Bacterial leucyl aminopeptidase
Aminopeptidases catalyse the hydrolysis of a wide range of N-terminal amino acid residues from proteins and polypeptides. These enzymes have a broad substrate specificity and are widely distributed in bacteria, yeast, plant and animal tissues. Functions of aminopeptidases include protein maturation, protein degradation, hormone level regulation and cell cycle control. Since aminopeptidase activity has been reported on the surface of tumour cells, they are very likely key players in tumour growth and metastatic proliferation.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q01693
 (3.4.11.10)
(3.4.11.10)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Vibrio proteolyticus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1lok
- The 1.20 Angstrom Resolution Crystal Structure of the Aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica Complexed with Tris: A Tale of Buffer Inhibition
(1.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.630.10
 (see all for 1lok)
(see all for 1lok)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.11.10)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
A zinc-activated water molecule, deprotonated by glutamate, attacks the carbonyl carbon of the substrate. The tetrahedral oxyanion transition state is stabilised by one of the zinc ions. The transition state collapses, breaking the peptide bond, and the leaving group is protonated by the glutamate residue, returning the enzyme to its native state.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1lok) | ||
| Glu257 | Glu151A | Deprotonates the nucleophilic water molecule, protonates the leaving group. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp223 | Asp117A | Binds both the zinc ions. | metal ligand |
| Asp285, His203 | Asp179A, His97A | Forms part of the zinc 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| His362, Glu258 | His256A, Glu152A | Forms part of the zinc 2 binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, rate-determining stepReferences
- Chen G et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 4278-4286. Mechanistic Studies on the Aminopeptidase fromAeromonas proteolytica: A Two-Metal Ion Mechanism for Peptide Hydrolysis†. DOI:10.1021/bi9618676. PMID:9100023.
- Chen SL et al. (2008), J Phys Chem B, 112, 2494-2500. Peptide hydrolysis by the binuclear zinc enzyme aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica: a density functional theory study. DOI:10.1021/jp710035j. PMID:18247603.
- Desmarais W et al. (2006), J Biol Inorg Chem, 11, 398-408. The high-resolution structures of the neutral and the low pH crystals of aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica. DOI:10.1007/s00775-006-0093-x. PMID:16596389.
- Desmarais WT et al. (2002), Structure, 10, 1063-1072. The 1.20 A resolution crystal structure of the aminopeptidase from Aeromonas proteolytica complexed with tris: a tale of buffer inhibition. DOI:10.2210/pdb1lok/pdb. PMID:12176384.
- Stamper C et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 7035-7046. Inhibition of the Aminopeptidase fromAeromonas proteolyticabyl-Leucinephosphonic Acid. Spectroscopic and Crystallographic Characterization of the Transition State of Peptide Hydrolysis†. DOI:10.1021/bi0100891. PMID:11401547.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp117A | metal ligand |
| His97A | metal ligand |
| Glu152A | metal ligand |
| His256A | metal ligand |
| Asp179A | metal ligand |
| Glu151A | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation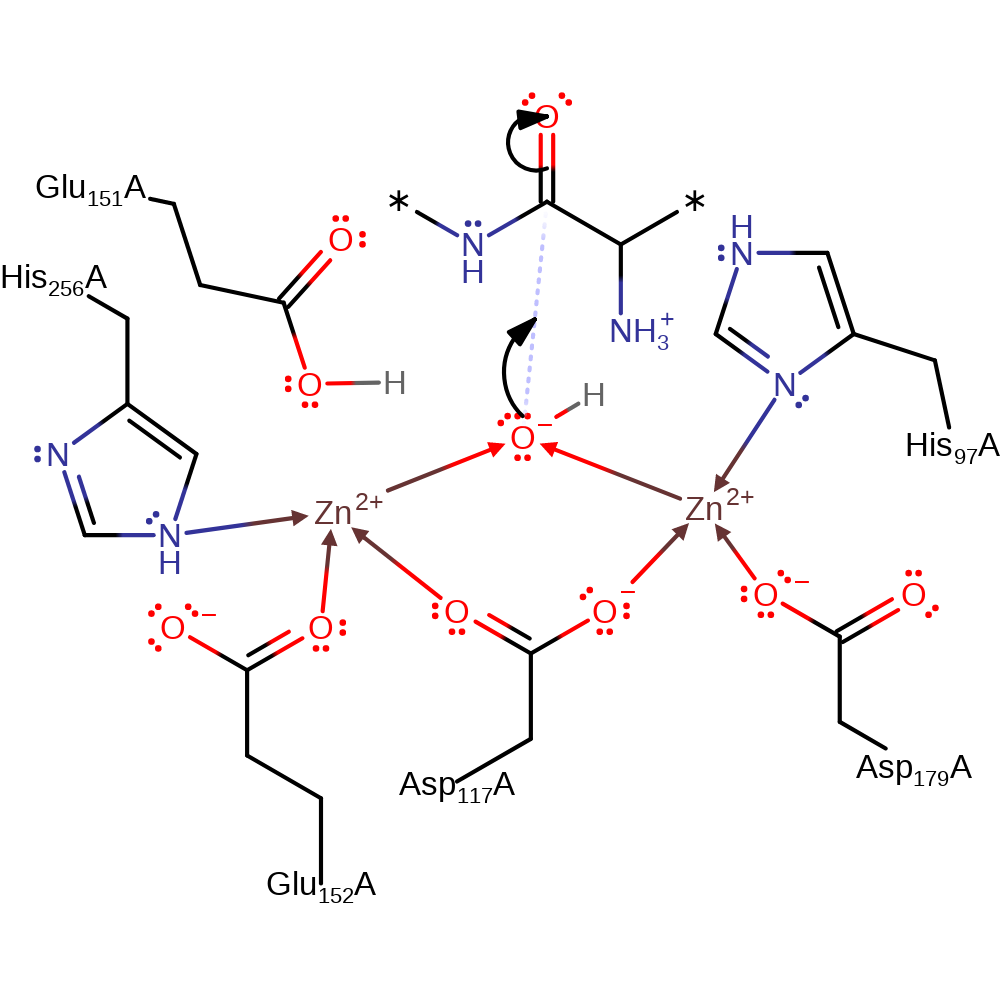
Step 2. The activated hydroxide attacks the peptide carbonyl in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp117A | metal ligand |
| His97A | metal ligand |
| Glu152A | metal ligand |
| His256A | metal ligand |
| Asp179A | metal ligand |
| Glu151A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation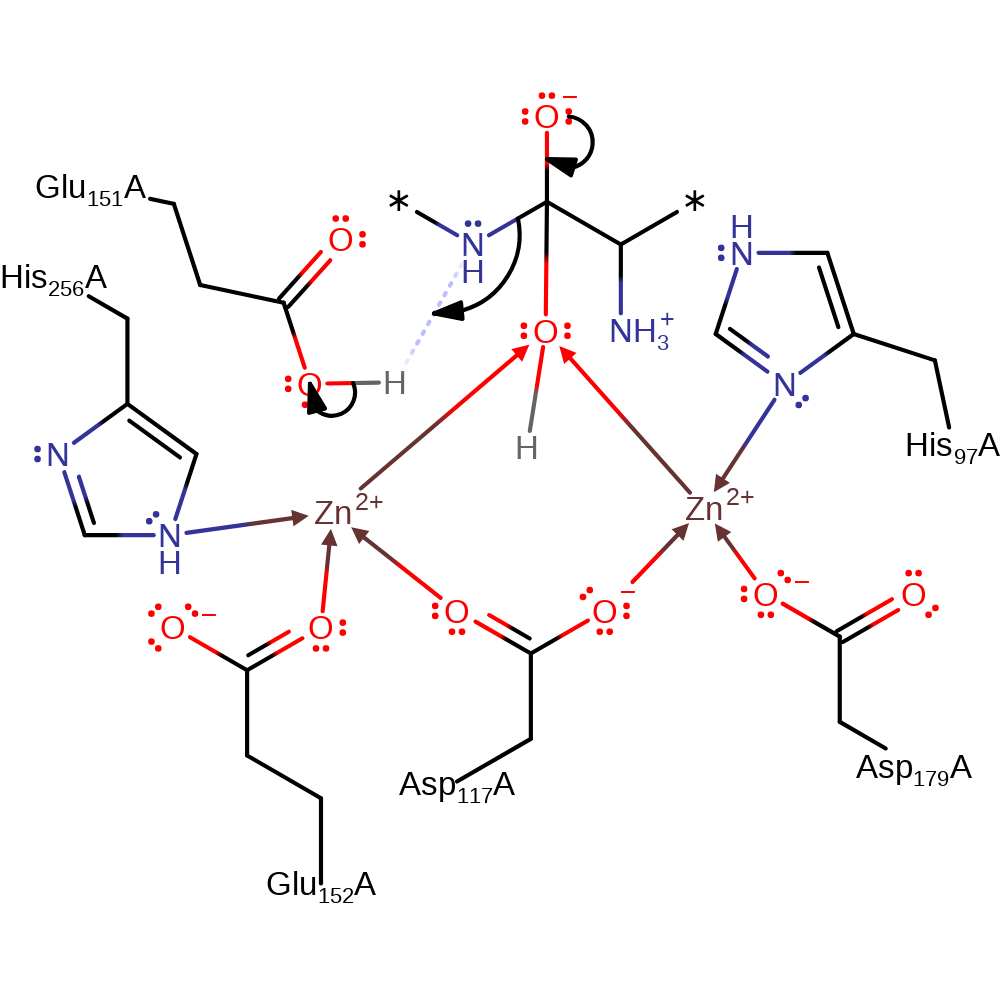
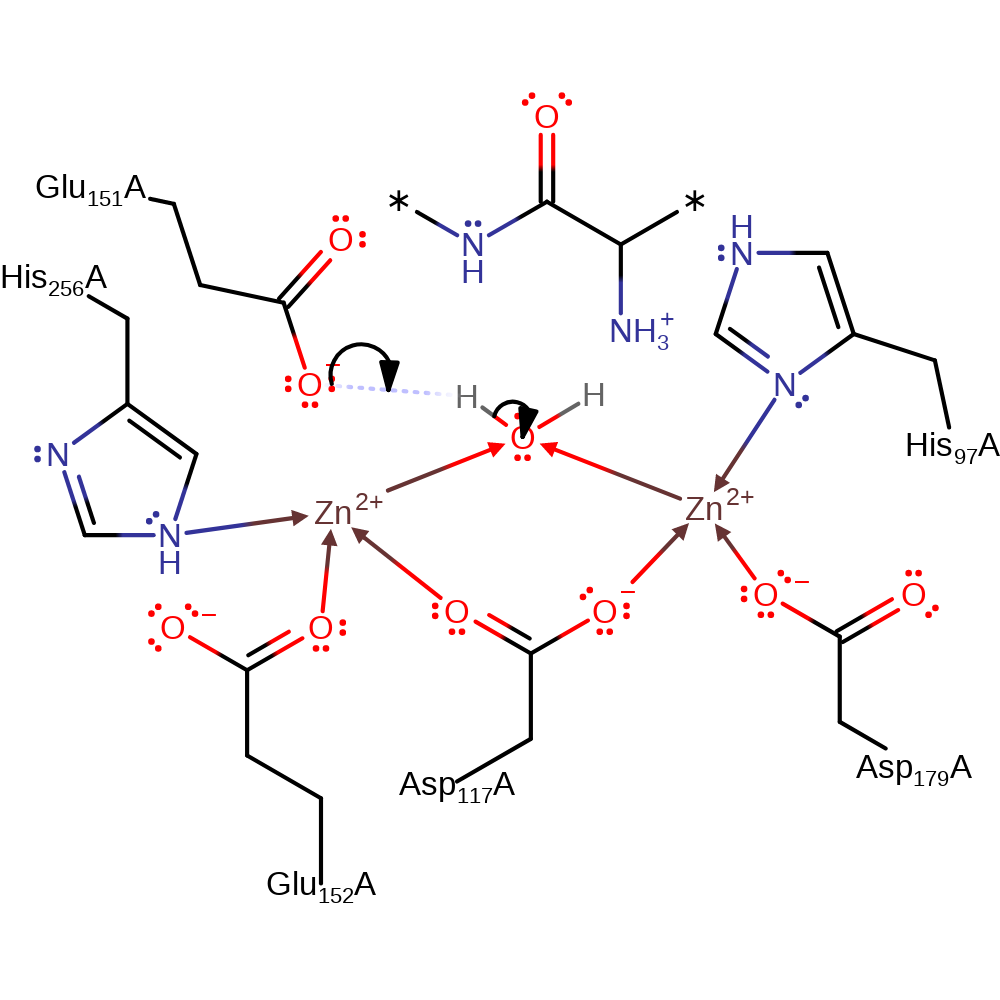
Step 3. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves the peptide bond and releases the protein's new N-terminal amino acid, which protonates from Glu151, and the amino acid product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His97A | metal ligand |
| Asp117A | metal ligand |
| Glu152A | metal ligand |
| Asp179A | metal ligand |
| His256A | metal ligand |
| Glu151A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton donor |



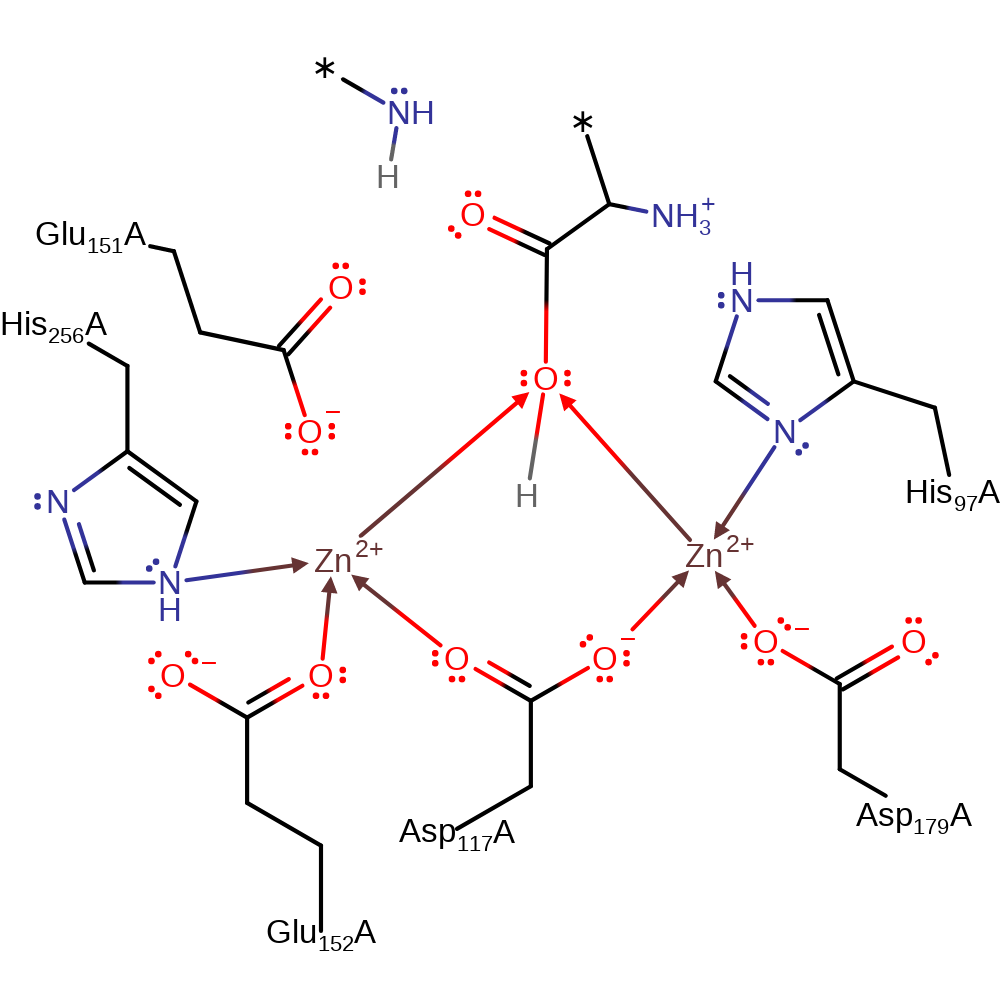 Download:
Download: