4-cresol dehydrogenase (hydroxylating)
4-Cresol dehydrogenase is a flavocytochrome c protein. It is the first enzyme in the protocatechuate metabolic pathway and is responsible for the degradation of toxic phenol p-cresol. The active site is buried deeply in the enzyme's interior. The route of substrate access has been shown to follow a swinging gate mechanism.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P09788
 (1.17.9.1)
(1.17.9.1)
P09787
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas putida (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1dii
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF P-CRESOL METHYLHYDROXYLASE AT 2.5 A RESOLUTION
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.45.10
 1.10.760.10
1.10.760.10  3.30.465.10
3.30.465.10  3.40.462.10
3.40.462.10  (see all for 1dii)
(see all for 1dii)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1), Heme b (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.17.9.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
The enzyme first catalyses the oxidation of p-cresol to p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol, utilising one atom of oxygen derived from water and yielding one molecule of reduced FAD. An enzymic base, Tyr473 removes the proton from the hydroxyl group of p-cresol and a hydride ion is transferred from the methyl group to the N5 atom of FAD. This results in a quinone methide intermediate which then undergoes nucleophilic attack by water at the methylene group, yielding p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol. Another tyrosine; Tyr95, is important in the catalytic mechanism, it is responsible for the the orientation and stabilisation of the substrate during the reaction. His436 may also form part of a proton relay system to deprotonate transiently the catalytic tyrosine prior to proton abstraction from p-cresol to form the quinone-methide intermediate. A water molecule is positioned close to the methyl group of the substrate is suitably located for nucleophilic attack in the hydroxylation step of the mechanism, this could be activated by either Glu380 or Glu427 through polarisation or depolarisation. A key feature of the active site is Arg474 which can use its gaunidinium group to stabilise the negative charge that develops at the N1/O2 locus in the hydroquinone and semiquinone intermediates during catalysis. A hydrogen bonding network between Asp440 and Tyr384 may assist the aspartic acid group to abstract a proton during the self-catalysed covalent flavinylation process.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dii) | ||
| Ala82 (main-C), Met83 | Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C), Met650(50)C(B) | Part of the electron relay chain that transfers a single electron from FAD, via the covalently attached Tyr384, the main chain carbonyl of Ala649C, side chain of Met650C and the heme cofactor to the external electron acceptor. | single electron relay, polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
| Glu380 | Glu380A | The residue activates a water molecule to act as a nucleophile at the substrate methyl group by abstracting a proton. It has been hypothesised that the residue is deprotonated through a proton relay with Tyr367 and Glu286. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr384 | Tyr384A | Binds the FAD cofactor through a covalent interaction, modulating its redox potential and acting as part of the electron relay chain that transfers a single electron from FAD, via the covalently attached Tyr384, the main chain carbonyl of Ala649C, side chain of Met650C and the heme cofactor to the external electron acceptor. | single electron relay, covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
| Glu177 | Glu177A | Part of the proton relay chain from bulk solvent to the active site. Glu177 contacts the surface of the enzyme and connects to Tyr473. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Tyr367, Glu286 | Tyr367A, Glu286A | Glu380 is deprotonated through the proton relay chain of Tyr367, water, Glu286 and bulk solvent. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| His436 | His436A | The residue is correctly aligned to abstract a proton from Tyr473, and therefore activate the phenolic oxygen to act as a general base towards the p-cresol substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Tyr473 | Tyr473A | The residue acts as a general base towards the p-cresol group. It is activated for catalysis by His436. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Arg474 | Arg474A | The positively charged gaunidinium group stabilises the negative charge that develops at the N1/O2 locus in the hydroquinone and semiquinone intermediates during catalysis | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp167, Arg512 | Asp167A, Arg512A | Arg474 is linked to Asp167 which in turn is linked to Arg512 to form a hydrogen bonding network that may increase the electropositivity of Arg474 and enhance its ability to stabilise the anionic hydroquinone and semiquinone forms of the flavin. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
aromatic bimolecular elimination, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton relay, proton transfer, overall product formed, electron transfer, radical formation, native state of cofactor regenerated, electron relay, radical termination, intermediate terminated, bimolecular elimination, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Cunane LM et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 295, 357-374. Structures of the flavocytochrome p-cresol methylhydroxylase and its enzyme-substrate complex: gated substrate entry and proton relays support the proposed catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3290. PMID:10623531.
- Efimov I et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 6138-6148. Insight into covalent flavinylation and catalysis from redox, spectral, and kinetic analyses of the R474K mutant of the flavoprotein subunit of p-cresol methylhydroxylase. DOI:10.1021/bi035772x. PMID:15147198.
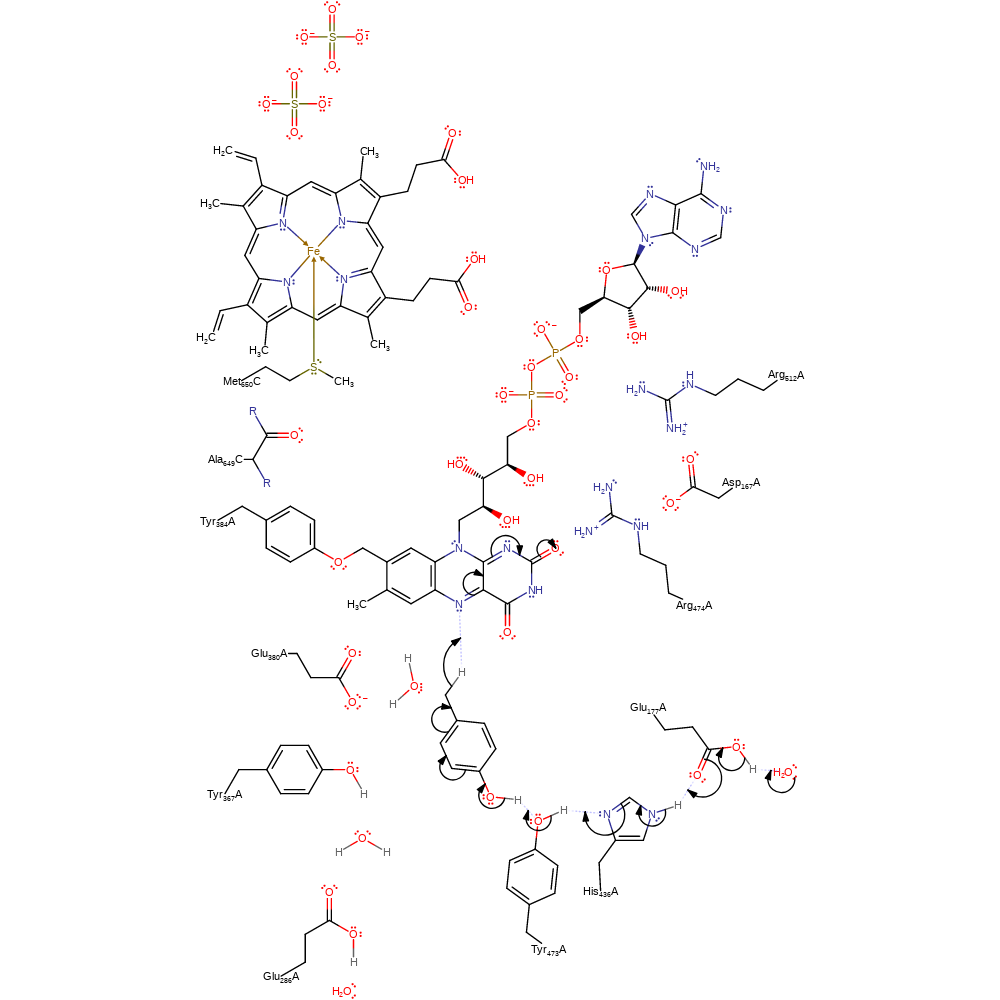
Step 1. Proton relay from bulk solvent through Glu177, His436 and Tyr473 to the substrate 4-cresol, resulting in a hydride transfer from the 4-cresol to the cofactor FAD599.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| His436A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton relay |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction |
| Glu177A | proton donor |
| Tyr473A | proton donor |
| His436A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu177A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr473A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular elimination, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton relay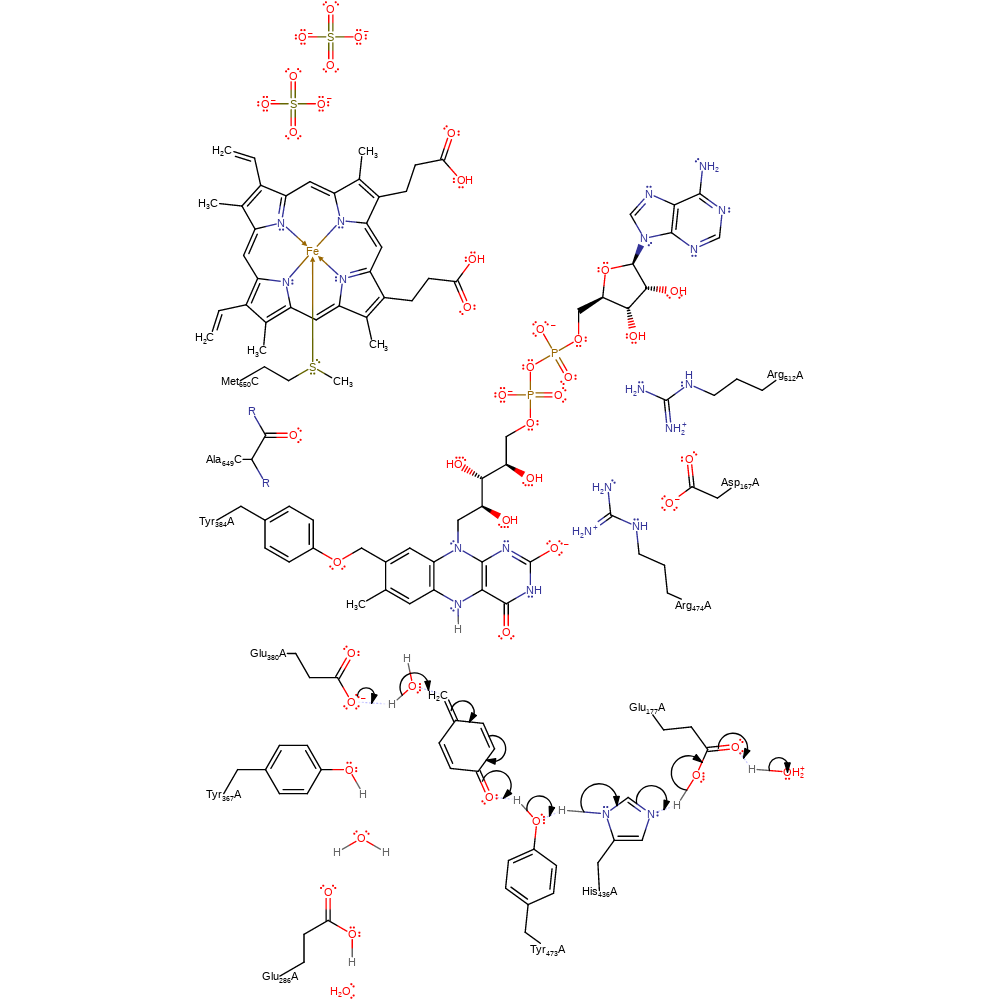
Step 2. Glu380 deprotonates water, activating it for a nucleophilic addition to the creosol intermediate. This intermediate is re-protonated via the proton relay chain through Tyr473, His436 and Glu177 to bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| His436A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction |
| Tyr473A | proton donor |
| Glu177A | proton acceptor |
| Glu380A | proton acceptor |
| His436A | proton acceptor |
| Glu177A | proton donor |
| Tyr473A | proton acceptor |
| His436A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay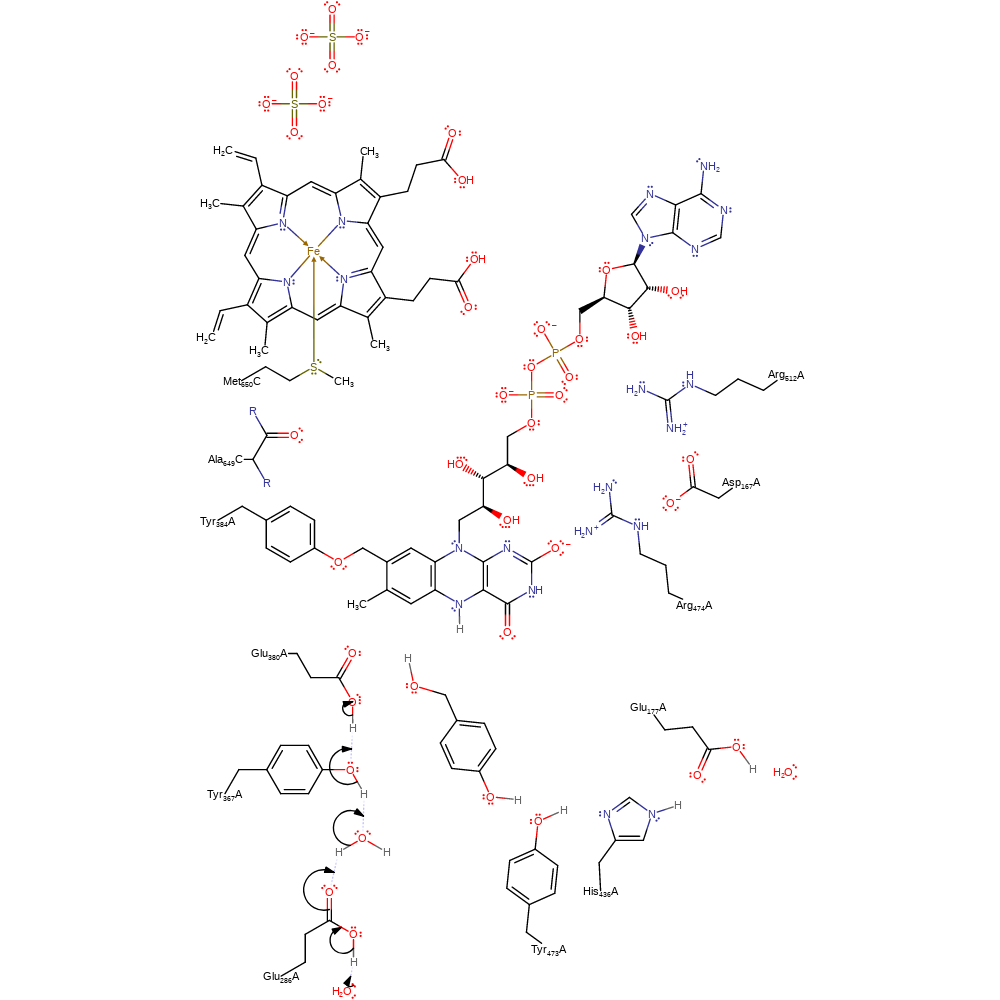
Step 3. Glu380 is deprotonated through the proton relay chain of Tyr367, water, Glu286 and bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction |
| Tyr367A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Glu380A | proton donor |
| Glu286A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, proton relay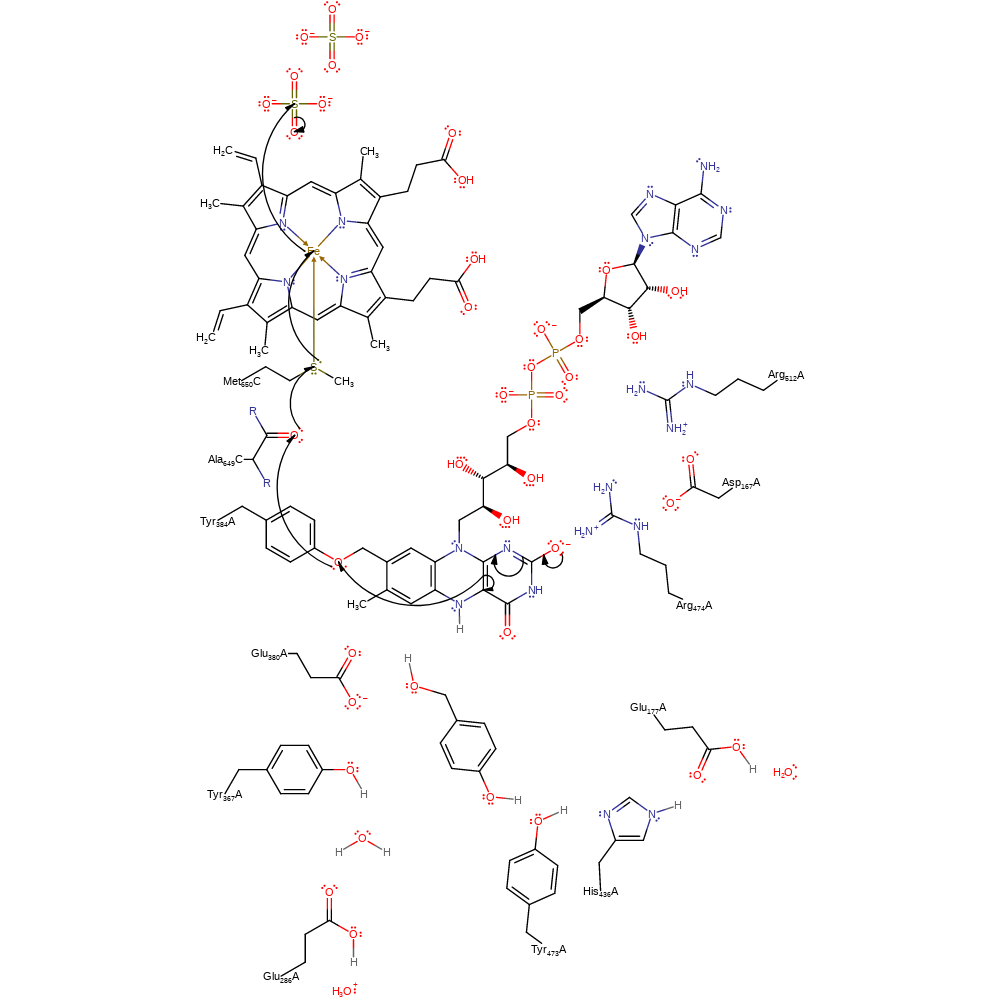
Step 4. FAD599 loses a single electron through the Tyr384 covalently attached to the FAD, the main chain carbonyl of Ala649C, side chain of Met650C and the heme cofactor to the external electron acceptor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction, single electron acceptor |
| Tyr384A | single electron relay |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron relay |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron relay |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron donor |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron donor |
| Tyr384A | single electron donor |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron acceptor |
| Tyr384A | single electron acceptor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, radical formation, overall reactant used, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate formation, electron relay
Step 5. Glu380 deprotonates the activated FAD599, resulting in the second electron transfer through the Tyr384 covalently attached to the FAD, the main chain carbonyl of Ala649C, side chain of Met650C and the heme cofactor to the external electron acceptor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction, single electron acceptor |
| Glu380A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr384A | single electron relay |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron relay |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron relay |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron acceptor |
| Tyr384A | single electron donor |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron donor |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron donor |
| Tyr384A | single electron acceptor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, radical termination, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated, electron relay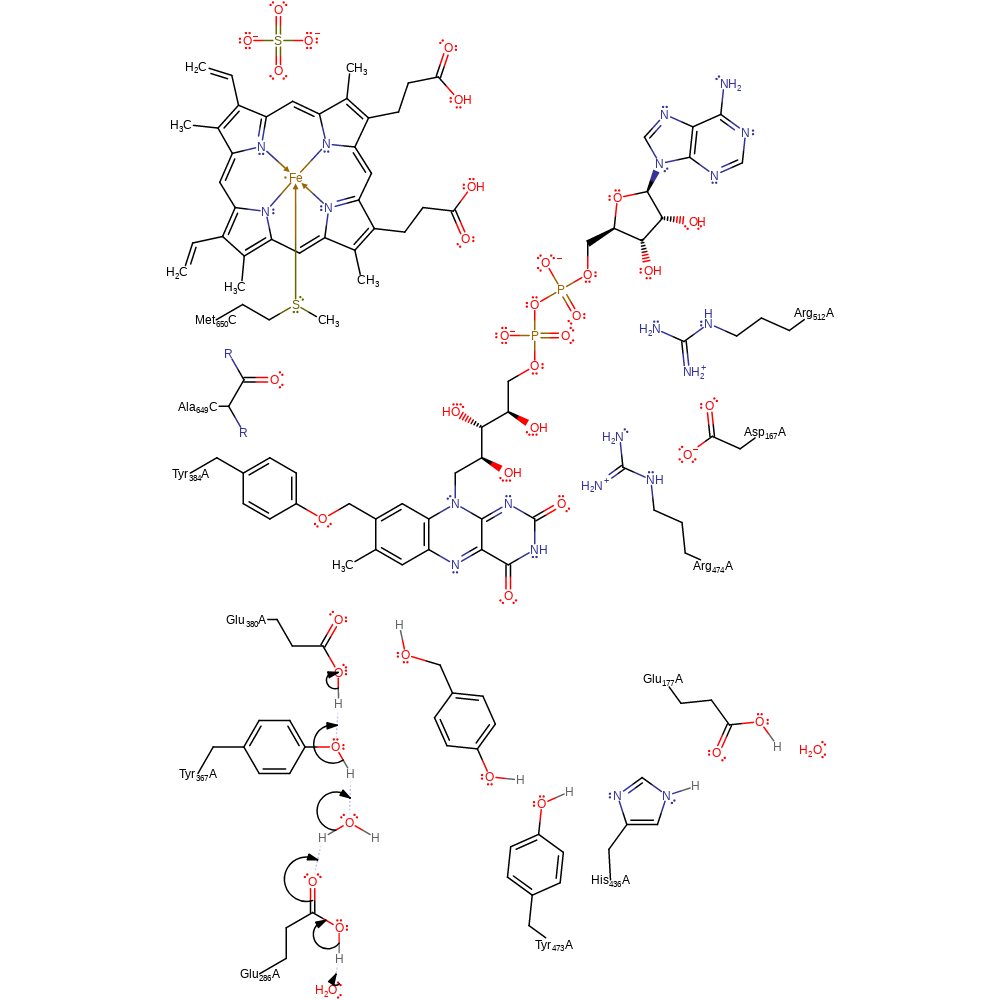
Step 6. Glu380 is deprotonated through the proton relay chain of Tyr367, water, Glu286 and bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction |
| Glu380A | proton donor |
| Glu286A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr367A | proton donor |
| Glu286A | proton donor |
| Tyr367A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, proton relay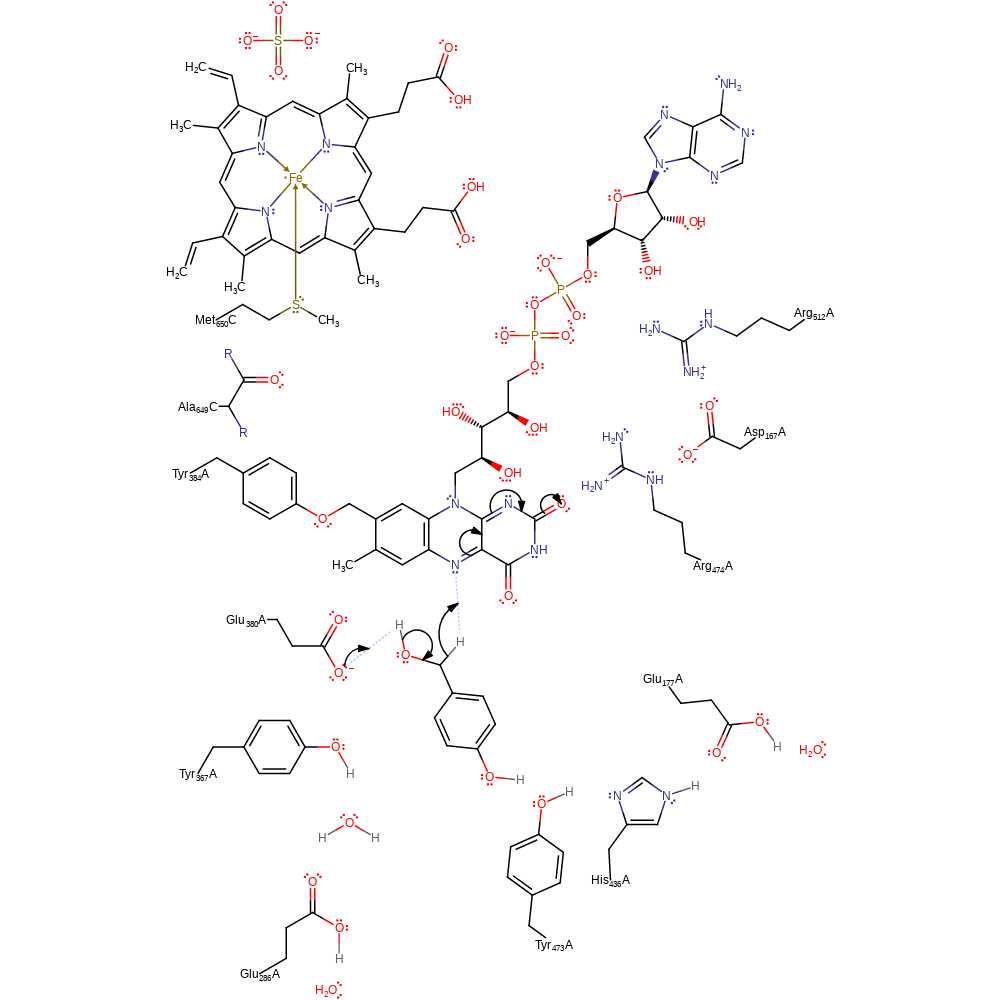
Step 7. Glu380 deprotonates the intermediate, causing a reduction of the primary alcohol to an aldehyde with concomitant transfer of a hydride to FAD599.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Glu380A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall product formed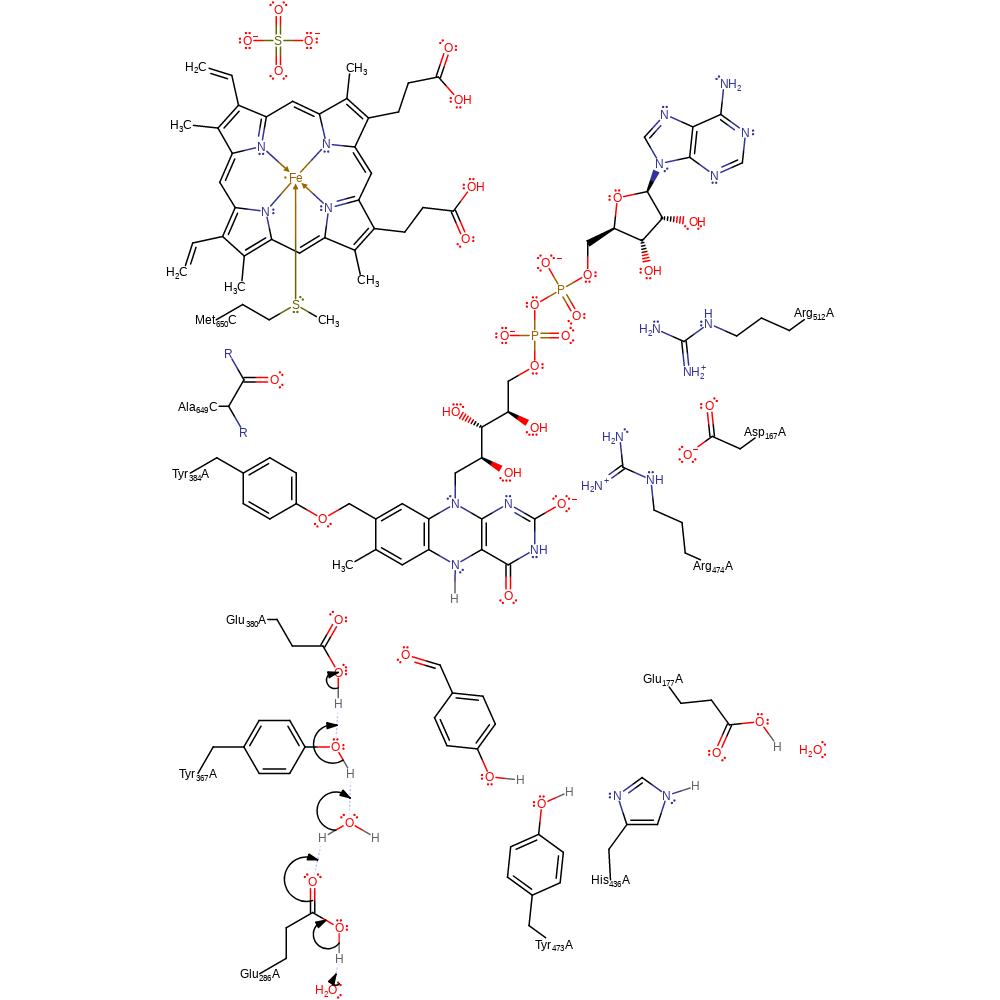
Step 8. Glu380 is deprotonated through the proton relay chain of Tyr367, water, Glu286 and bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction |
| Glu286A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr367A | proton acceptor |
| Glu286A | proton donor |
| Tyr367A | proton donor |
| Glu380A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, proton relay
Step 9. FAD599 loses a single electron through the Tyr384 covalently attached to the FAD, the main chain carbonyl of Ala649C, side chain of Met650C and the heme cofactor to the external electron acceptor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron donor |
| Tyr384A | single electron relay |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron relay |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron relay, single electron donor |
| Tyr384A | single electron acceptor |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron acceptor |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron acceptor |
| Tyr384A | single electron donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, radical formation, overall reactant used, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate formation, electron relay
Step 10. Glu380 deprotonates the activated FAD599, resulting in the second electron transfer through the Tyr384 covalently attached to the FAD, the main chain carbonyl of Ala649C, side chain of Met650C and the heme cofactor to the external electron acceptor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron donor |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron acceptor |
| Glu380A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr384A | single electron relay |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron relay |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron relay |
| Tyr384A | single electron donor |
| Met650(50)C(B) | single electron donor |
| Tyr384A | single electron acceptor |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | single electron acceptor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, radical termination, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated, electron relay
Step 11. Glu380 is deprotonated through the proton relay chain of Tyr367, water, Glu286 and bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg512A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp167A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg474A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr473A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His436A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu177A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu380A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr367A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Glu286A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Tyr384A | covalently attached, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Ala649(49)C(B) (main-C) | polar interaction, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Met650(50)C(B) | metal ligand, polar interaction |
| Tyr367A | proton donor |
| Glu380A | proton donor |
| Glu286A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Tyr367A | proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download: