Leukotriene-A4 hydrolase
Leukotriene A4 hydrolase/ Aminopeptidase is involved in the immune response in humans, and is unique in its ability to catalyse two very different reactions at the active site. Not only is it able to catalyse the hydrolysis of the epoxide Leukotriene A4 to produce the potent immune activator Leukotriene B4, it is also able to catalyse the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, acting on the first peptide bond after the N terminal. One active site is enough to confer such variety of function, so the enzyme represents a yardstick of evolutionary efficiency seldom reached in nature. It displays a characteristic Zinc binding motif at the active site (GXMEN) which places it in the family M1 of Zinc metalloproteases.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P09960
 (3.3.2.6, 3.4.11.4)
(3.3.2.6, 3.4.11.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1hs6
- STRUCTURE OF LEUKOTRIENE A4 HYDROLASE COMPLEXED WITH BESTATIN.
(1.95 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.390.10
 1.10.1740.60
1.10.1740.60  (see all for 1hs6)
(see all for 1hs6)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.3.2.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In the hydrolysis of Leukotriene, a water molecule, activated by Zinc acts as an acid to protonate the epoxide, causing ring opening. This leads to a carbocation, stabilised by delocalisation between the three double bonds. Nucleophilic attack by the OH- ion, activated this time by Glu 271, on the terminal double bond of the delocalised system leads to the final product Leukotriene B4. In the hydrolysis of peptides, a water molecule, activated by Glu 296 and Zinc, attacks the peptide bond leading to a tetrahedral intermediate with negative charge localised to the oxygen. This is stabilised by binding to Zn2+ and by favourable contacts between the N terminal section and Glu 271. Protonation of the leaving group by Tyr 383 leads to collapse of the intermediate and the formation of the products.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hs6) | ||
| Glu297 | Glu296(297)A | Activates a water molecule for nucleophilic attack by deprotonation in the peptidase reaction. In this mechanism it activates and stabilises the reactive intermediates formed. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu272 | Glu271(272)A | Has a vital role in both reaction. In the hydrolysis of the epoxide, acts to activate a water molecule towards nucleophilic attack. In the hydrolysis of the aminopeptide, acts to stabilise the tetrahedral intermediate by contact with the amino terminal. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr384 | Tyr383(384)A | Primarily functions as a general acid/base in the peptidase reaction by protonating the leaving group thus allowing collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate to occur. In this mechanism it likely helps to stabilise the intermediates formed. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp376 | Asp375(376)A | Acts as a general acid/base during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His300, His296, Glu319 | His299(300)A, His295(296)A, Glu318(319)A | Forms part of the zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, heterolysis, decyclisation, charge delocalisation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Rudberg PC et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 1398-1404. Leukotriene A4Hydrolase/Aminopeptidase: GLUTAMATE 271 IS A CATALYTIC RESIDUE WITH SPECIFIC ROLES IN TWO DISTINCT ENZYME MECHANISMS. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m106577200. PMID:11675384.
- Haeggström JZ et al. (2007), Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 83, 198-202. Structure and catalytic mechanisms of leukotriene A4 hydrolase. DOI:10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2007.01.006. PMID:17481555.
- Rudberg PC et al. (2002), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 99, 4215-4220. Leukotriene A4 hydrolase: Selective abrogation of leukotriene B4 formation by mutation of aspartic acid 375. DOI:10.1073/pnas.072090099. PMID:11917124.
- Thunnissen MM et al. (2001), Nat Struct Biol, 8, 131-135. Crystal structure of human leukotriene A(4) hydrolase, a bifunctional enzyme in inflammation. DOI:10.1038/84117. PMID:11175901.
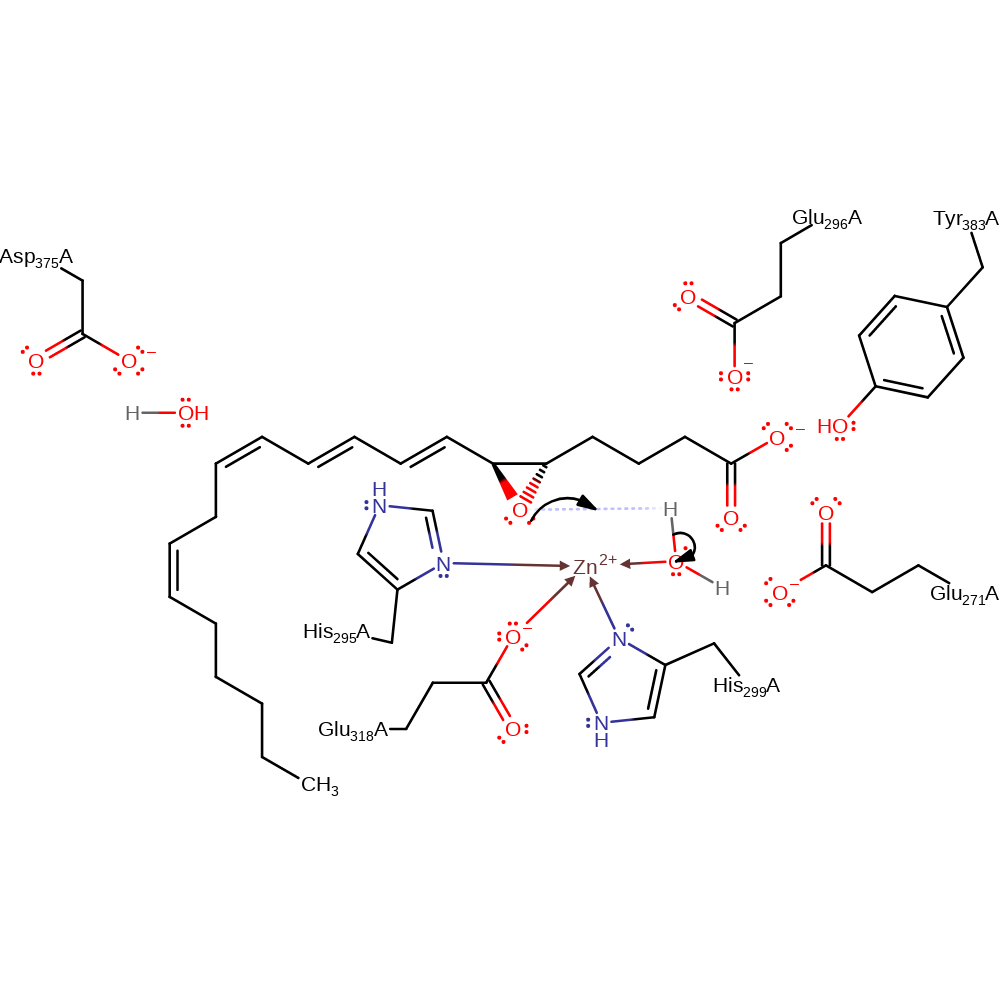
Step 1. The oxygen of the oxirane ring in leukotriene A4 deprotonates a water molecule activated by Glu271.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp375(376)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu271(272)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His299(300)A | metal ligand |
| His295(296)A | metal ligand |
| Glu318(319)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp375(376)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu271(272)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu296(297)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr383(384)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His299(300)A | metal ligand |
| His295(296)A | metal ligand |
| Glu318(319)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, decyclisation, intermediate formation, charge delocalisation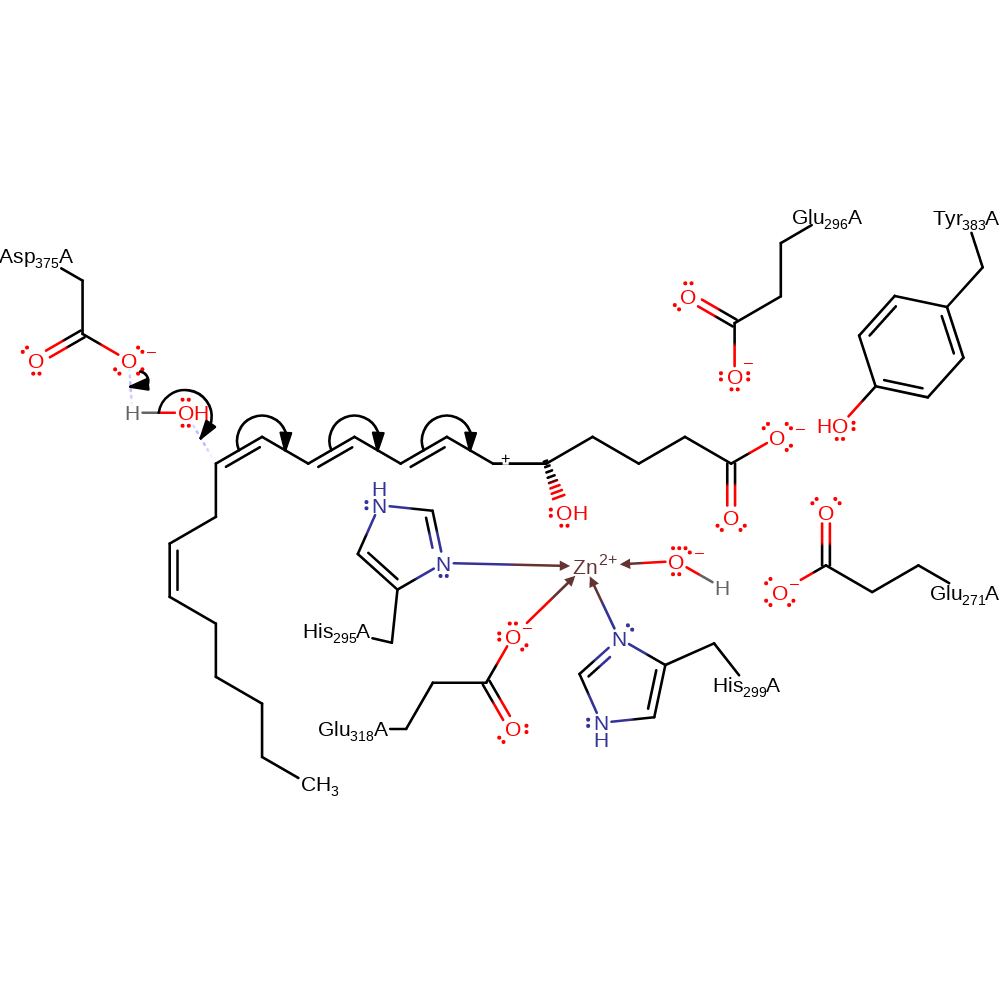
Step 3. Asp375 deprotonates a water molecule, which attacks the intermediate in a nucleophilic addition with attendant double bond rearrangement, producing the leukotriene B4 product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu296(297)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr383(384)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His299(300)A | metal ligand |
| His295(296)A | metal ligand |
| Glu318(319)A | metal ligand |
| Asp375(376)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu271(272)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp375(376)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate terminated, overall product formed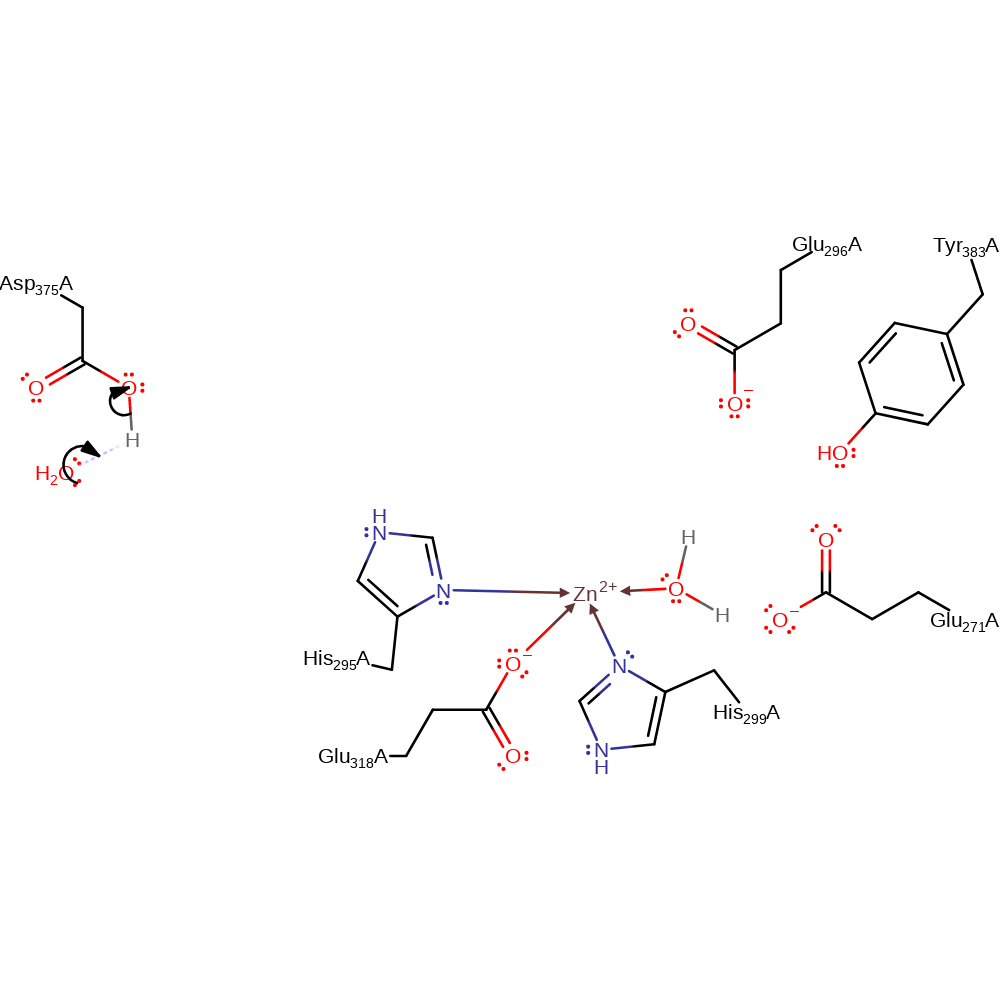
Step 4. Water deprotonates Asp375, regenerating the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His299(300)A | metal ligand |
| His295(296)A | metal ligand |
| Glu318(319)A | metal ligand |
| Asp375(376)A | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
This proposal proceeds via an ester intermediate. In this scheme, the zinc alone activates and opens the epoxide, and the carboxylate of Glu-271 attacks LTA4 at C6 to form an ester intermediate. In a concerted SN2′ reaction, this ester can then be attacked by an hydroxyl group or a carboxylate at C12, and the negative charge can move along the conjugated triene system, eventually leading to an alkyl-oxygen cleavage instead of a normal ester cleavage.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hs6) | ||
| Glu297 | Glu296(297)A | Activates the water molecule that donates its proton to the reactive intermediate. It also activates and stabilises the reactive intermediates formed. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu272 | Glu271(272)A | Acts as a nucleophile and forms a covalent bond with the substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Tyr384 | Tyr383(384)A | In this mechanism it likely helps to stabilise the intermediates formed. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp376 | Asp375(376)A | Acts as a general acid/base during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |
| His300, His296, Glu319 | His299(300)A, His295(296)A, Glu318(319)A | Forms part of the zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution with allylic rearrangement, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Rudberg PC et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 1398-1404. Leukotriene A4Hydrolase/Aminopeptidase: GLUTAMATE 271 IS A CATALYTIC RESIDUE WITH SPECIFIC ROLES IN TWO DISTINCT ENZYME MECHANISMS. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m106577200. PMID:11675384.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp375(376)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His299(300)A | metal ligand |
| His295(296)A | metal ligand |
| Glu318(319)A | metal ligand |
| Glu271(272)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation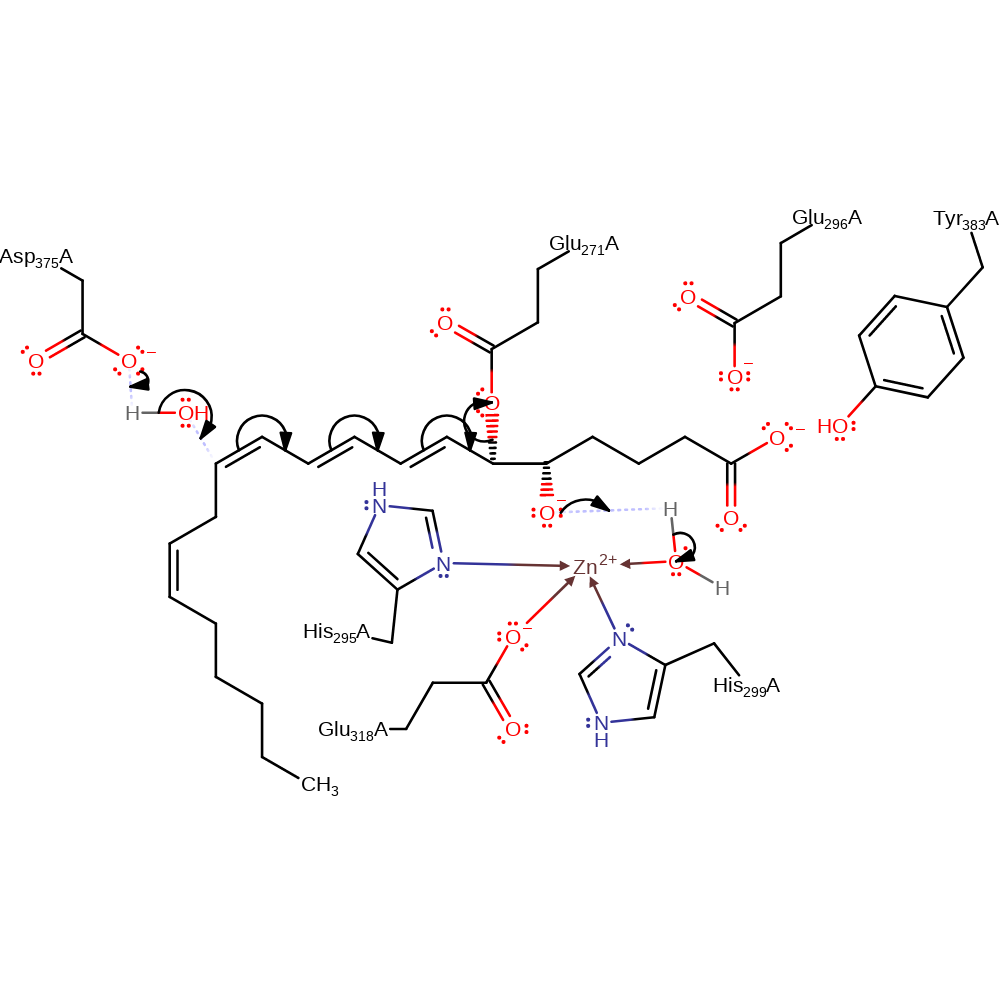
Step 2. Asp375 deprotonates a water molecule, which attacks the intermediate in a nucleophilic addition with attendant double bond rearrangement, producing the leukotriene B4 product with concomitant deprotonation of a zinc bound water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr383(384)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu296(297)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu271(272)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His299(300)A | metal ligand |
| His295(296)A | metal ligand |
| Glu318(319)A | metal ligand |
| Asp375(376)A | proton acceptor |
| Glu271(272)A | nucleofuge |



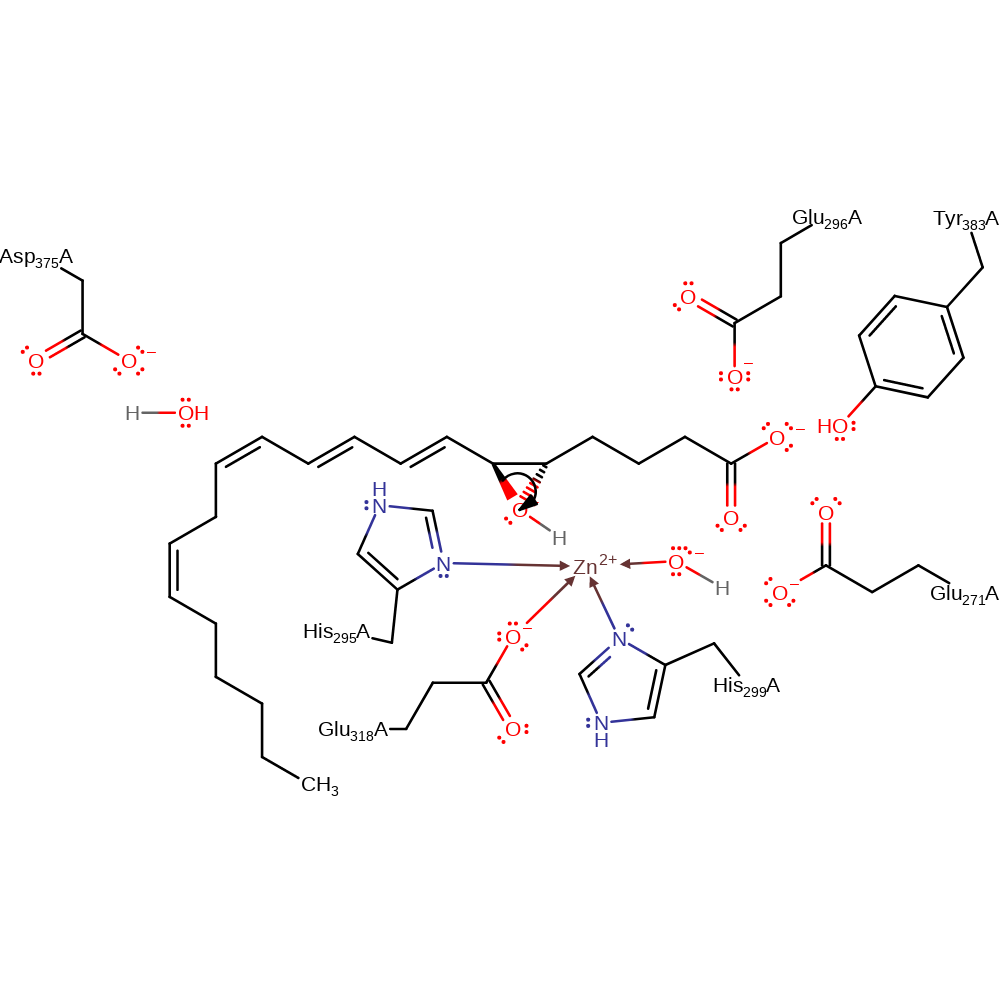
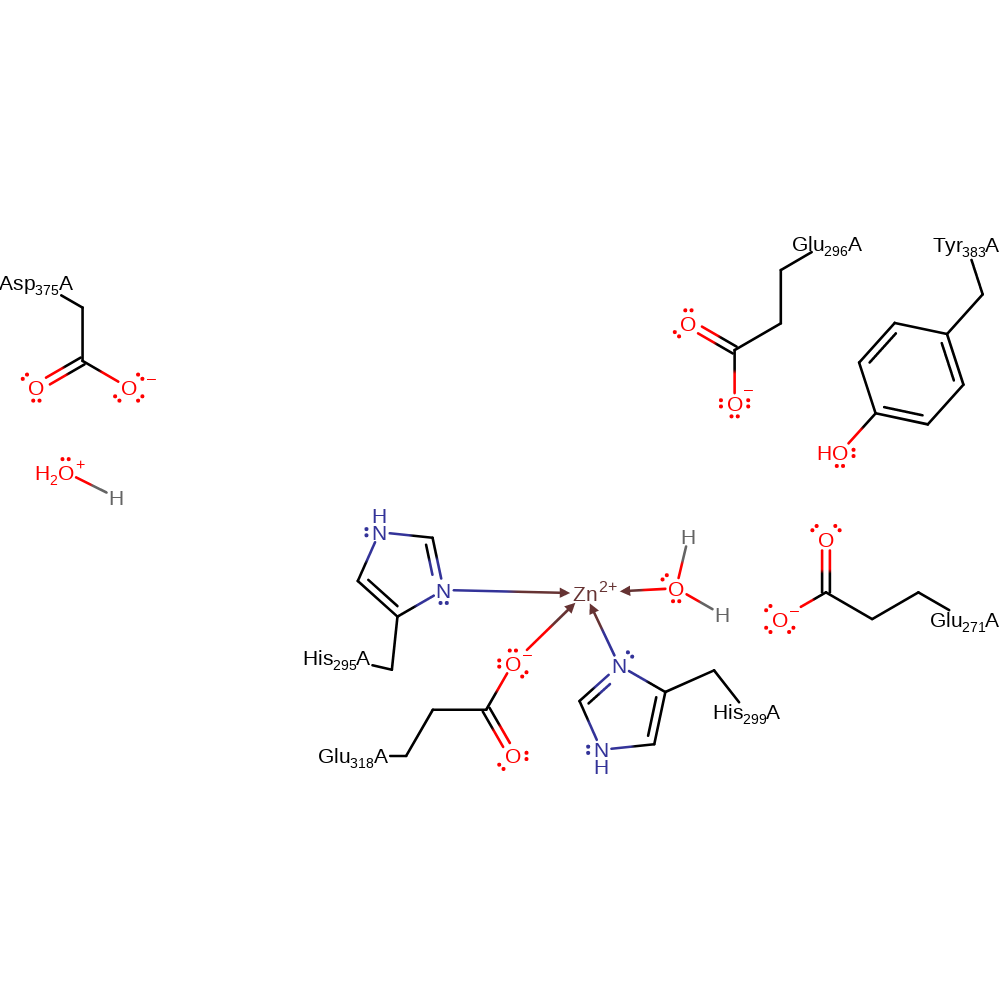 Download:
Download: 
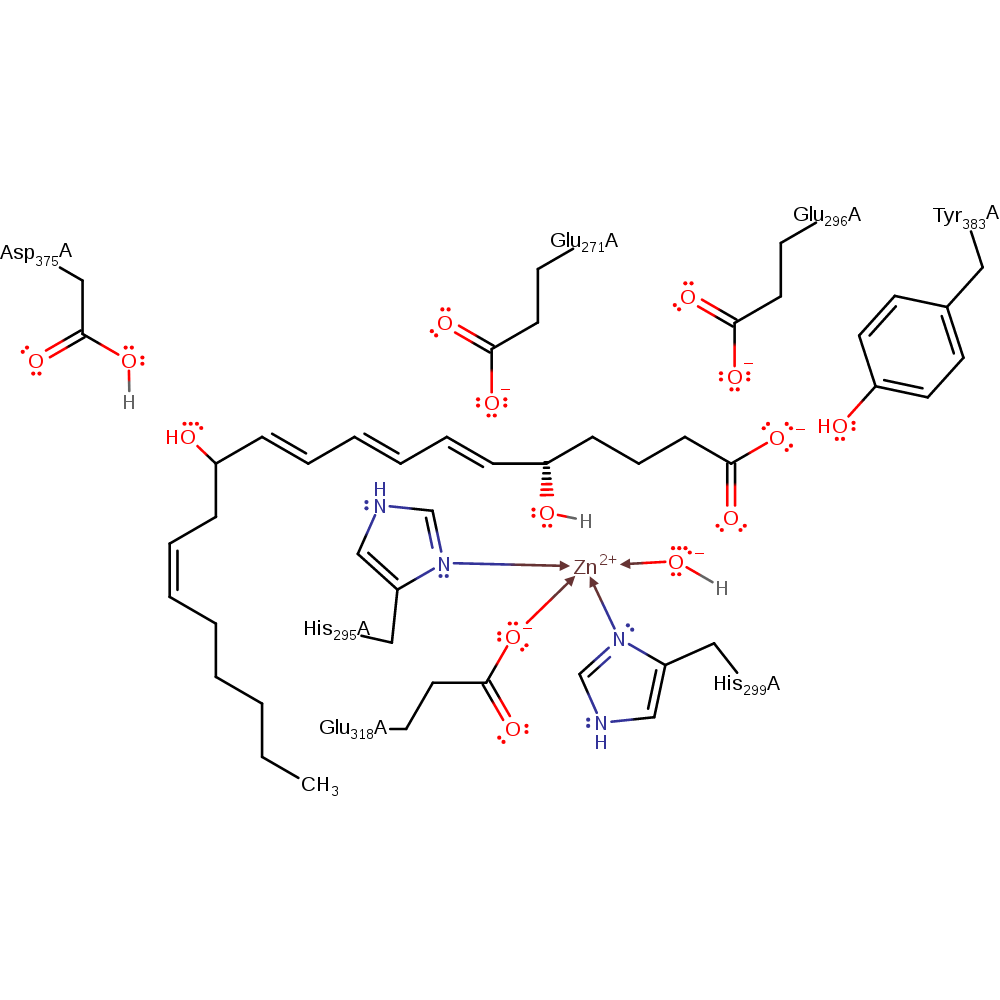 Download:
Download: