UDP-glucose 4-epimerase
UDP-glucose 4-epimerase (EC:5.1.3.2) interconverts UDP-glucose and UDP-galactose which are precursors of glucose- and galactose-containing exopolysaccharides (EPS) via the transient reduction of NAD.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P09147
 (5.1.3.2)
(5.1.3.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1xel
- UDP-GALACTOSE 4-EPIMERASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.720
 (see all for 1xel)
(see all for 1xel)
- Cofactors
- Nadph(4-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.1.3.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Tyr149 initiates the reaction via the abstraction of a proton from the substrate, which results in a hydride being transferred to the NAD cofactor. The intermediate then undergoes a conformational change in the active site. The rate-determining step of this reaction is the conformational change induced upon binding of the substrate. This is due to the fact that the mutation Tyr149Phe decreases the rate of the hydride transfer and the rate-determining conformational change by the same degree. In the final step, the hydride is returned and Tyr149 deprotonated.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xel) | ||
| Ser124 | Ser124A | Helps stabilise and activate the tyrosine residue. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr149 | Tyr149A | Acts as a general acid/base, initiating the hydride transfer from the substrate to the NAD coactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys153 | Lys153A | Activates the NAD cofactor in the reverse of the initial hydride transfer. | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Berger E et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 6699-6705. Acid−Base Catalysis by UDP-Galactose 4-Epimerase: Correlations of Kinetically Measured Acid Dissociation Constants with Thermodynamic Values for Tyrosine 149†. DOI:10.1021/bi0104571. PMID:11380265.
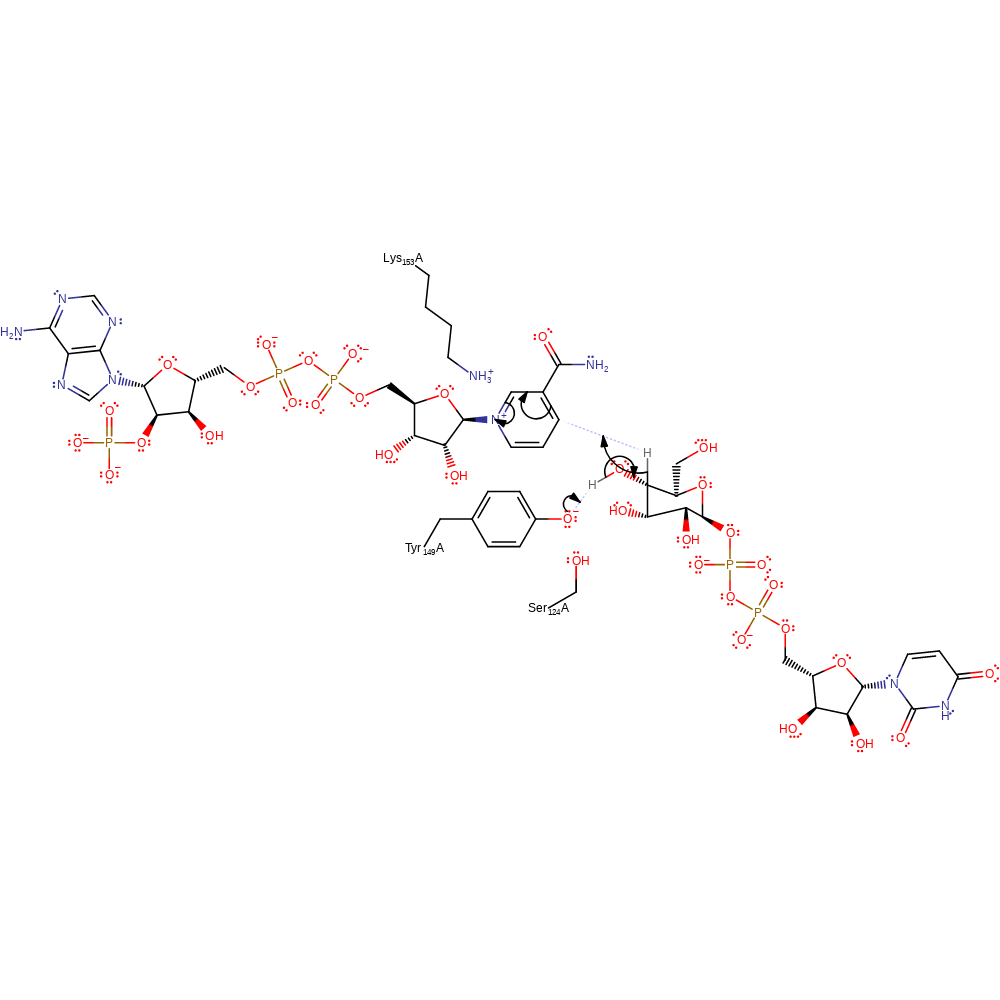
Step 1. Tyr149 deprotonates the 4-hydroxide of the substrate, resulting in an elimination of the hydride from the C4 position. The hydride then attacks the NAD cofactor in a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys153A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr149A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser124A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr149A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation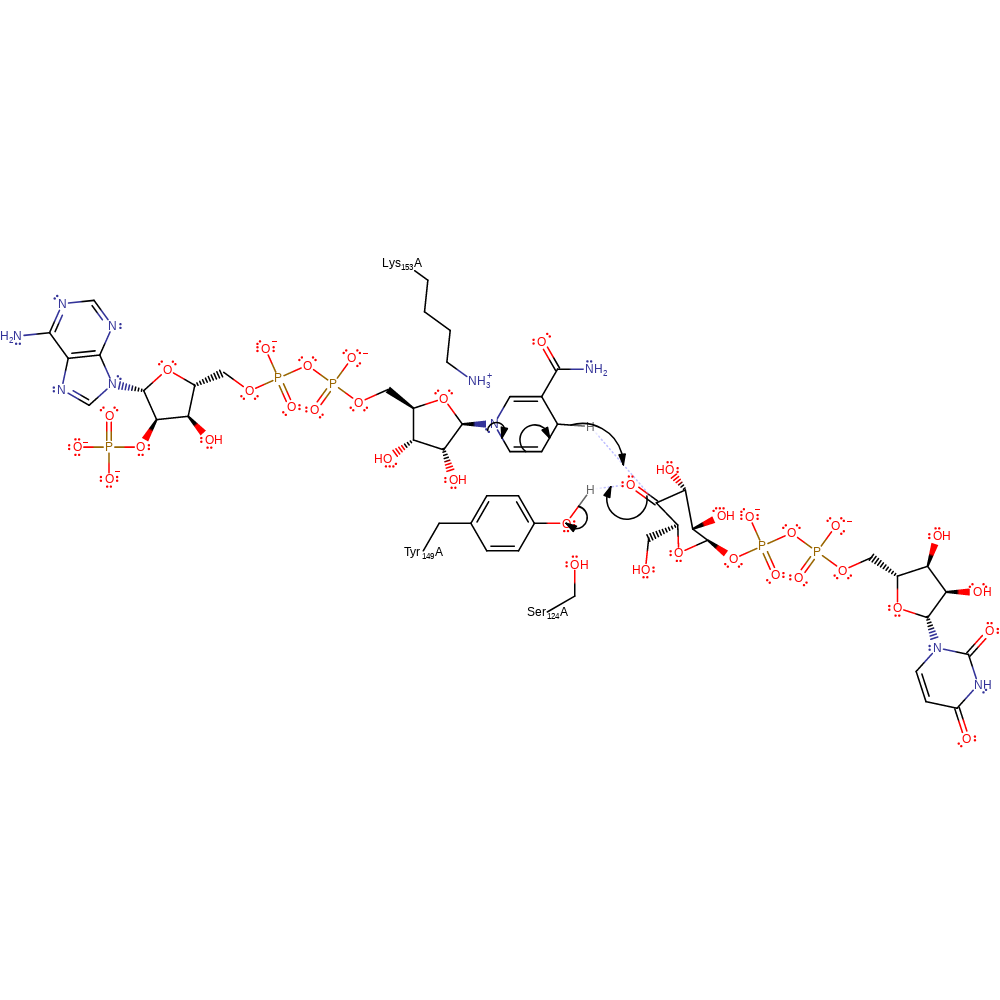
Step 2. The 4-ketohexopyranosyl ring of the intermediate rotates to place opposite faces of the 4-keto group in position for hydride from NADH. This conformational change potentates non-stereospecific hydride transfer, an essential mechanistic process in epimerisation [PMID:11380265]. The hydride transfer initiates the deprotonation of Tyr149.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys153A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Tyr149A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser124A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Tyr149A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
An alternate mechanism to the first one, where serine is directly involved in proton transfer acting as a proton relay, this is mechanism is thought to be more consistent with the E.coli enzyme while the first mechanism is more applicable to the human enzyme. The remainder of the mechanism is consistent with the first one.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xel) | ||
| Ser124 | Ser124A | Acts as a proton relay to initiate hydride transfer to the cofactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr149 | Tyr149A | Acts as a general acid/base, initiating the hydride transfer from the substrate to the coactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys153 | Lys153A | Activates the NAD cofactor in the reverse of the initial hydride transfer | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Frey PA et al. (2013), Acc Chem Res, 46, 1417-1426. Chemical and stereochemical actions of UDP-galactose 4-epimerase. DOI:10.1021/ar300246k. PMID:23339688.

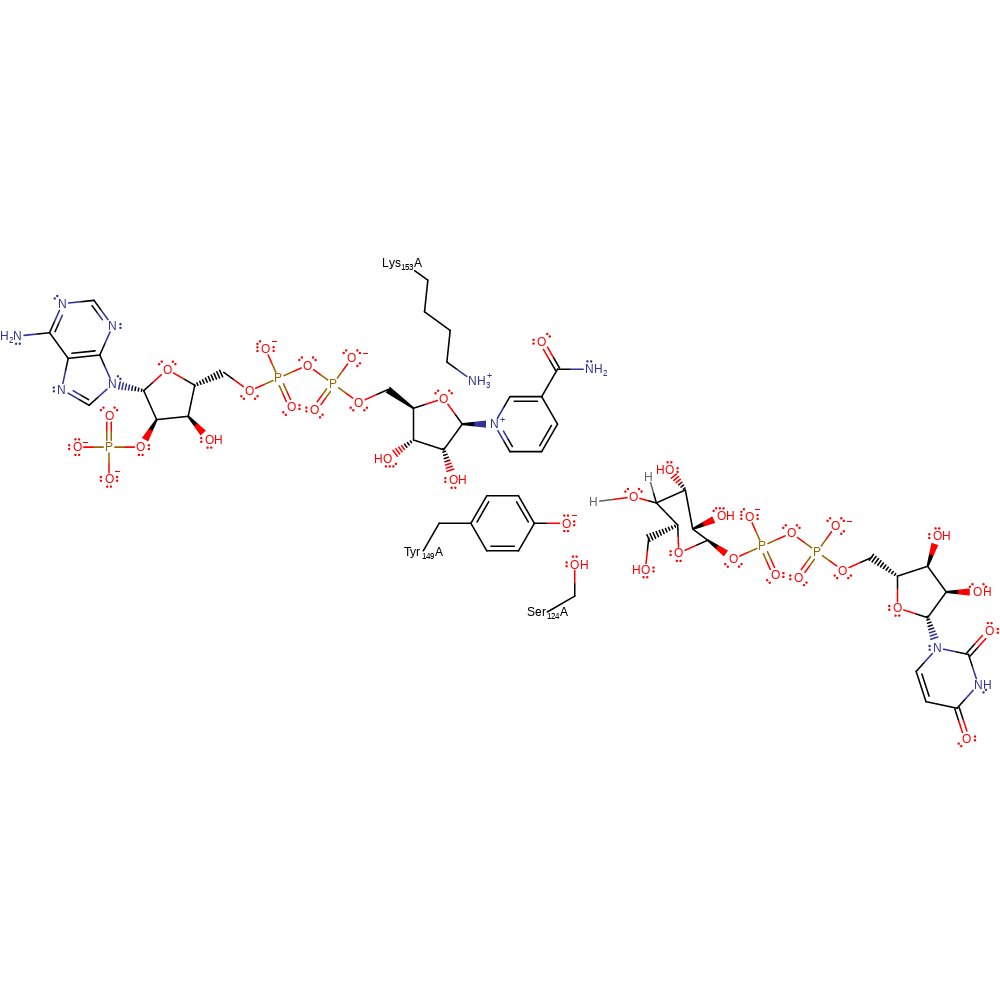
Step 1. In this alternate mechanism Tyr149 deprotonates Ser124 which simultaneously deprotonates the 4-hydroxide of the substrate, resulting in an elimination of the hydride from the C4 position. The hydride then attacks the NAD cofactor in a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser124A | proton relay |
| Ser124A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys153A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser124A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr149A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser124A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser124A | proton donor |
| Tyr149A | proton acceptor |
| Ser124A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton relay
Step 2. The 4-ketohexopyranosyl ring of the intermediate rotates to place opposite faces of the 4-keto group in position for hydride from NADH. This conformational change potentates non-stereospecific hydride transfer, an essential mechanistic process in epimerisation. The hydride transfer intiates the proton relay from the product via Ser 124 to Tyr 149.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys153A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Ser124A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr149A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser124A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr149A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser124A | proton relay, proton acceptor |
| Tyr149A | proton donor |
| Ser124A | proton donor |


 Download:
Download: 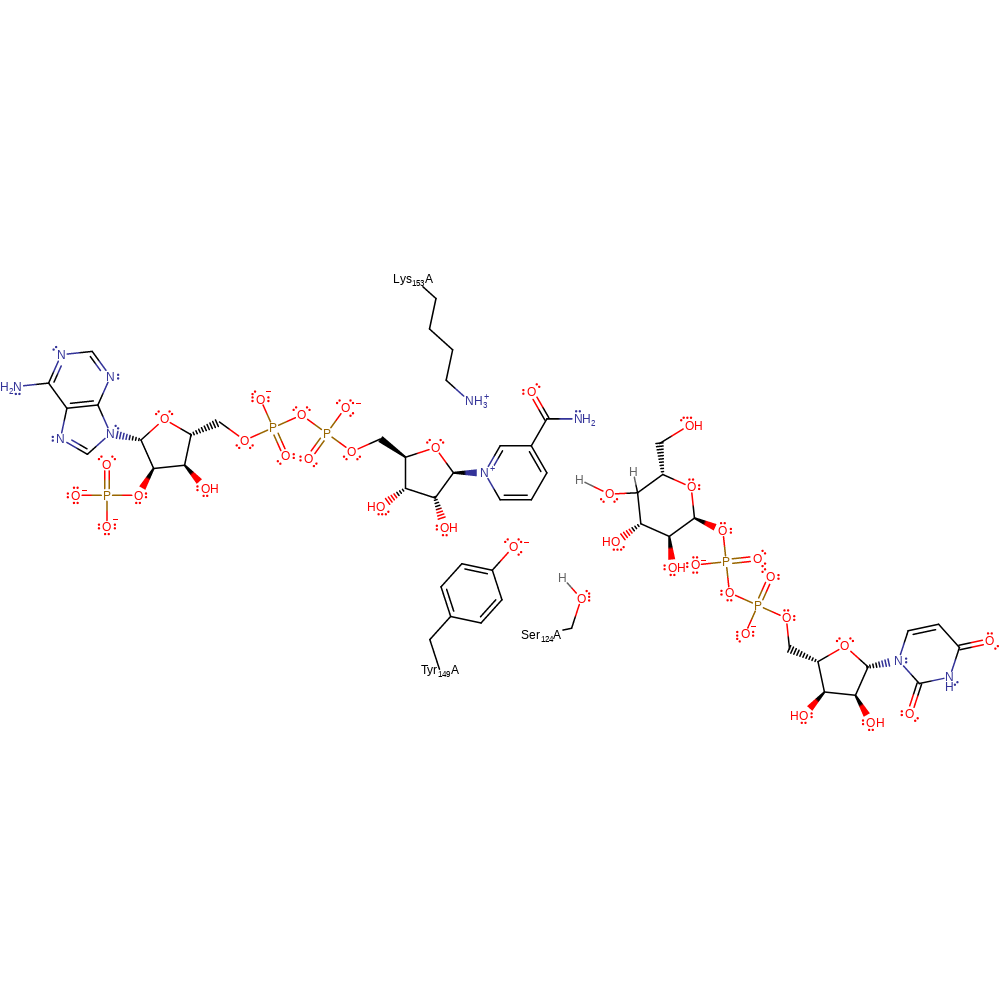 Download:
Download: