Arsenate reductase
Arsenate reductase (ArsC) from Staphylococcus aureus catalyses the reduction of arsenate to arsenite. It participates in the arsenic detoxification system of the gram-positive bacterium. ArsC also catalyses dephosphorylation in addition to reduction, although at a reduced efficiency.
Arsenate reductase has a PTPase-I fold typical for low molecular weight tyrosine phosphatases which includes the catalytic P-loop and the similarity is corresponds to the similarity between arsenate and phosphate ions. The structural similarity of this fold has resulted in arsenate reductase displaying phosphatase activity in vitro as well as being able to reduce arsenate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A006
 (1.20.4.4)
(1.20.4.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Staphylococcus aureus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ljl
- Wild Type pI258 S. aureus arsenate reductase
(2.01 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.2300
 (see all for 1ljl)
(see all for 1ljl)
- Cofactors
- Potassium(1+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.20.4.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In the following mechanism, the main chain residues that are activating and stabilising the arsenite and Cys10 thiolate are omitted for clarity.
Ser 17 hydrogen bonds to the thiol hydrogen of Cys 10, lowering the pKa and increasing the nucleophilicity of the thiol S atom. Arg 16 polarises the substrate, making the As atom more electrophilic. S atom of Cys 10 nucleophilically attacks the As of the arsenate substrate. The transition state is stabilised by Asp 105 via a water molecule. A hydroxyl group of arsenate is protonated by an acidic water molecule, and leaves, forming a Cys 10-HAsO3- intermediate. The Cys 82 S atom nucleophilically attacks Cys 10 S atom, forming a Cys10-Cys82 disulphide intermediate. Electrons from the As-S bond shuttle to the arsenic, giving the release of arsenite. The Cys 89 S atom attacks Cys 82 S atom, forming a Cys 82 - Cys 89 disulphide intermediate, and breaking the Cys 10 - Cys 82 disulphide and regenerating Cys 10. The Cys 89 S atom is nucleophilically attacked by an S atom of thioredoxin at the surface of ArsC. This breaks the Cys 82 - Cys 89 disulphide, and forms one between Cys 89 and thioredoxin. The second S atom of thioredoxin nucleophilically attacks the first S atom of thioredoxin, breaking the Cys 89 - thioredoxin disulphide, and forming reduced thioredoxin.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ljl) | ||
| Thr63, Asp65, Asn13, Ser36 | Thr63A, Asp65A, Asn13A, Ser36A | Form K+ binding site | |
| Cys10 | Cys10A | Nucleophilically attacks the As atom of arsenate, resulting in the loss of a water molecule. | electrophile, electrofuge, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Asp105 | Asp105A | Stabilises the transition state via a water molecule. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys82 | Cys82A | Nucleophilically attacks the S atom of Cys 10, forming a disulphide bridge, breaking the As-S bond and causing the release of arsenite. | hydrogen bond acceptor, nucleofuge, nucleophile, electrofuge, electrophile |
| Cys89 | Cys89A | Nucleophilically attacks the S atom of Cys 82, forming a disulphide between Cys 82 and Cys 89, and breaking the one between Cys 10 and Cys 82, reforming Cys 10. | hydrogen bond acceptor, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Ser14 (main-N), Arg16 (main-N), Thr11 (main-N), Gly12 (main-N), Asn13 (main-N), Ser17, Cys15 (main-N), Arg16 | Ser14A (main-N), Arg16A (main-N), Thr11A (main-N), Gly12A (main-N), Asn13A (main-N), Ser17A, Cys15A (main-N), Arg16A | Stabilises the nucleophilic thiolate form of Cys 10. Also helps stabilise the negatively charged intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, cyclisation, decyclisation, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Messens J et al. (2002), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 99, 8506-8511. All intermediates of the arsenate reductase mechanism, including an intramolecular dynamic disulfide cascade. DOI:10.1073/pnas.132142799. PMID:12072565.
- Roos G et al. (2006), J Mol Biol, 360, 826-838. Interplay Between Ion Binding and Catalysis in the Thioredoxin-coupled Arsenate Reductase Family. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.05.054. PMID:16797027.
- Messens J et al. (2006), J Mol Biol, 362, 1-17. Arsenate Reduction: Thiol Cascade Chemistry with Convergent Evolution. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.002. PMID:16905151.
- Evans B et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 13609-13617. Site-Directed Mutagenesis, Kinetic, and Spectroscopic Studies of the P-Loop Residues in a Low Molecular Weight Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase†. DOI:10.1021/bi9605651. PMID:8885840.
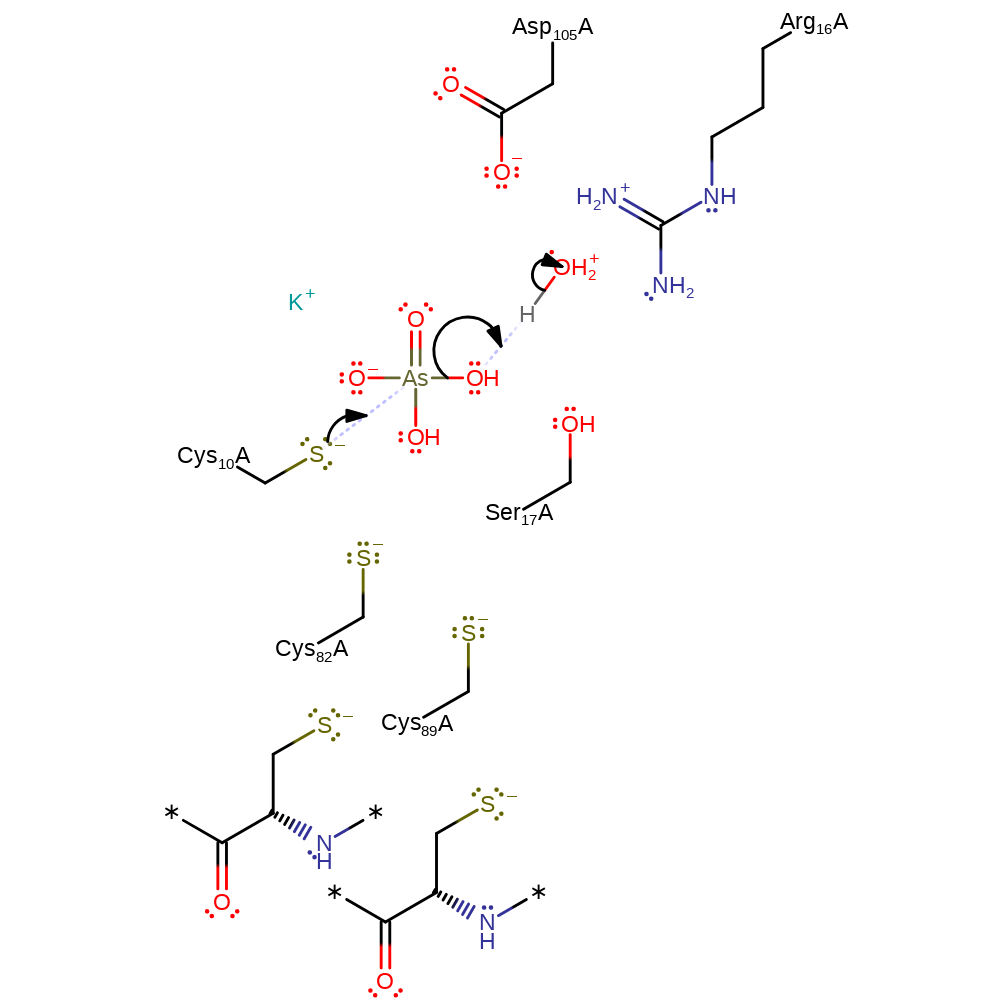
Step 1. Thiolate of Cys10 attacks the arsenate substrate in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that releases water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg16A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr11A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly12A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn13A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser14A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys15A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg16A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser17A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys82A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp105A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys10A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall product formed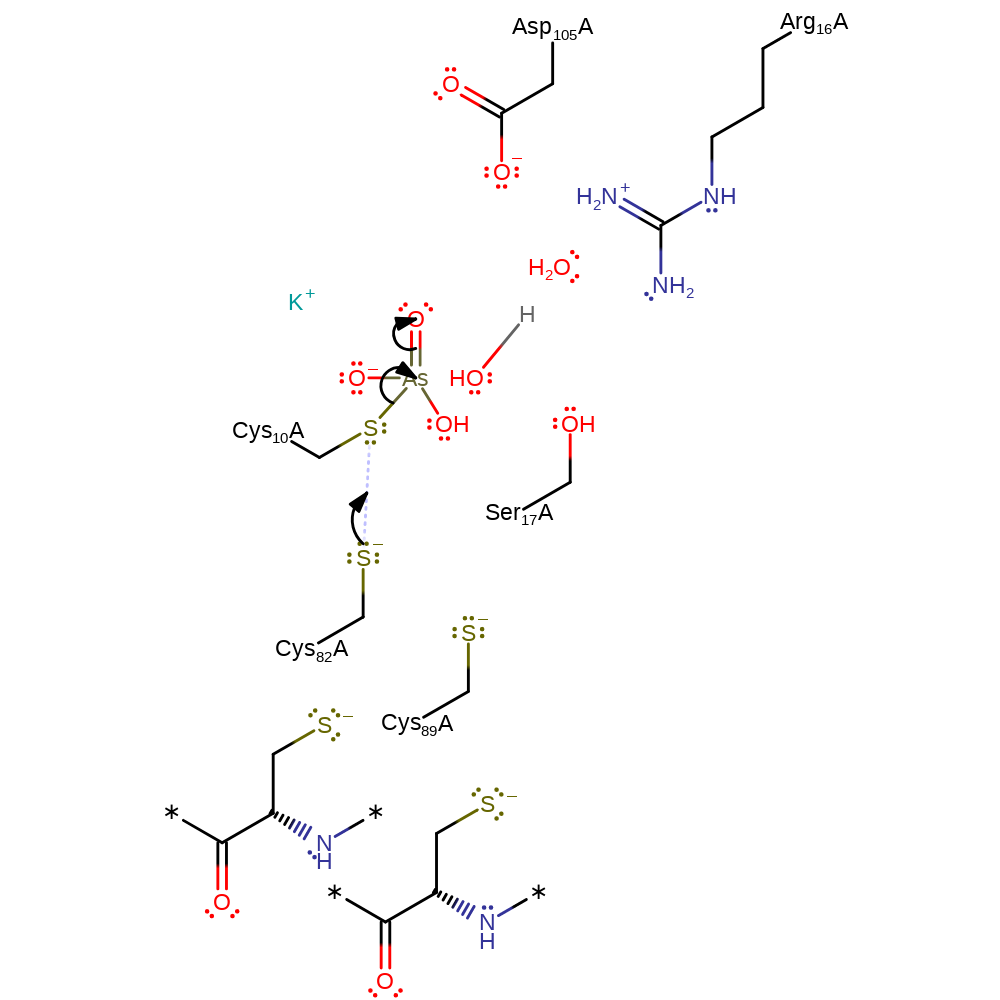
Step 2. Thiolate of Cys82 attacks the sulfur of Cys10 in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that releases the arsenite product, and creates a disulfide bond between Cys10 and Cys82.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr11A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly12A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn13A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser14A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys15A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg16A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser17A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys82A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp105A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys82A | nucleophile |
| Cys10A | electrophile, electrofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, cyclisation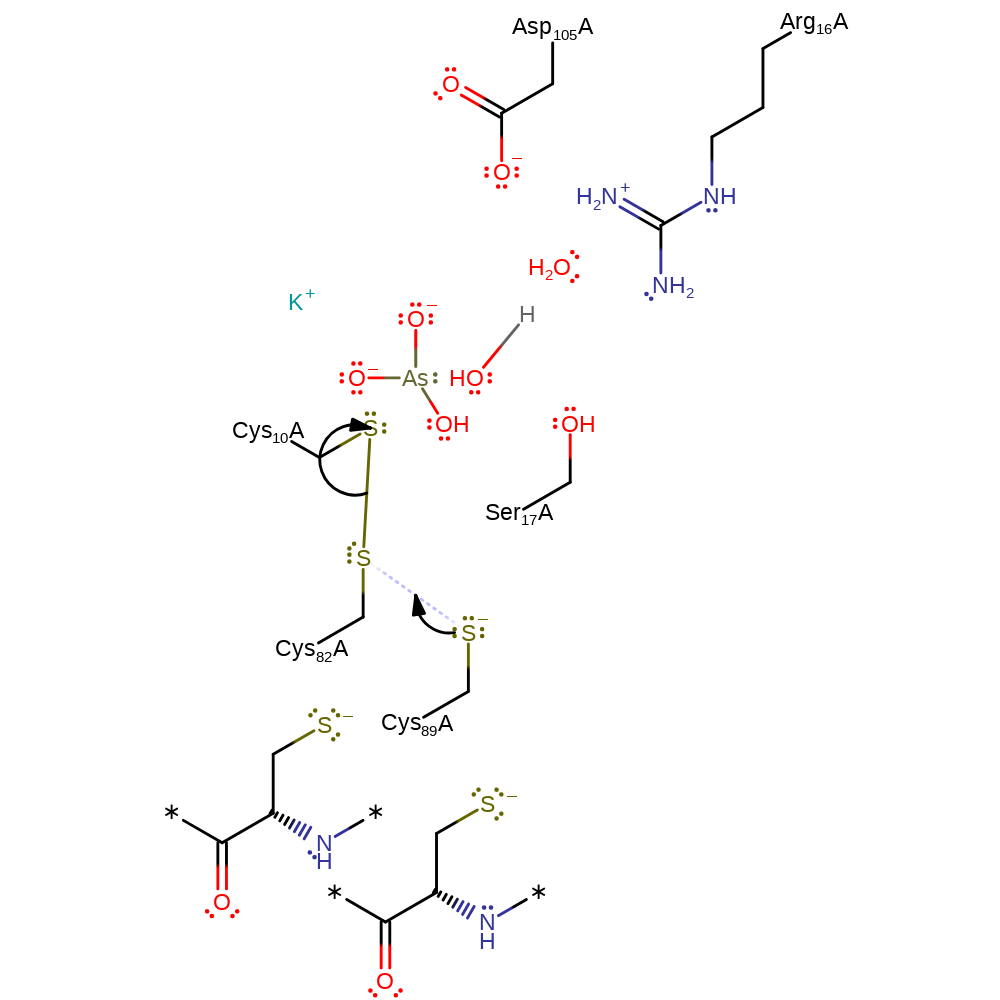
Step 3. Thiolate of Cys89 attacks the sulfur of Cys82 in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that transfers the disulfide bond to Cys89-Cys82 and releases Cys10.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr11A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly12A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn13A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser14A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys15A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg16A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser17A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys82A | electrofuge, electrophile |
| Cys10A | nucleofuge |
| Cys89A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation, decyclisation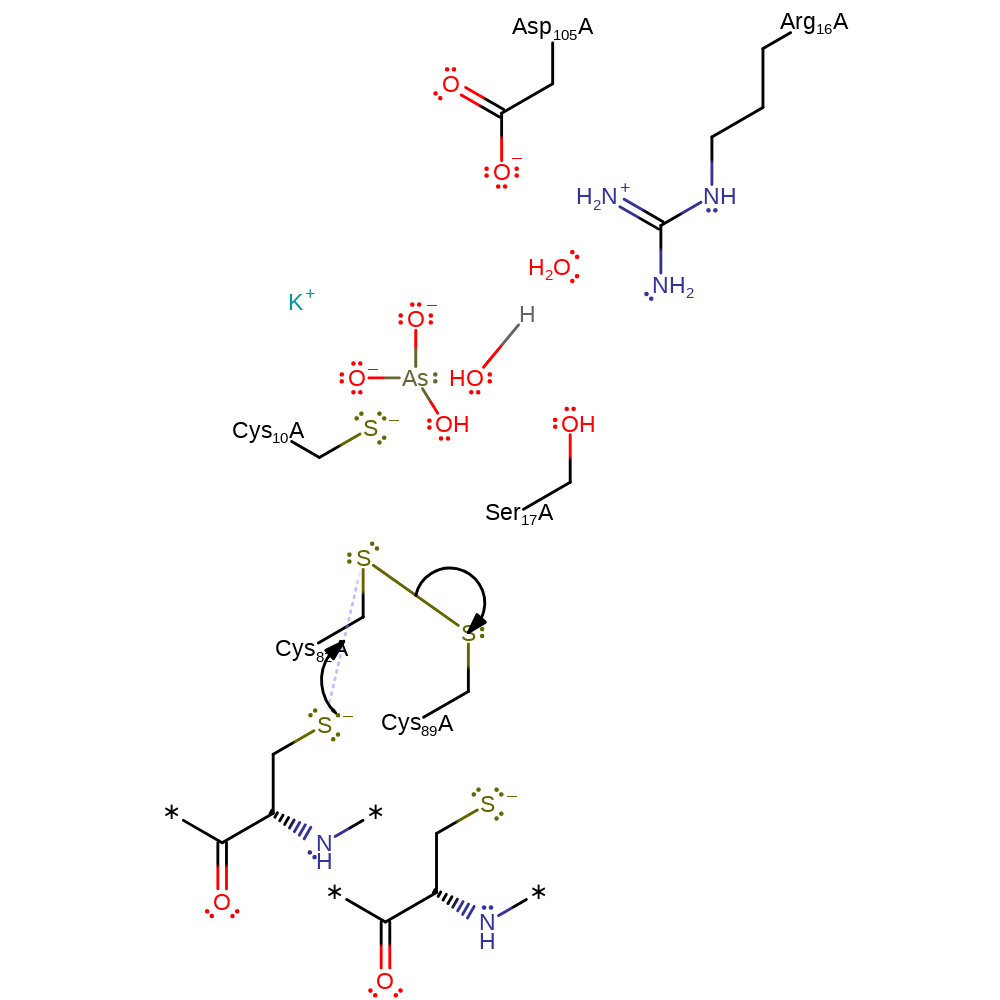
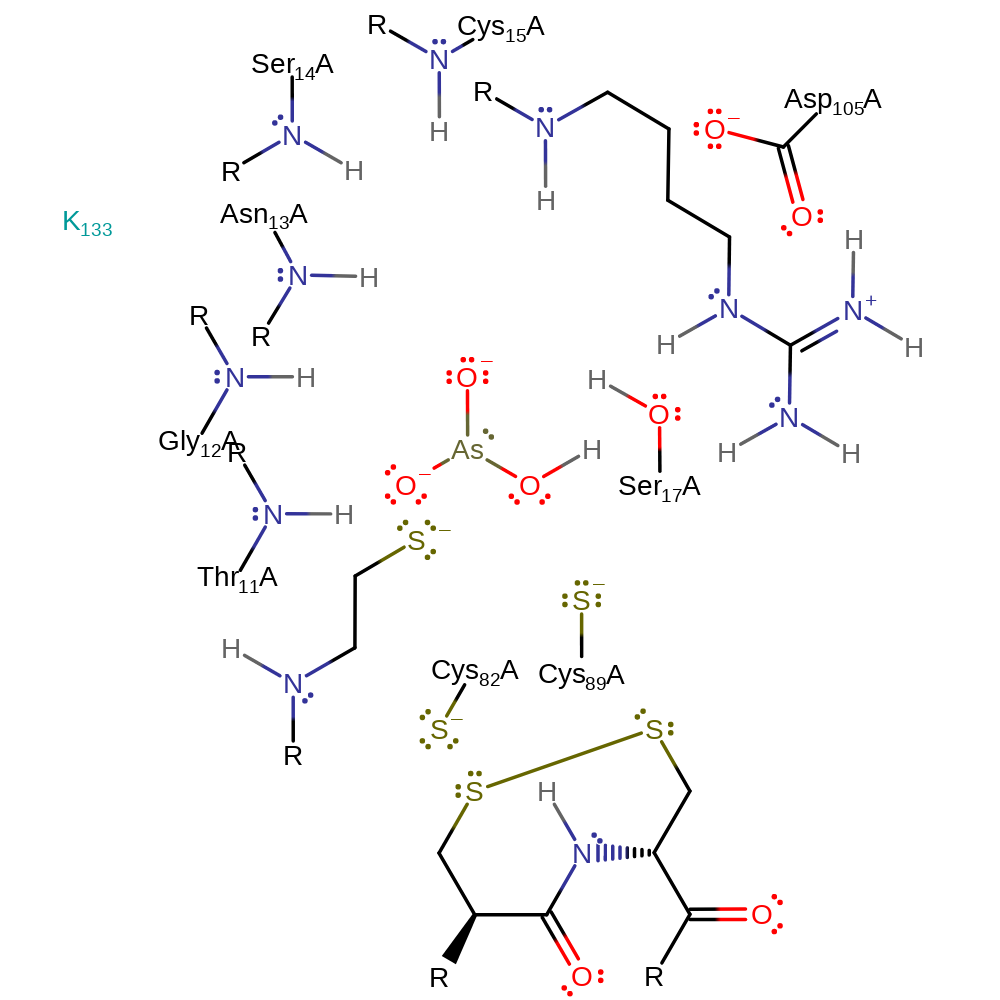
Step 4. The disulfide bond between Cys82 and Cys89 is transferred to Cys82 and the thioredoxin acceptor in a nucleophilic substitution reaction that releases Cys89.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr11A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly12A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn13A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser14A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys15A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg16A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser17A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys82A | electrofuge, electrophile |
| Cys89A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, decyclisation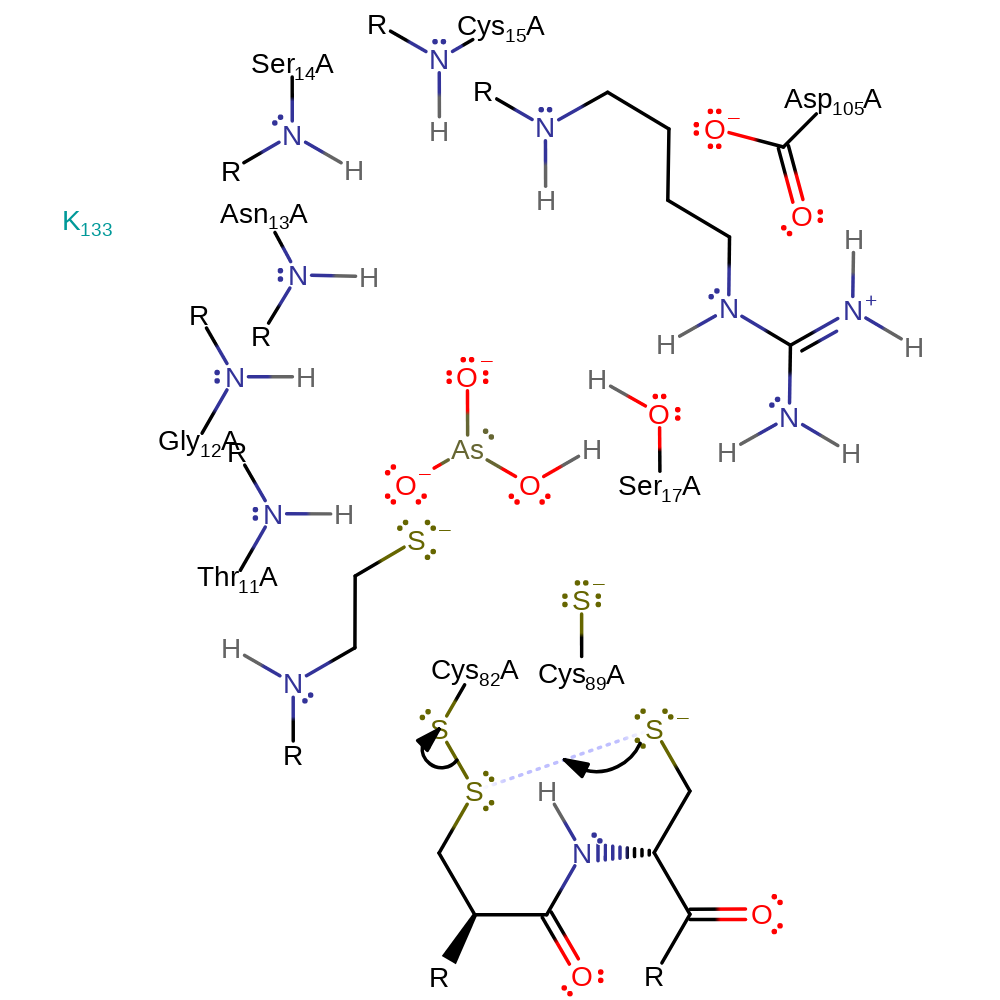
Step 5. The disulfide bond between Cys82 and thioredoxin is transferred to the second thiolate of thioredoxin in a nucleophilic substitution reaction, regenerating the enzyme and producing the fully oxidised thioredoxin.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr11A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly12A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn13A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser14A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys15A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg16A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser17A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys89A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys82A | nucleofuge |






 Download:
Download: