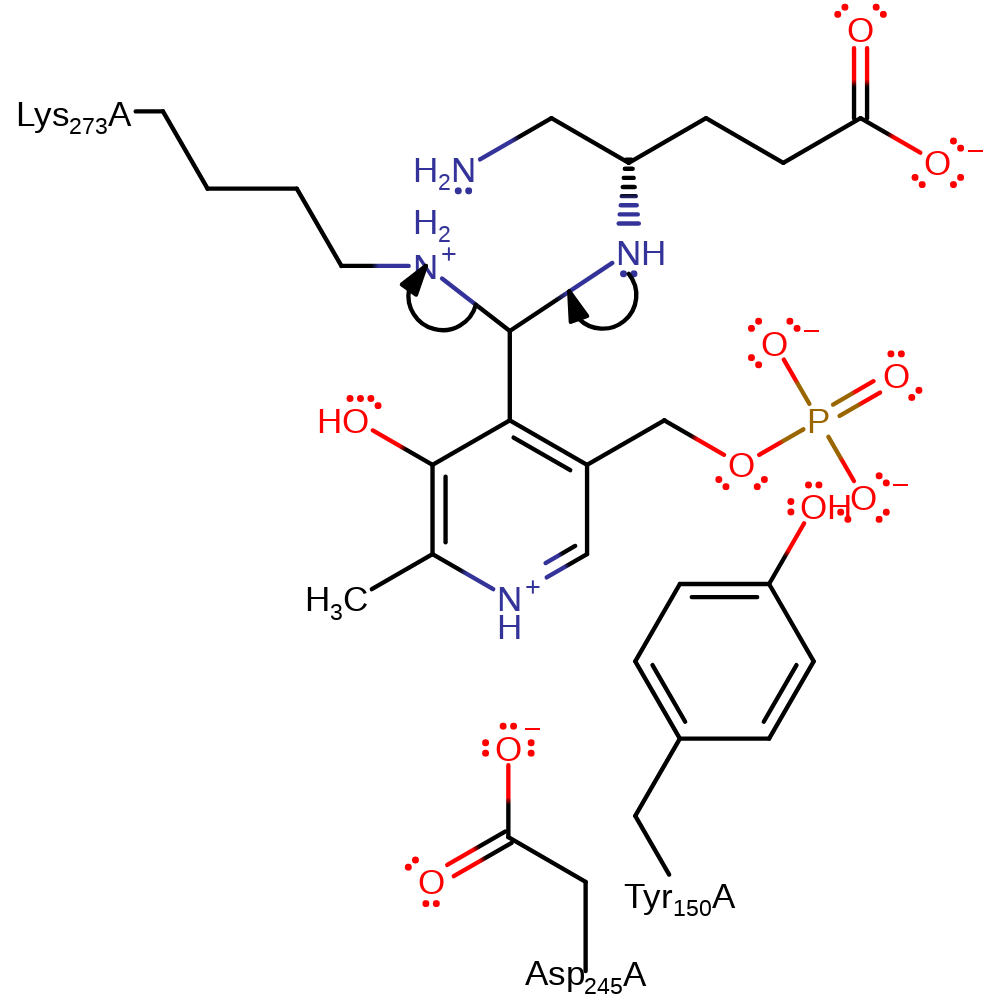
Step 8. The secondary amine that results from the attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound lysine, resulting in free PMP and lysine in a neutral state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, schiff base formed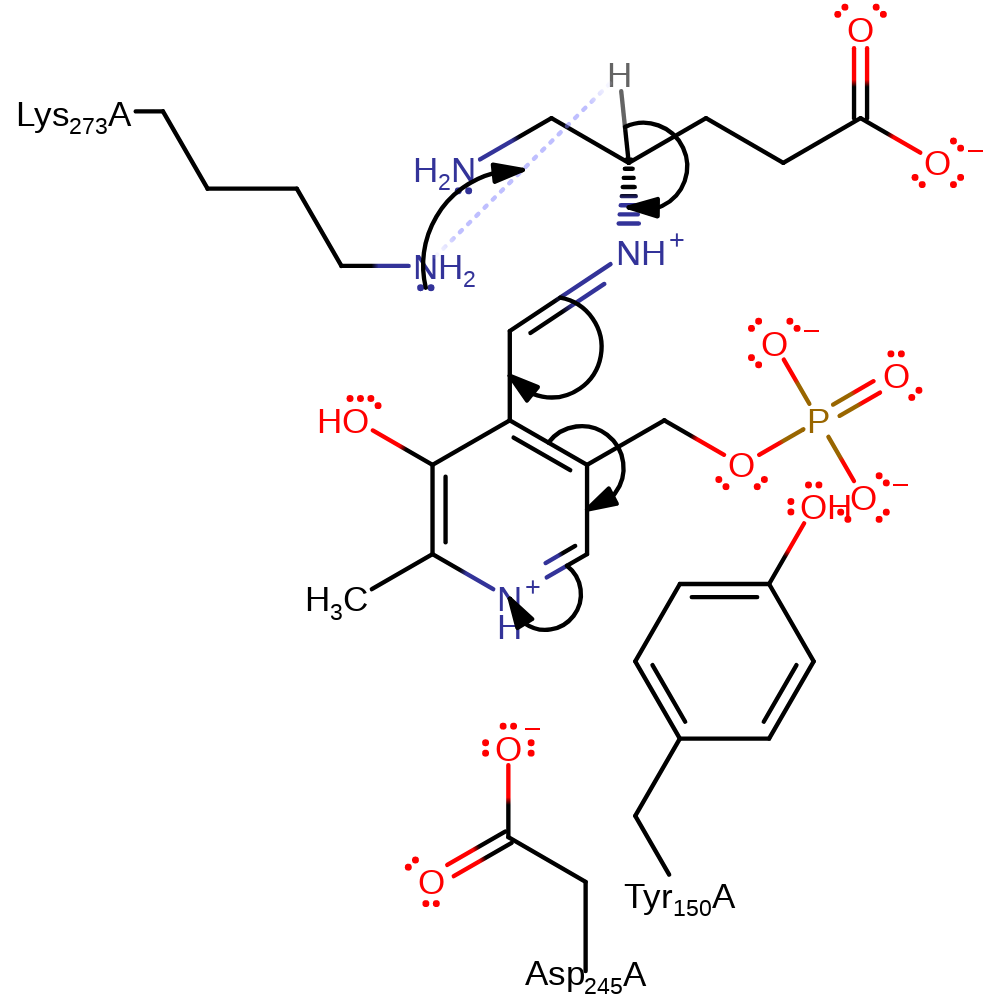
Step 9. Lys273 deprotonates the carbon next to the covalently attached nitrogen, which initiates a double bond rearrangement through the conjugated pi-bond system of PMP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys273(272)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation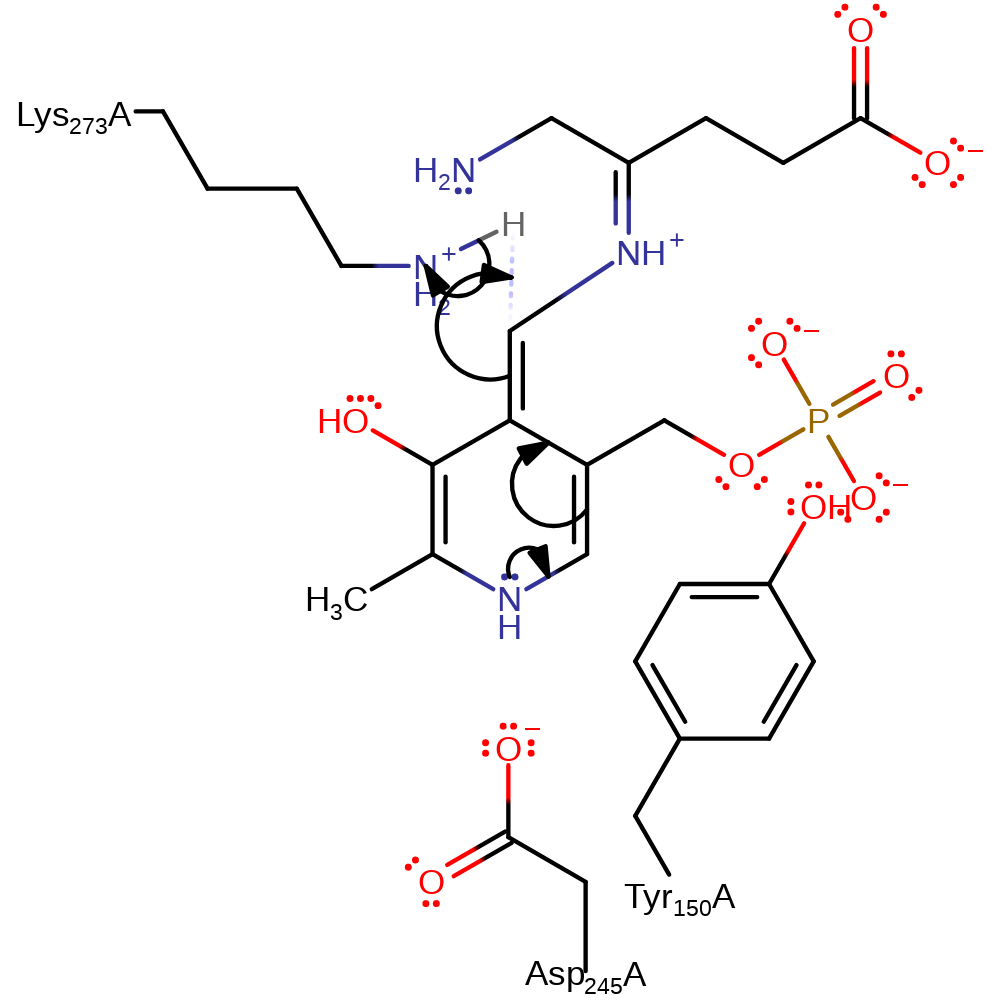
Step 10. The PMP initiates a deprotonation of the Lys273 through its conjugated pi-bond system, resulting in the protonation at the C1 of the PMP cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys273(272)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 11. Water attacks the imine in a nucleophilic addition reaction, which deprotonates the attacking water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation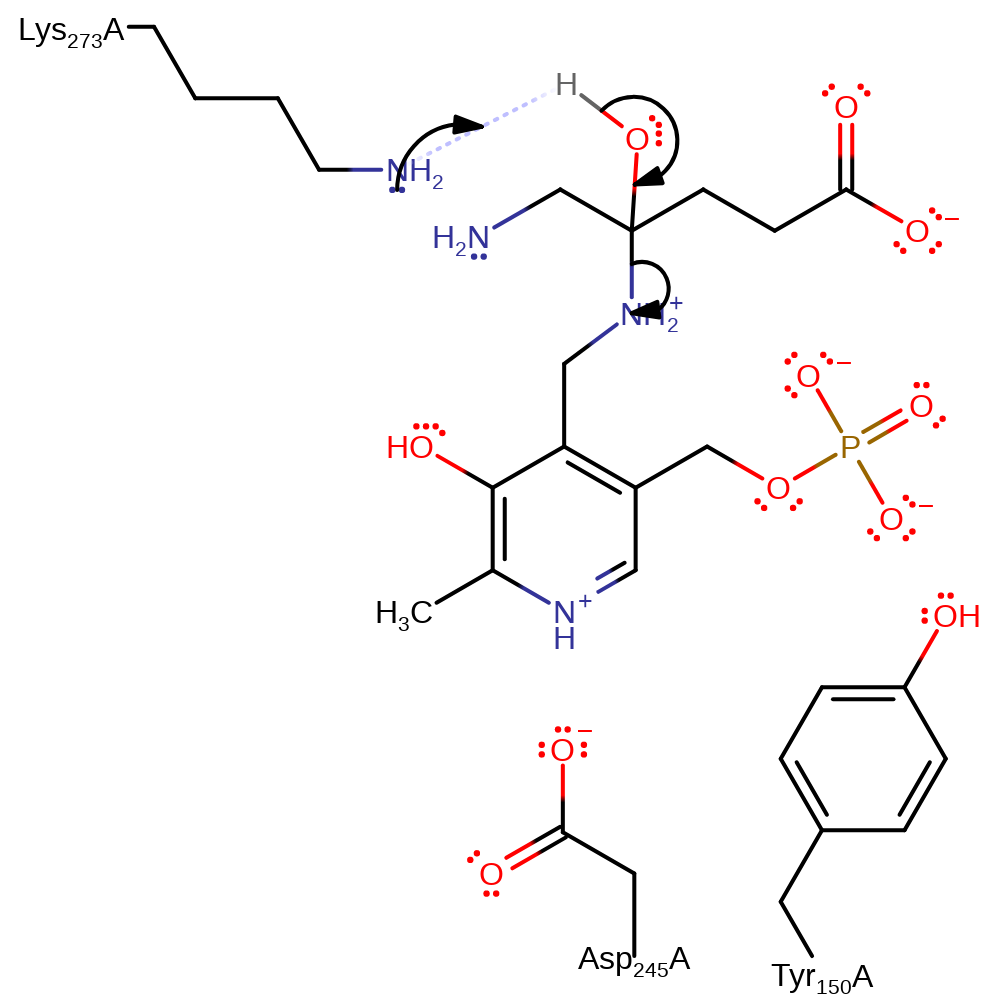
Step 12. Lys273 deprotonates the hydroxyl group, initiating an elimination of the PMP cofactor and 5-aminolevulinate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp245(244)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys273(272)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr150(149)A | steric role |
| Lys273(272)A | proton acceptor |


 Download:
Download: