Ribonuclease 1
Ribonuclease-A (RNase-A) from Bos taurus catalyses the depolymerisation of RNA. It does this by breaking down the 3'-5' phosphodiester linkages of single stranded RNA. It is specific for pyrimidine bases at the 3' position of the phosphodiester bond that is cleaved, and a purine at the 5' end. RNase-A also shows a preference for polynucleotide substrates over oligonucleotides.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P61823
 (4.6.1.18)
(4.6.1.18)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bos taurus (Cattle)

- PDB
-
1ruv
- RIBONUCLEASE A-URIDINE VANADATE COMPLEX: HIGH RESOLUTION RESOLUTION X-RAY STRUCTURE (1.3 A)
(1.25 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.10.130.10
 (see all for 1ruv)
(see all for 1ruv)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.6.1.18)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction occurs in two distinct phases:
- Transphosphorylation. His 12 acts as a general base by abstracting a proton from the 2' O atom, activating it for nucleophilic attack. The activated 2' O nucleophilically attacks the phosphorus atom, causing the P-5'O atom to break, forming a 2',3'-cyclic phosphodiester. The transition state is stabilised by the positively charged Lys 41. The leaving group R-5'O is protonated by the general acid His 119.
- Hydrolysis. His 119 acts as a general base, abstracting a proton from a water molecule, activating it for nucleophilic attack. The hydroxide nucleophilically attacks the phosphorus atom, breaking the P-2'O bond. The transition state is stabilised by the positively charged Lys 41. The 2'O atom is protonated by the general acid His12.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ruv) | ||
| Lys67 | Lys41A | Positively charged Lys 41 stabilises the negatively charged transition state. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His38 | His12A | In the transphosphorylation step, His 12 acts as a general base, deprotonating the 2' O atom. In the hydrolysis step, His 12 acts as a general acid, protonating the leaving group 2' O atom. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His145 | His119A | In the transphosphorylation step, His 119 acts as a general acid, protonating the leaving group R-5'O. In the hydrolysis step, His 119 acts as a general base, deprotonating a water molecule, activating it for nucleophilic attack. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp147 | Asp121A | Modifes the pKa of His119 to activate it as the general acid. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe146 (main-N) | Phe120A (main-N) | Helps stabilise the negatively charged transition states and intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, cyclisation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate terminated, decyclisation, hydrolysis, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Raines RT (1998), Chem Rev, 98, 1045-1066. Ribonuclease A. DOI:10.1021/cr960427h. PMID:11848924.
- Kasireddy C et al. (2016), Chem Phys Lett, 666, 58-61. Tautomeric stabilities of 4-fluorohistidine shed new light on mechanistic experiments with labeled ribonuclease A. DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2016.10.072. PMID:28603294.
- Harris ME et al. (2015), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1854, 1801-1808. Integration of kinetic isotope effect analyses to elucidate ribonuclease mechanism. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.04.022. PMID:25936517.
- Gu H et al. (2013), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 110, 13002-13007. Experimental and computational analysis of the transition state for ribonuclease A-catalyzed RNA 2'-O-transphosphorylation. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1215086110. PMID:23878223.
- Nogués MV et al. (1995), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1253, 16-24. Bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A as a model of an enzyme with multiple substrate binding sites. DOI:10.1016/0167-4838(95)00138-k. PMID:7492594.

Step 1. His12 deprotonates the alcohol of the 5' RNA ribose, which initiates an intramolecular nucleophilic substitution on the phosphate bond of the RNA molecule. The leaving alcohol group is reprotonated from His119.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His12A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys41A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His119A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe120A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp121A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His119A | proton donor |
| His12A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, cyclisation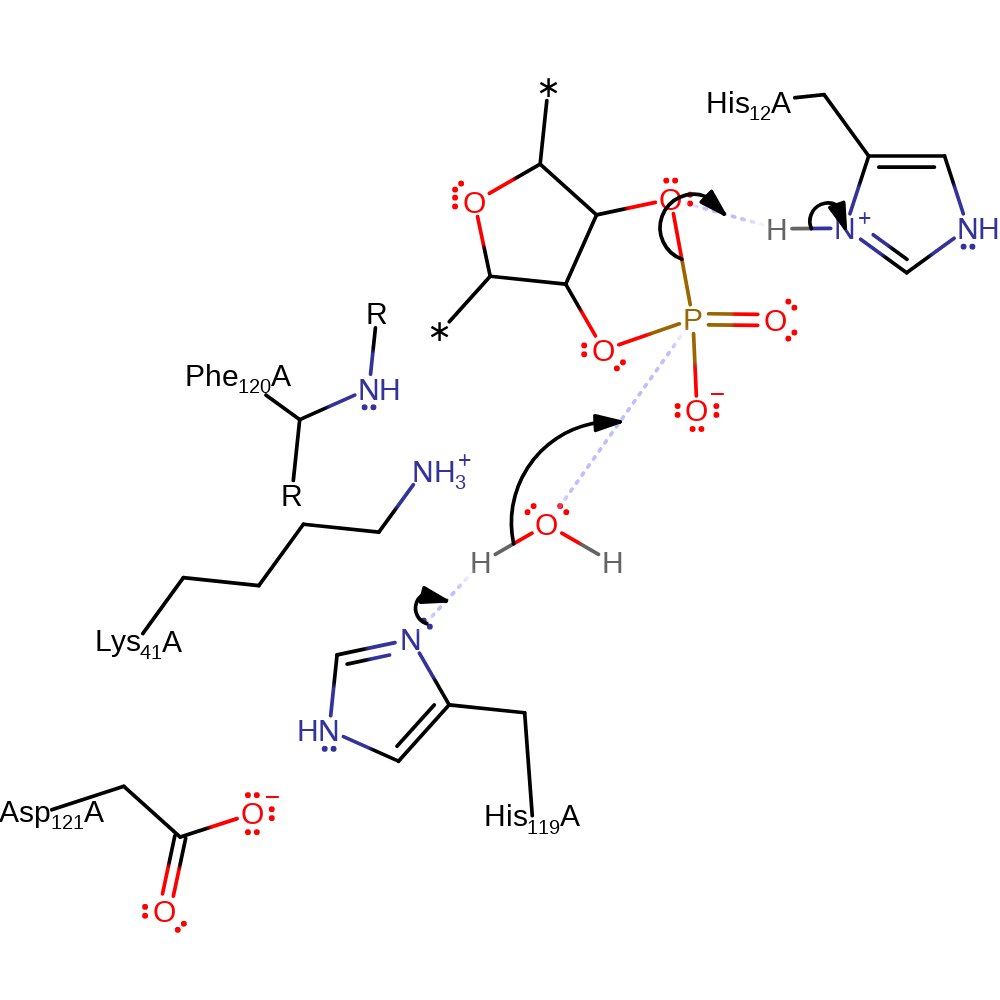
Step 2. His119 deprotonates water which attacks the cyclic phosphate intermediate in a nucleophilic substitution. The leaving alcohol group is reprotonated from His12.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His12A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys41A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His119A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe120A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp121A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His12A | proton donor |
| His119A | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: