Phosphomannomutase/ phosphoglucomutase
Phosphomannomutase or phosphoglucomutase (PMM/PGM) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa can catalyse the same reaction in two different substrates. It catalyses the transfer of a phosphoryl group from the 6 position to the 1 position in either mannose 6-P or glucose 6-P. PMM/PGM activity is required for the biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P26276
 (5.4.2.2, 5.4.2.8)
(5.4.2.2, 5.4.2.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1p5d
- Enzyme-ligand complex of P. aeruginosa PMM/PGM
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.120.10
 (see all for 1p5d)
(see all for 1p5d)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.4.2.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Residues Arg 20, His 109, Lys 118, Arg247 and His 329 along with cofactor Mg(II) form a positive electrostatic field. This decreases the pKa of the proton on the hydroxyl of C1 to such an extent as to cause spontaneous ionization. The substrate O atom then nucleophilically attacks the phosphorus of Sep 108, which acts as an electrophile, and the Serine O-P bond is broken. The above residues (and co-factor) then act to stabilise the Ser 108 alkoxide. Rotation of the substrate occurs, arranging the C6 phospho group toward Ser 108. Ser 108 then nucleophilically attacks the C6 phosphorus atom, breaking the P-O bond of the substrate. The substrate is then re-protonated to form the 1-P product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1p5d) | ||
| Ser108 | Sep108X(A) | Ser108 is post-translationally modified to contain a phosphate group. It donates this phospho group to the C1 position, then removes a phospho group from the C6 position of the substrate. It also forms part of the magnesium binding site (through the phosphate group). | nucleophile, nucleofuge, metal ligand |
| Arg20, His109, Lys118, His329, Arg247 | Arg20X(A), His109X(A), Lys118X(A), His329X(A), Arg247X(A) | Helps form a positive electrostatic field which decreases the pKa of the proton on the hydroxyl of C1 to such an extent as to cause spontaneous ionization. Also helps stabilise the Ser 108 alkoxide. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp244, Asp242, Asp246 | Asp244X(A), Asp242X(A), Asp246X(A) | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Naught LE et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 9946-9951. Roles of Active Site Residues inPseudomonas aeruginosaPhosphomannomutase/Phosphoglucomutase†. DOI:10.1021/bi034673g. PMID:12924943.
- Lee Y et al. (2014), J Biol Chem, 289, 4674-4682. Promotion of enzyme flexibility by dephosphorylation and coupling to the catalytic mechanism of a phosphohexomutase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.532226. PMID:24403075.
- Lee Y et al. (2013), FEBS J, 280, 2622-2632. Identification of an essential active-site residue in the α-D-phosphohexomutase enzyme superfamily. DOI:10.1111/febs.12249. PMID:23517223.
- Regni C et al. (2004), Structure, 12, 55-63. Structural Basis of Diverse Substrate Recognition by the Enzyme PMM/PGM from P. aeruginosa. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2003.11.015. PMID:14725765.
- Naught LE et al. (2001), Arch Biochem Biophys, 396, 111-118. Kinetic Mechanism and pH Dependence of the Kinetic Parameters of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Phosphomannomutase/Phosphoglucomutase. DOI:10.1006/abbi.2001.2618. PMID:11716469.
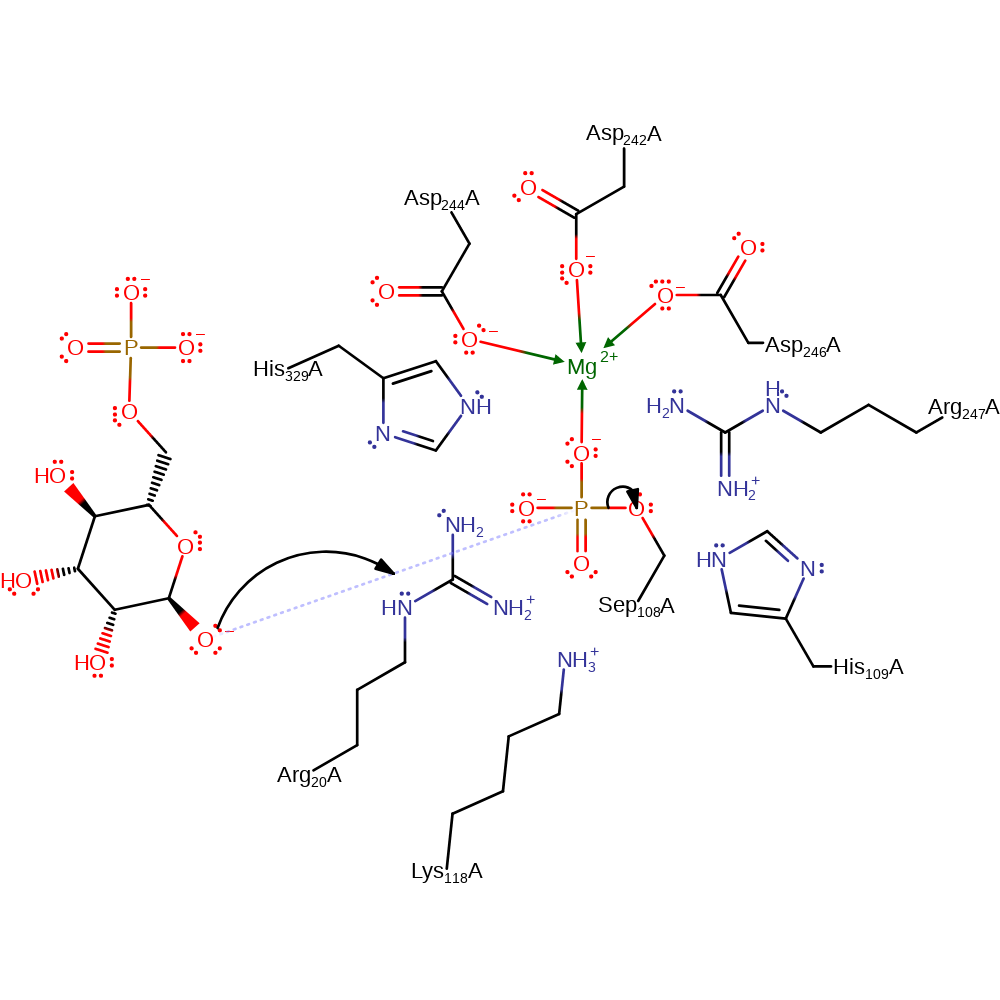
Step 1. D-mannose 6-phosphate attacks the phosphorylated Ser108 in a nucleophilic substitution, resulting in phosphorylation of the 1 position.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His329X(A) | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg247X(A) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His109X(A) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys118X(A) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg20X(A) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp246X(A) | metal ligand |
| Asp242X(A) | metal ligand |
| Asp244X(A) | metal ligand |
| Sep108X(A) | metal ligand, nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate formation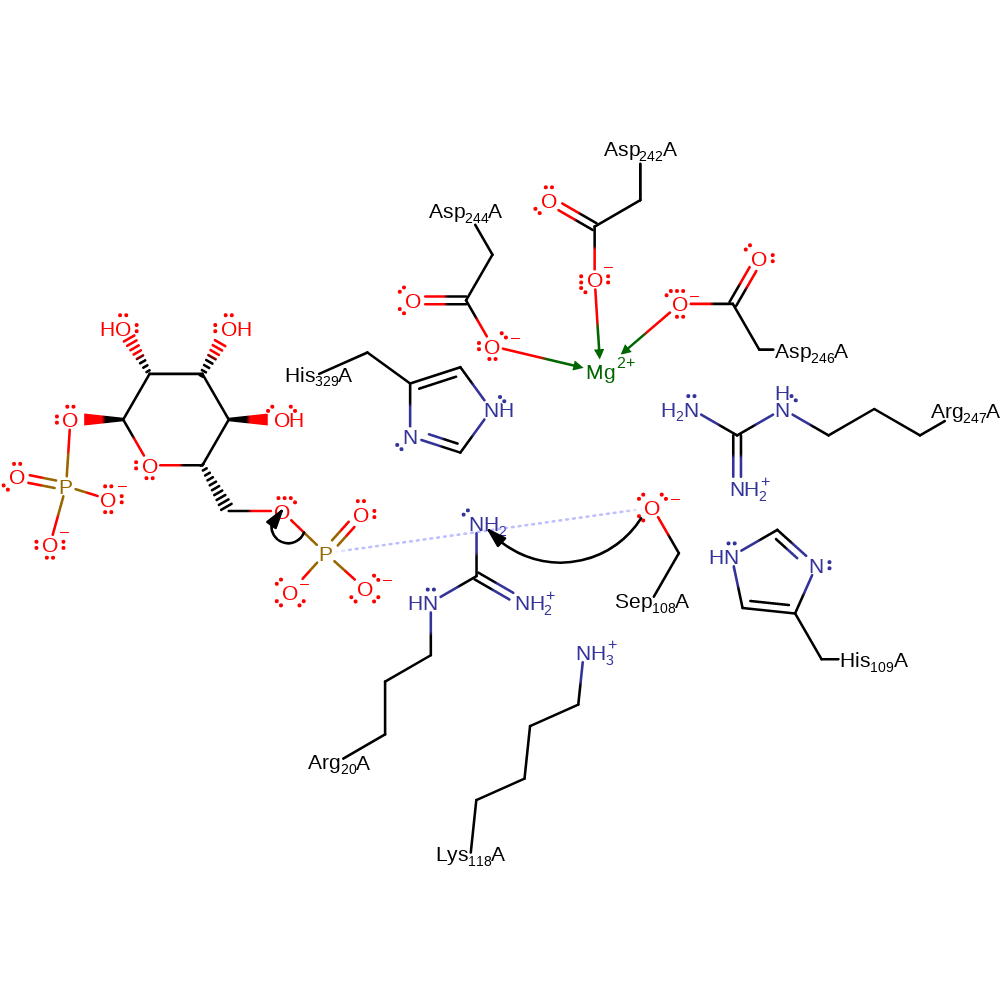
Step 2. The 1,6-biphosphate rotates in the active site before Ser108 attacks the 6 phosphate in a nucleophilic substitution reaction, resulting in regeneration of the phosphorylated serine and the D-mannose 1-phosphate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His329X(A) | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg247X(A) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His109X(A) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys118X(A) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg20X(A) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp246X(A) | metal ligand |
| Asp242X(A) | metal ligand |
| Asp244X(A) | metal ligand |
| Sep108X(A) | nucleophile |


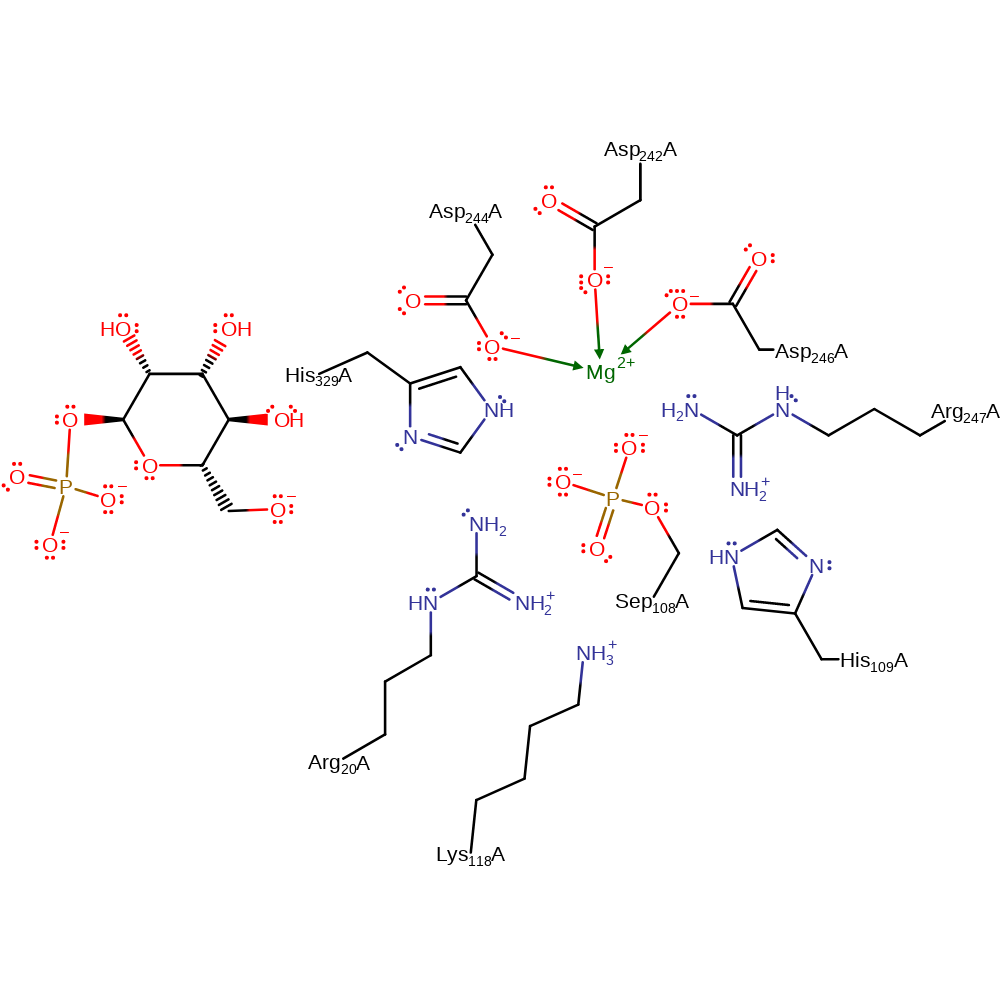 Download:
Download: