Thiosulfate sulfurtransferase (eukaryotic)
Thiosulfate sulfurtransferase (rhodanese) is an ubiquitous enzyme that in vitro catalyses the transfer of a sulfur atom from suitable donors to nucleophilic acceptors by way of a double displacement mechanism. During the catalytic process the enzyme cycles between a sulfur-free and a persulfide-containing form, via formation of a persulfide linkage to a catalytic Cys residue.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00586
 (2.8.1.1)
(2.8.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bos taurus (Cattle)

- PDB
-
1rhs
- SULFUR-SUBSTITUTED RHODANESE
(1.36 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.250.10
 (see all for 1rhs)
(see all for 1rhs)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.8.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Cys247, held in its thiolate form by the positively charged electrostatic field of the active site, attacks the thiosulfate substrate in a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The resulting persulfate bond is well stabilised by the active site eletrostatic field. Cyanate then binds and attacks the sulfonates cysteine residue (in a double displacement mechanism), resulting in the thiocyanate substrate and the regeneration of Cys247.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1rhs) | ||
| Lys250, Arg187 | Lys249A, Arg186A | The positively charged side chains contribute to active site electrostatic field, which interacts with the anionic substrate and creates hydrogen bonds to the persulfate at Cys 247 (Css 247). | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly251 (main-N), Val252 (main-N), Thr253 (main-N), Ser275 (main-N), Arg249 (main-N) | Gly250A (main-N), Val251A (main-N), Thr252A (main-N), Ser274A (main-N), Arg248A (main-N) | The residue backbone NH is directed towards active pocket and the anionic substrate, allowing the formation of hydrogen bonds with the substrate as well as the persulfate residue. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys248 | Cys247A | Acts as a catalytic nucleophile, and the resulting persulfide bond at the sulfydryl group is stabilised by the positive electostatic interactions. | nucleofuge, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Bordo D et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 298, 691-704. The crystal structure of a sulfurtransferase from Azotobacter vinelandii highlights the evolutionary relationship between the rhodanese and phosphatase enzyme families. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3651. PMID:10788330.
- Salgado MPSC. (2005), J Mol Biol, 127, 149-162. Structural studies of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. DOI:to delete. PMID:to delete.
- Cianci M et al. (2000), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1481, 103-108. Specific interaction of lipoate at the active site of rhodanese. PMID:11004580.
- Trevino RJ et al. (1999), J Biol Chem, 274, 13938-13947. NH2-terminal Sequence Truncation Decreases the Stability of Bovine Rhodanese, Minimally Perturbs Its Crystal Structure, and Enhances Interaction with GroEL under Native Conditions. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.20.13938.
- Gliubich F et al. (1996), J Biol Chem, 271, 21054-21061. Active site structural features for chemically modified forms of rhodanese. DOI:10.2210/pdb1ora/pdb. PMID:8702871.
- Luo GX et al. (1994), J Biol Chem, 269, 8220-8225. The sulfurtransferase activity and structure of rhodanese are affected by site-directed replacement of Arg-186 or Lys-249. PMID:8132546.
- Ploegman JH et al. (1979), J Mol Biol, 127, 149-162. The structure of bovine liver rhodanese. II. The active site in the sulfur-substituted and the sulfur-free enzyme. PMID:430559.

Step 1. The thiolate of Cys247 attacks the thiosulfate substrate in a nucleophilic substitution, resulting in the formation of the sulfite product an a sulfonated cysteine residue.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg186A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg248A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly250A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Val251A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr252A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys249A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser274A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys247A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation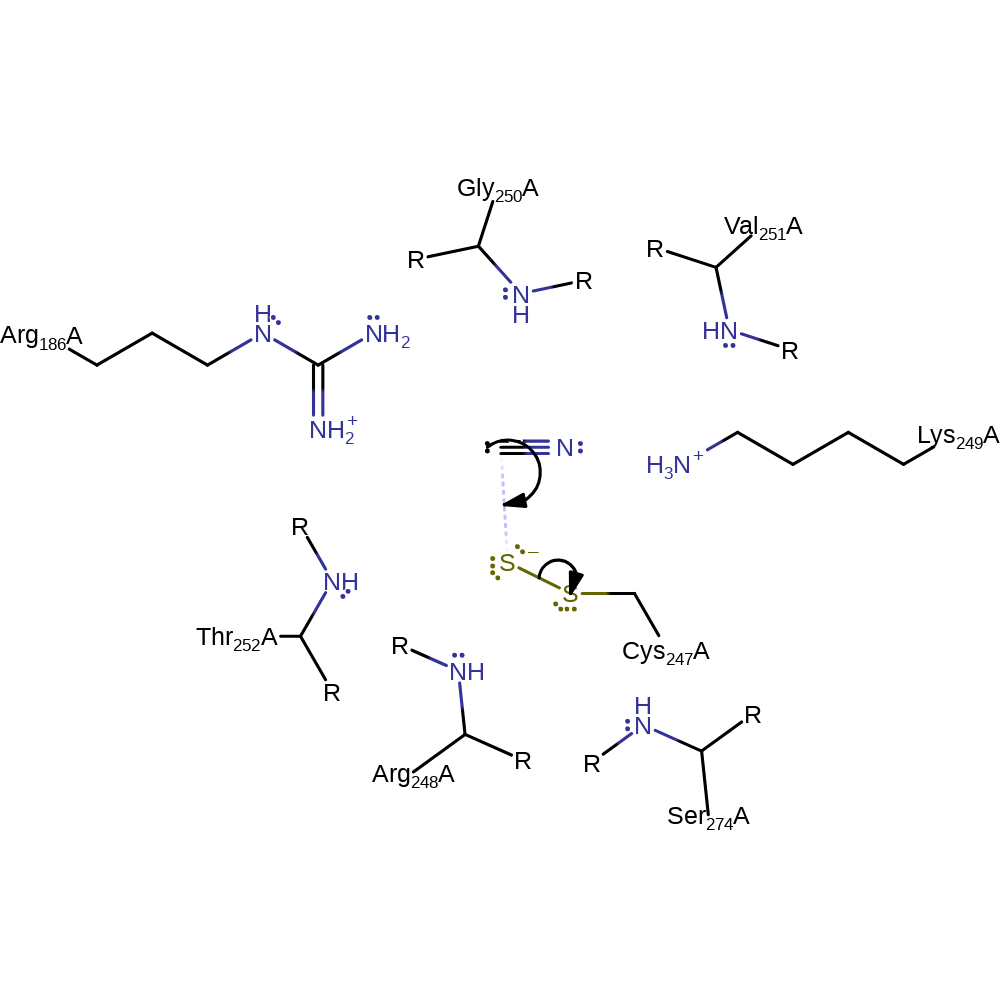
Step 2. The cyanate substrate attacks the sulfonated Cys247 in a nucleophilic substitution, resulting in the thiocyanate product and the regeneration of Cys247.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg248A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly250A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Val251A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr252A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg186A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys249A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser274A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys247A | nucleofuge |





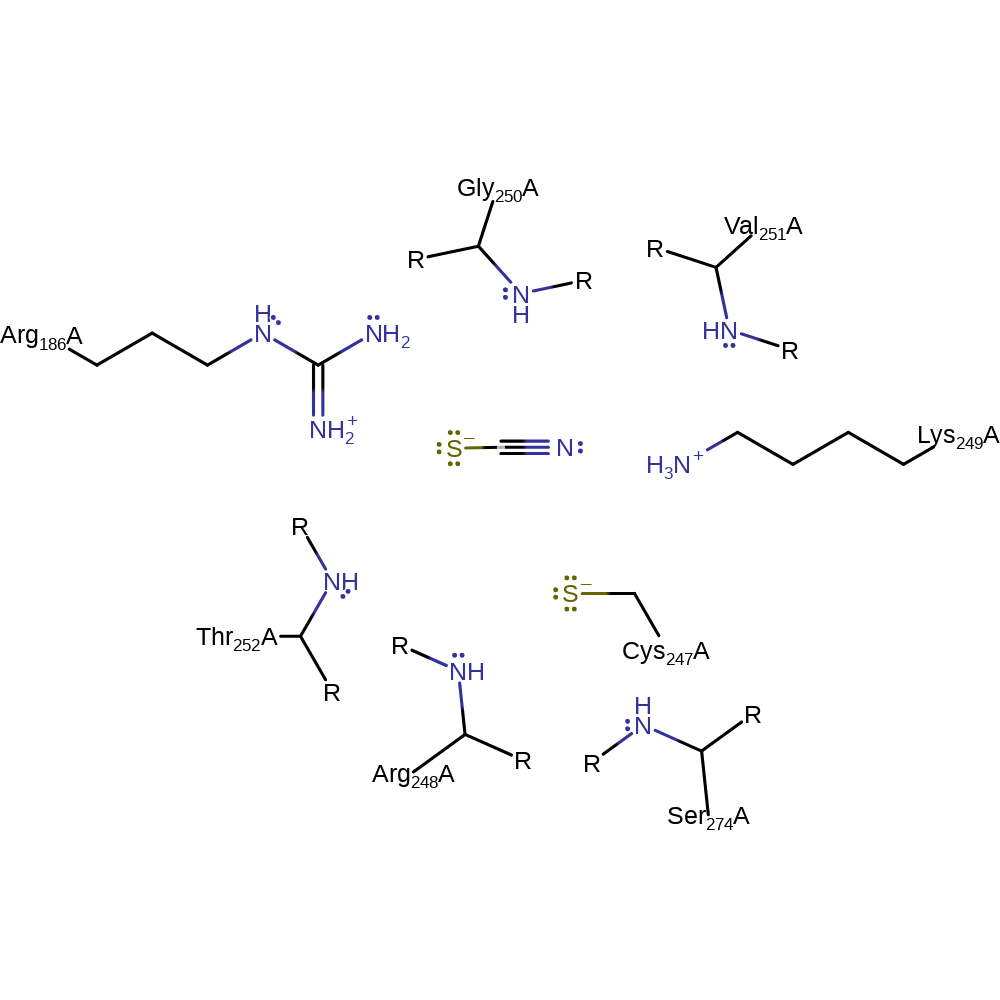 Download:
Download: