Amine dehydrogenase
Methylamine dehydrogenase is a heterotetrameric, periplasmic quinoprotein found in several forms of constitutive and facultative methylotrophic bacteria. The enzyme catalyses the oxidative deamination of primary amines to their corresponding aldehydes with the release of two electrons and two protons. The enzyme is induced when the methylotrophic bacteria are grown on media containing methylamine as the sole carbon, and therefore energy, source.
The electron acceptor, Amicyanin, binds first to MADH to be reduced and then dissociates from MADH to react with cytochrome c-551i or cytochrome aa3 via the same binding site to be regenerated. Electrons can reach the terminal oxidase via different routes, and it cannot be concluded that one specific interaction is preferred.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P29894
 (1.4.9.1)
(1.4.9.1)
P22619 (1.4.9.1)
(1.4.9.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Paracoccus denitrificans (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2bbk
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE QUINOPROTEIN METHYLAMINE DEHYDROGENASE FROM PARACOCCUS DENITRIFICANS AT 1.75 ANGSTROMS
(1.75 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.130.10.10
 2.60.30.10
2.60.30.10  (see all for 2bbk)
(see all for 2bbk)
- Cofactors
- Tqq cofactor (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.4.9.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
Methylamine dehydrogenase carries out the oxidation of methylamine. The enzyme forms a complex with the type I blue copper protein amicyanin and cytochrome. Electron transfer procedes from the protein-derived tryptophan tryptophylquinone (TTQ) cofactor to the copper in amicyanin and then to the heme group of the cytochrome.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2bbk) | ||
| Thr179 | Thr122(116)L(B) | Helps stabilise the negatively charged intermediates. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp133, Asp89 | Asp76(70)L(B), Asp32(26)L(B) | Acts as a general acid/base performing several proton abstractions throughout the reaction. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Trp114 (ptm), Trp165 (ptm) | Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm), Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | The covalent linkage between these two residues forms the TQQ cofactor. The cofactor acts as an electron sink and donates two electrons (in two single electron transfer steps) to an external electron acceptor. | proton acceptor |
| Tyr176, Phe110 | Tyr119(113)L(B), Phe66(48)H(A) | For a hydrophobic environment in the active site, and also ensure that nothing larger than methylamine can enter the site. | steric role |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, bimolecular elimination, electron transfer, intramolecular elimination, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Sun D et al. (2002), Progress in Reaction Kinetics and Mechanism, 27, 209-241. MECHANISMS OF CATALYSIS AND ELECTRON TRANSFER BY TRYPTOPHAN TRYPTOPHYLQUINONE ENZYMES. DOI:10.3184/007967402103165397.
- Choi M et al. (2011), Biochemistry, 50, 1265-1273. Proline 96 of the Copper Ligand Loop of Amicyanin Regulates Electron Transfer from Methylamine Dehydrogenase by Positioning Other Residues at the Protein−Protein Interface. DOI:10.1021/bi101794y. PMID:21268585.
- Davidson VL (2005), Bioorg Chem, 33, 159-170. Structure and mechanism of tryptophylquinone enzymes. DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2004.10.001. PMID:15888309.
- Davidson VL (2003), Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteomics, 1647, 230-233. Probing mechanisms of catalysis and electron transfer by methylamine dehydrogenase by site-directed mutagenesis of αPhe55. DOI:10.1016/s1570-9639(03)00056-6.
- Singh V et al. (2000), J Am Chem Soc, 122, 931-938. Characterization of the Tryptophan Tryptophyl-Semiquinone Catalytic Intermediate of Methylamine Dehydrogenase by Electron Spin−Echo Envelope Modulation Spectroscopy. DOI:10.1021/ja9934246.
- Davidson VL (2000), Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Vitamin B6 and PQQ-dependent Proteins, 197-202. Tryptophan Tryptophylquinone Enzymes: Structure and Function. DOI:10.1007/978-3-0348-8397-9_32.
- Zhu Z et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 4862-4867. Identification of a New Reaction Intermediate in the Oxidation of Methylamine Dehydrogenase by Amicyanin†. DOI:10.1021/bi982939r. PMID:10200175.
- Chen L et al. (1998), J Mol Biol, 276, 131-149. Refined crystal structure of methylamine dehydrogenase from Paracoccus denitrificans at 1.75 Å resolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1511. PMID:9514722.
- Zhu Z et al. (1998), J Biol Chem, 273, 14254-14260. Redox Properties of Tryptophan Tryptophylquinone Enzymes: CORRELATION WITH STRUCTURE AND REACTIVITY. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.23.14254.
- Chen L et al. (1994), Science, 264, 86-90. Structure of an electron transfer complex: methylamine dehydrogenase, amicyanin, and cytochrome c551i. DOI:10.1126/science.8140419. PMID:8140419.
- Chen L et al. (1992), Biochemistry, 31, 4959-4964. Crystal structure of an electron-transfer complex between methylamine dehydrogenase and amicyanin. DOI:10.2210/pdb1mda/pdb. PMID:1599920.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation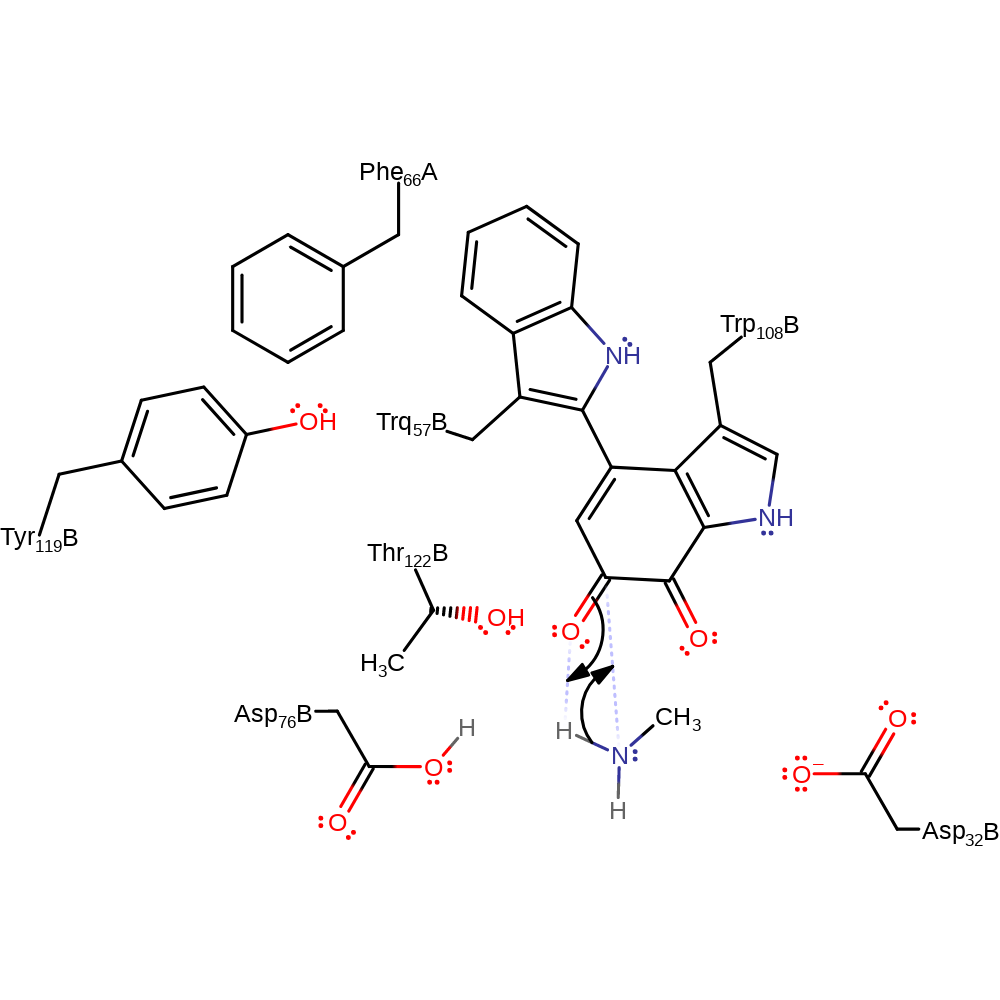
Step 2. Methylamine initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the TQQ cofactor in an addition reaction with concomitant deprotonation of the amine nitrogen.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 3. The amine nitrogen lone pair initiates the elimination of water with concomitant deprotonation of the amine nitrogen.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate baseCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed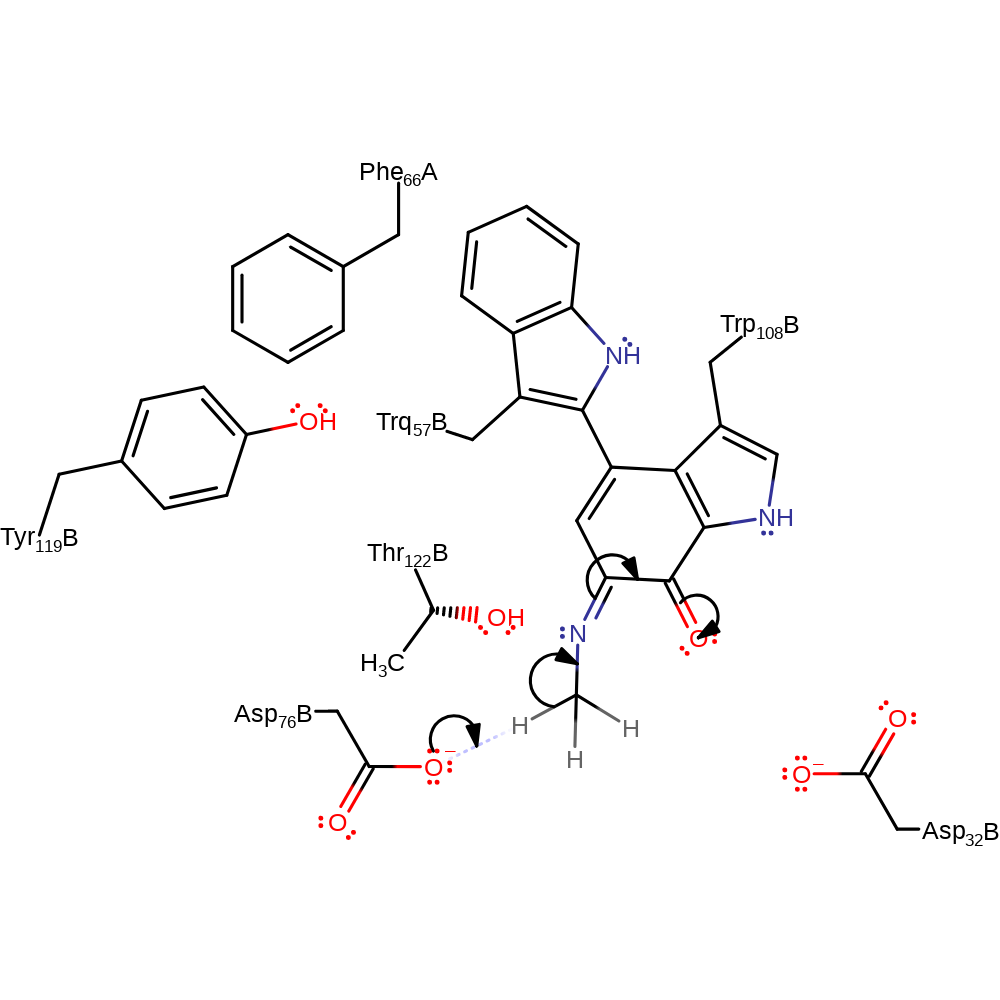
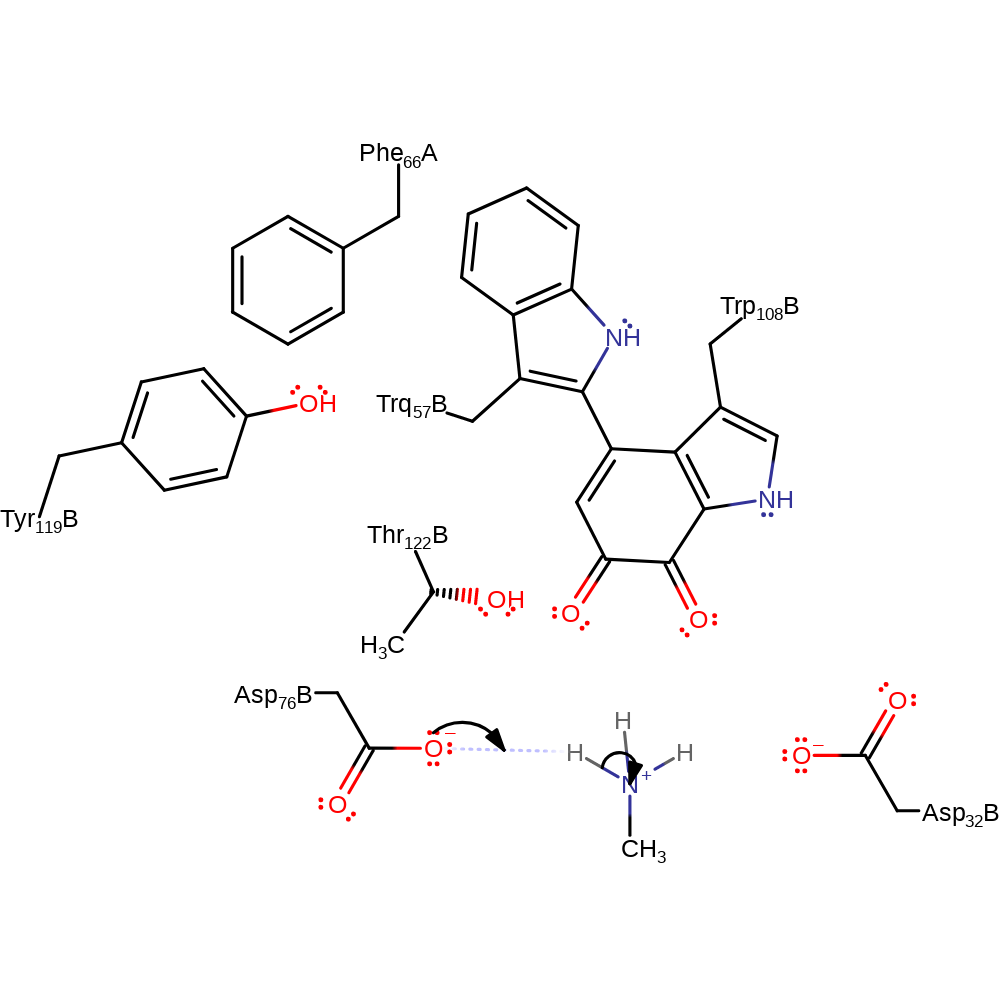
Step 5. Asp76 deprotonated the alpha-carbon with concomitant double bond rearrangement into the TQQ cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
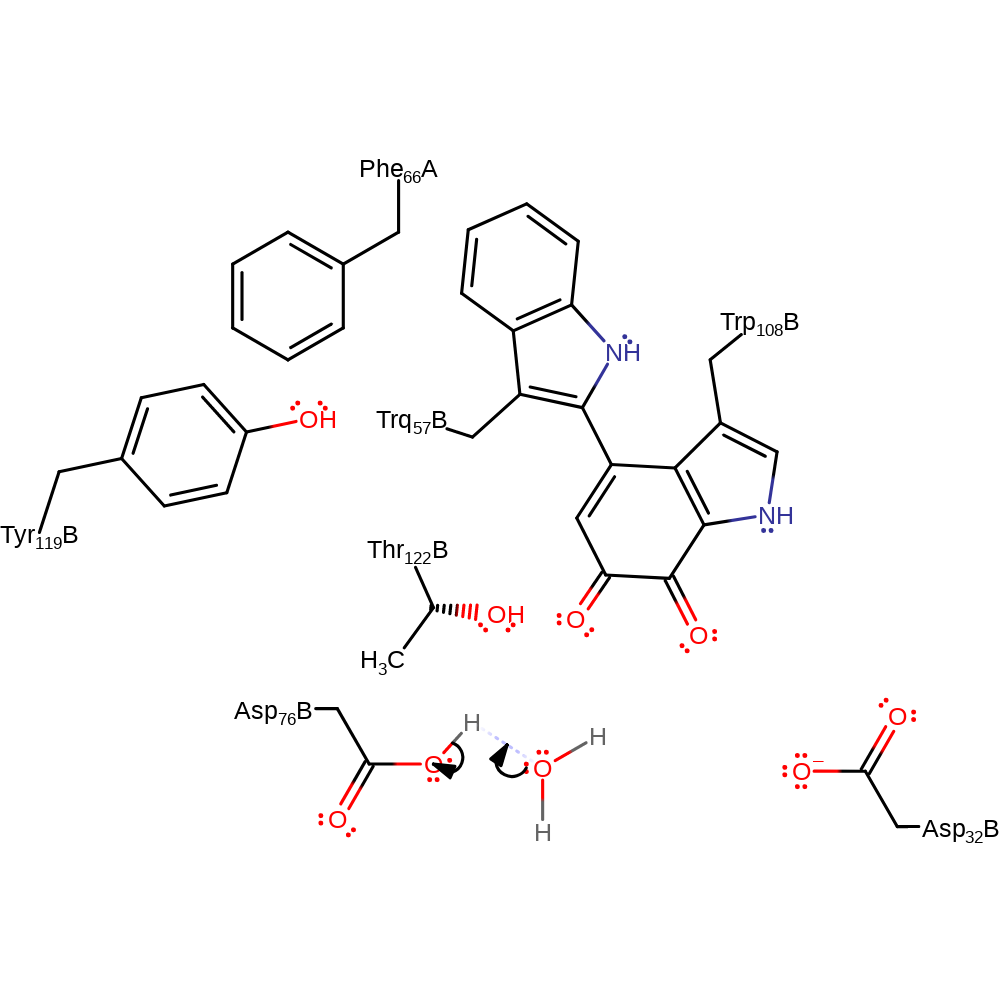
Step 6. The amide nitrogen deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the alpha-carbon in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp32(26)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
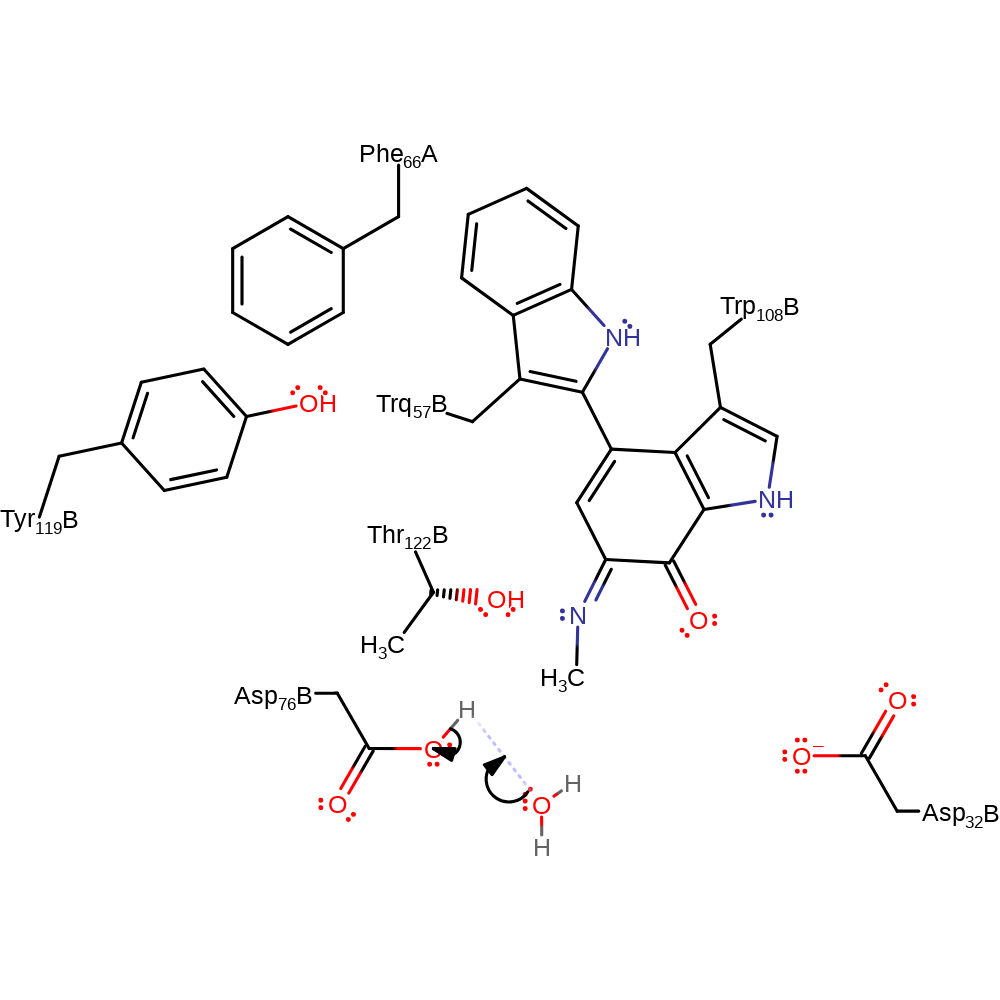
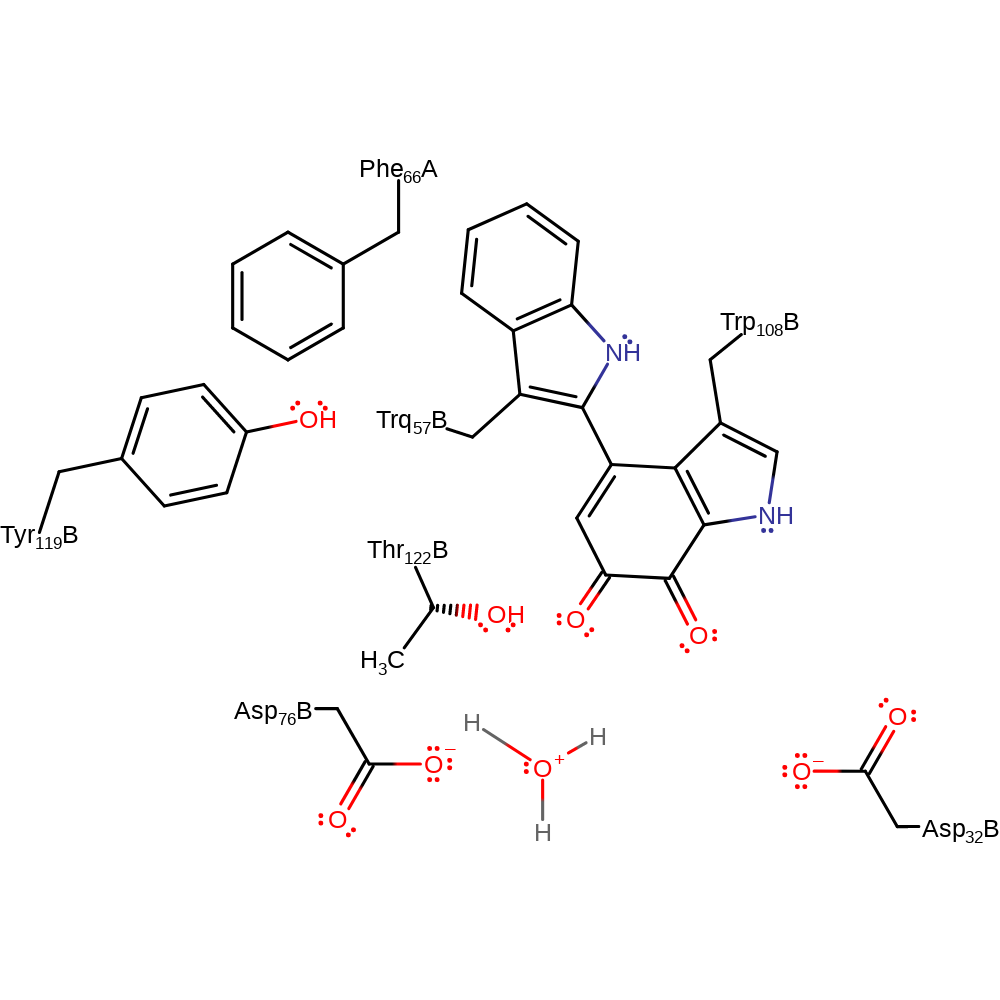
Step 7. Asp32 deprotonates the newly added hydroxyl group, eliminating the cofactor with concomitant deprotonation of Asp76, the formaldehyde products is released.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton donor |
| Asp32(26)L(B) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall product formed
Step 8. Asp76 deprotonates the amine nitrogen, with concomitant double bond rearrangement and a single electron transfer from the cofactor to amicyanin. Produces a delocalised radical charge over the intermediate N-C=C-O and the aromatic ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | single electron donor |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer
Step 9. A single electron is transferred to the heme group of the cytochrome.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | single electron donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer
Step 10. The amide nitrogen deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbon of the cofactor in an addition reaction
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 11. The amine nitrogen deprotonates the newly added hydroxyl group, which eliminates ammonia.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular elimination, native state of cofactor regenerated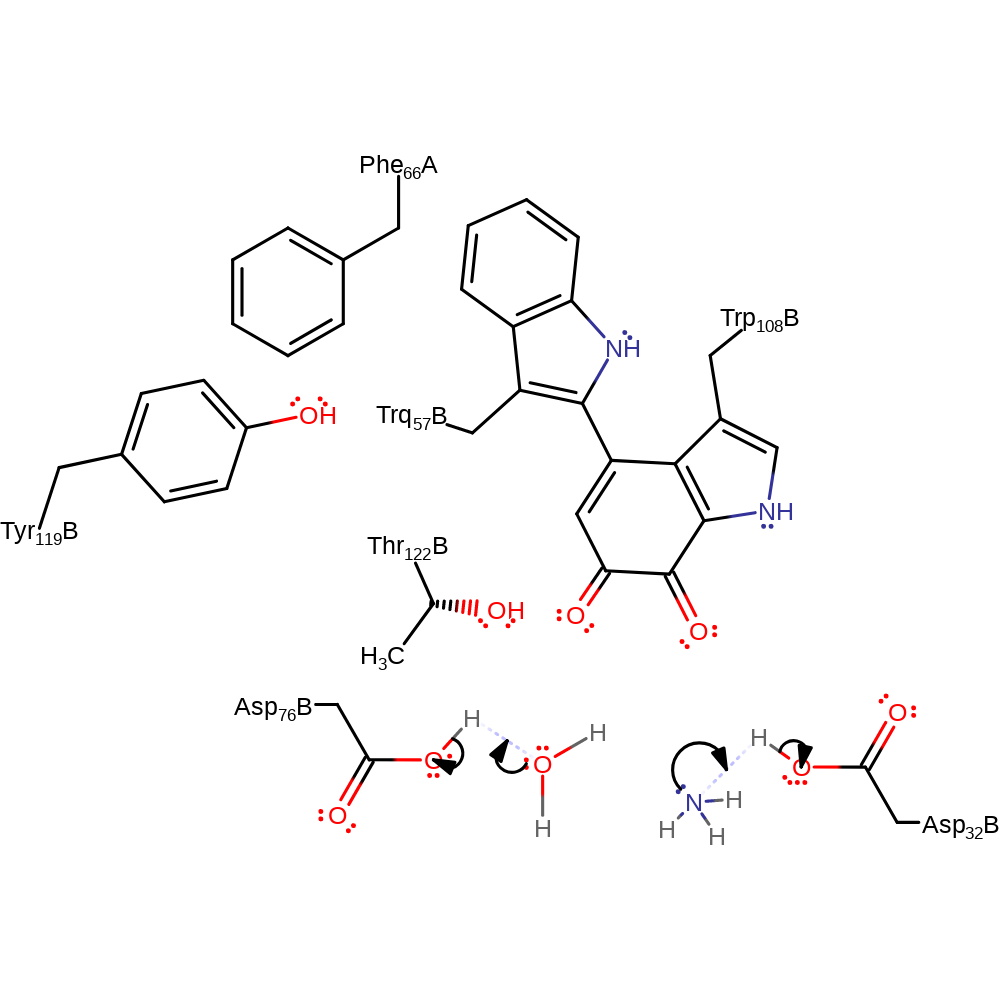
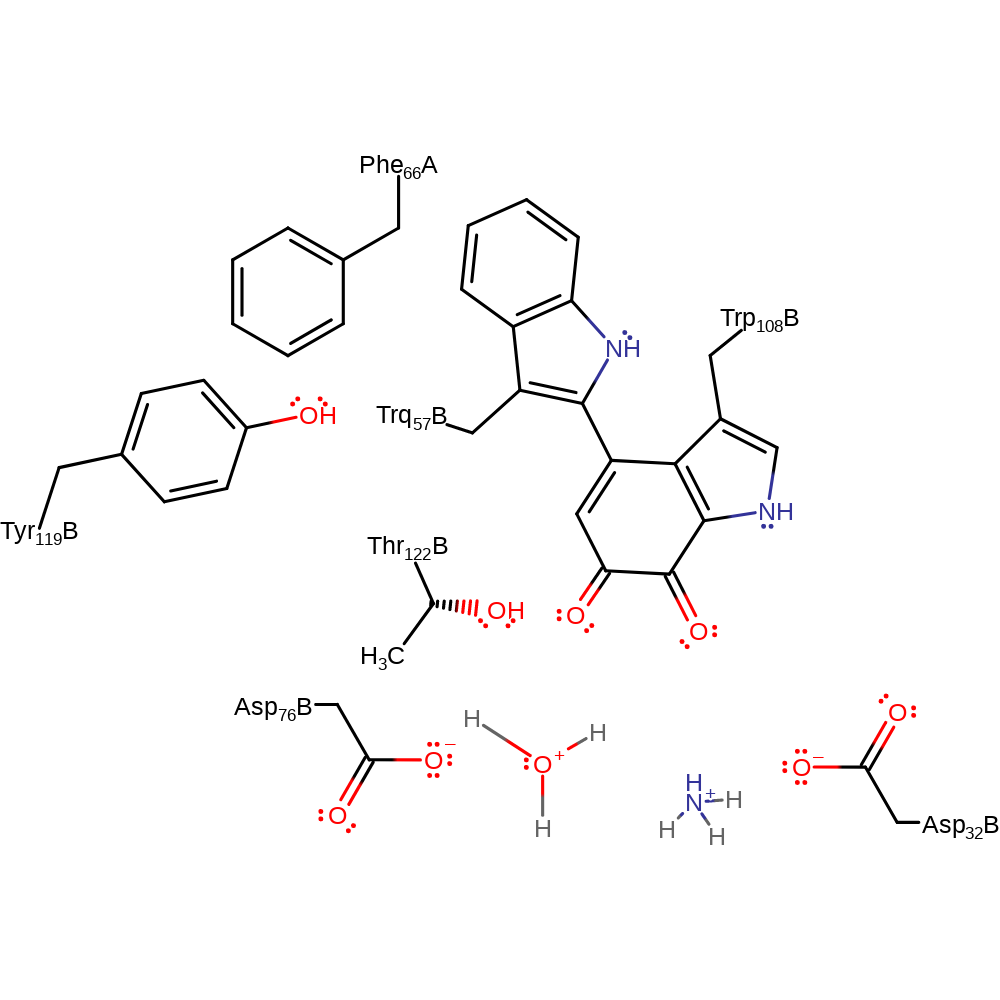
Step 12. Ammonia deprotonates Asp32 and water deprotonates Asp76 in an inferred return step.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton donor |
| Asp32(26)L(B) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
Methylamine dehydrogenase carries out the oxidation of methylamine. In this alternative mechanism the only difference to the first mechanism proposed is that steps 3 and 5 are performed by bases external to the cofactor-substrate complex, and after step 5 the identities of the Asp residues are flipped.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2bbk) | ||
| Thr179 | Thr122(116)L(B) | Help stabilise the negatively charged intermediates. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp133, Asp89 | Asp76(70)L(B), Asp32(26)L(B) | Acts as a general acid/base performing several proton abstractions throughout the reaction. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Trp114 (ptm), Trp165 (ptm) | Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm), Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | The covalent linkage between these two residues forms the TQQ cofactor. The cofactor acts as an electron sink and donates two electrons (in two single electron transfer steps) to an external electron acceptor. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr176, Phe110 | Tyr119(113)L(B), Phe66(48)H(A) | Form a hydrophobic environment in the active site, and also ensure that nothing larger than methylamine can enter the site. | steric role |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, cofactor used, bimolecular elimination, electron transfer, radical formation, redox reaction, charge delocalisation, radical termination, intramolecular elimination, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Singh V et al. (2000), J Am Chem Soc, 122, 931-938. Characterization of the Tryptophan Tryptophyl-Semiquinone Catalytic Intermediate of Methylamine Dehydrogenase by Electron Spin−Echo Envelope Modulation Spectroscopy. DOI:10.1021/ja9934246.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. Methylamine initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the TQQ cofactor in an addition reaction with concomitant deprotonation of the amine nitrogen.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer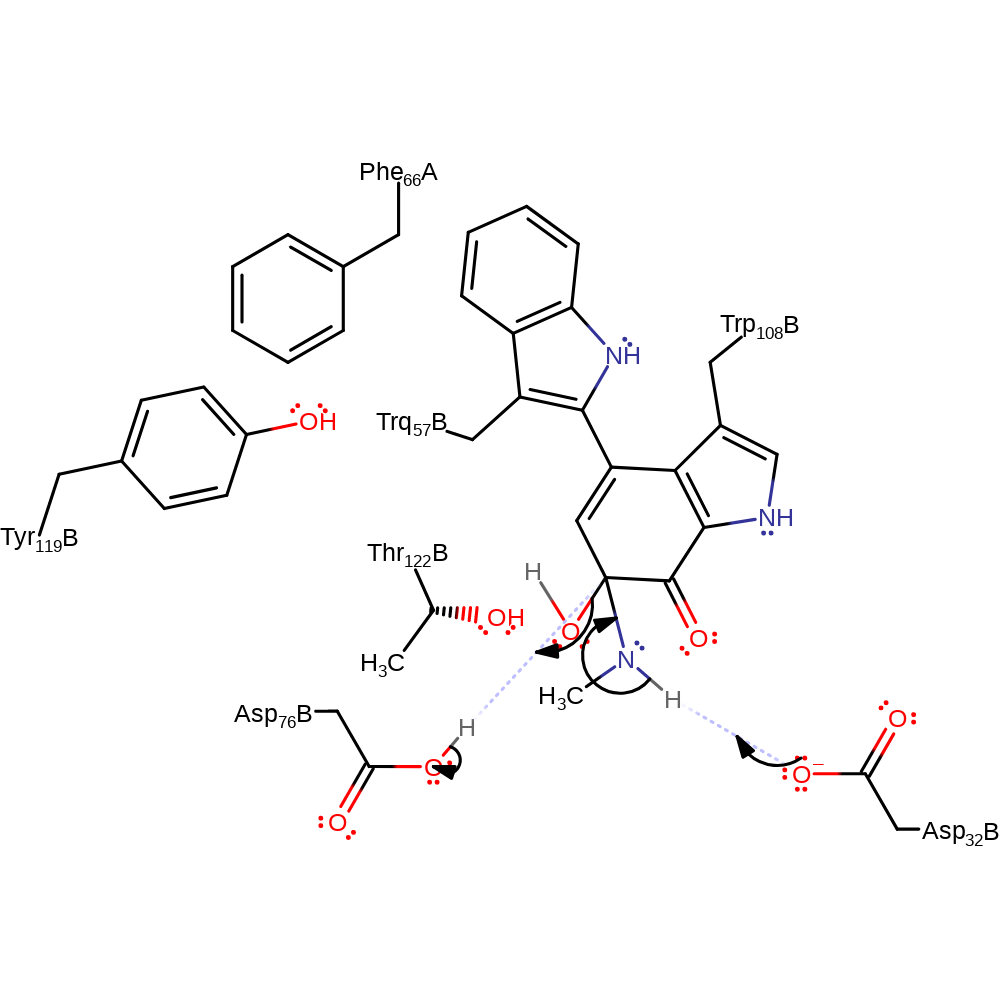
Step 3. In this base activated dehydration, it is likely one of the Asp residues (likely Asp32) acts as the base.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp32(26)L(B) | proton acceptor |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton donor |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton relay |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton relay |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, cofactor used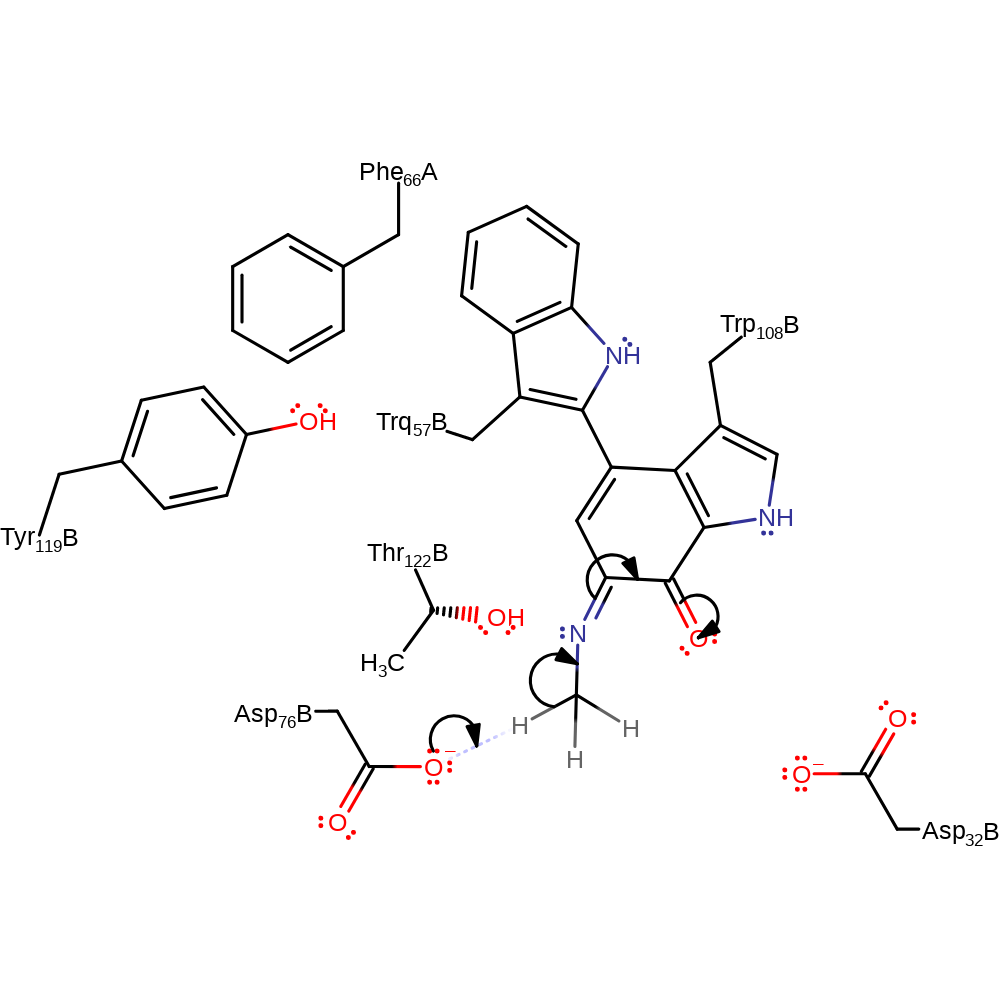
Step 4. Asp76 deprotonated the alpha-carbon with concomitant double bond rearrangement into the TQQ cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton donor |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton donor |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 5. Asp32B deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the alpha-carbon in an addition reaction, the nitrogen of the intermediate is reprotonated from Asp73B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton donor |
| Asp32(26)L(B) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition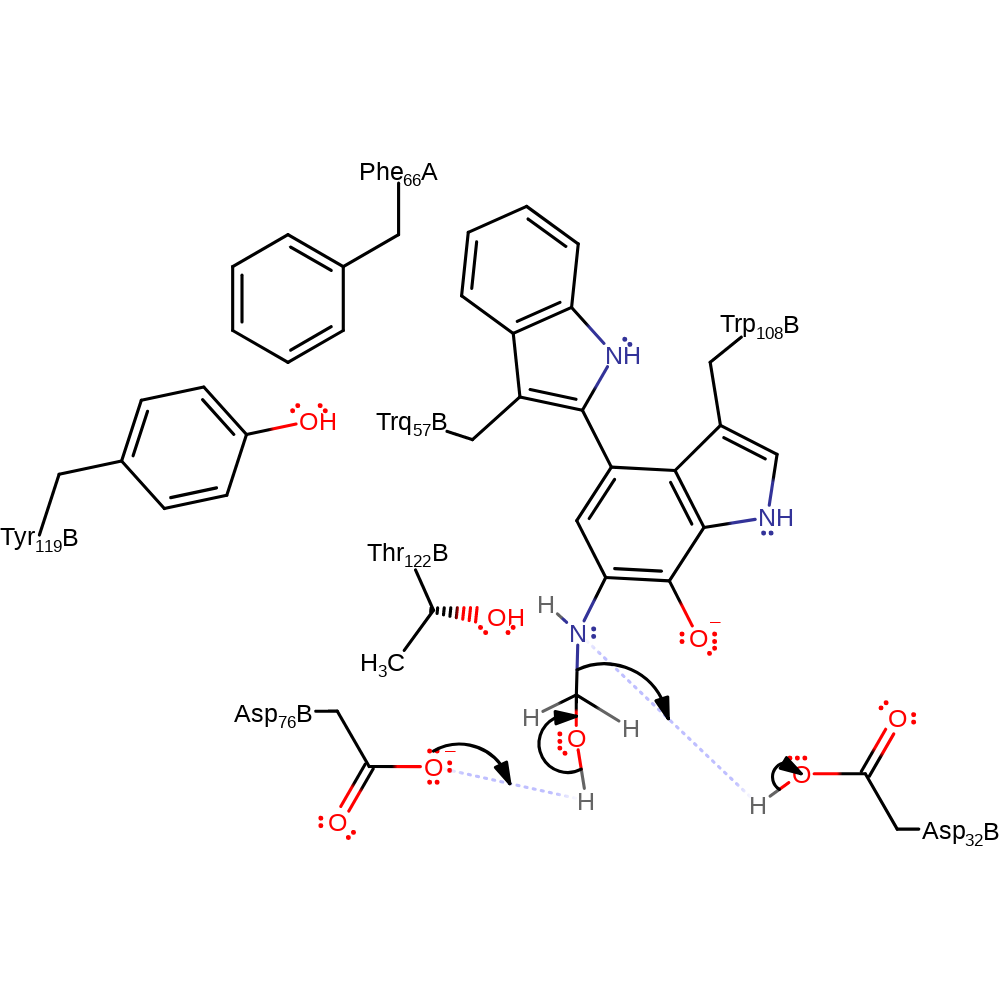
Step 6. Asp76 deprotonates the newly added hydroxyl group, eliminating the cofactor with concomitant deprotonation of Asp32, the formaldehyde products is released.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton acceptor |
| Asp32(26)L(B) | proton donor |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton relay |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton relay |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination
Step 7. Asp32 deprotonates the amine nitrogen, with concomitant double bond rearrangement and a single electron transfer from the cofactor to amicyanin.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | single electron donor, proton donor |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton donor |
| Asp32(26)L(B) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, radical formation, redox reaction, charge delocalisationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | single electron donor |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, radical termination, electron transfer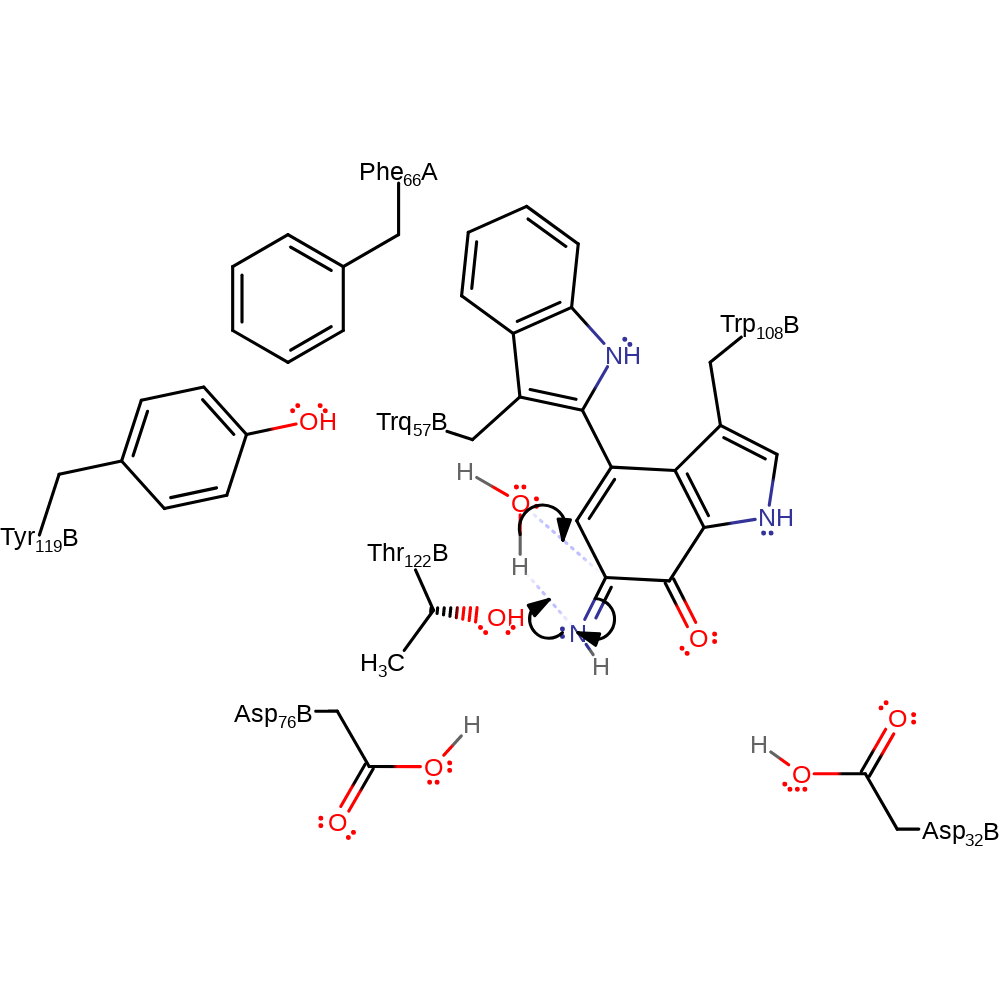
Step 9. The amide nitrogen deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbon of the cofactor in an addition reaction
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer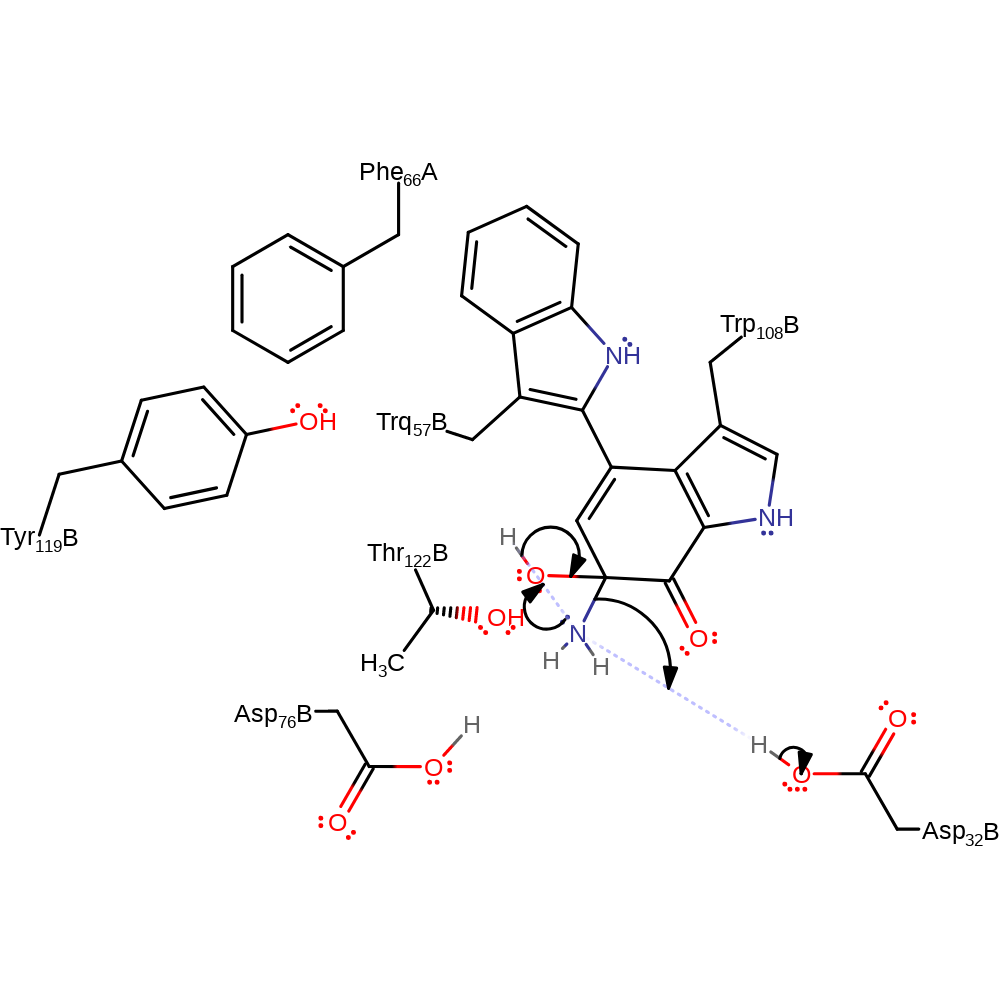
Step 10. The amine nitrogen deprotonates the newly added hydroxyl group, which eliminates ammonia. Ammonia reprotonates from Asp32B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp32(26)L(B) | proton donor |
| Trq57(51)L(B) (ptm) | proton relay |
| Trp108(102)L(B) (ptm) | proton relay |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, proton transfer, native state of cofactor regeneratedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe66(48)H(A) | steric role |
| Tyr119(113)L(B) | steric role |
| Thr122(116)L(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp76(70)L(B) | proton donor |







 Download:
Download: 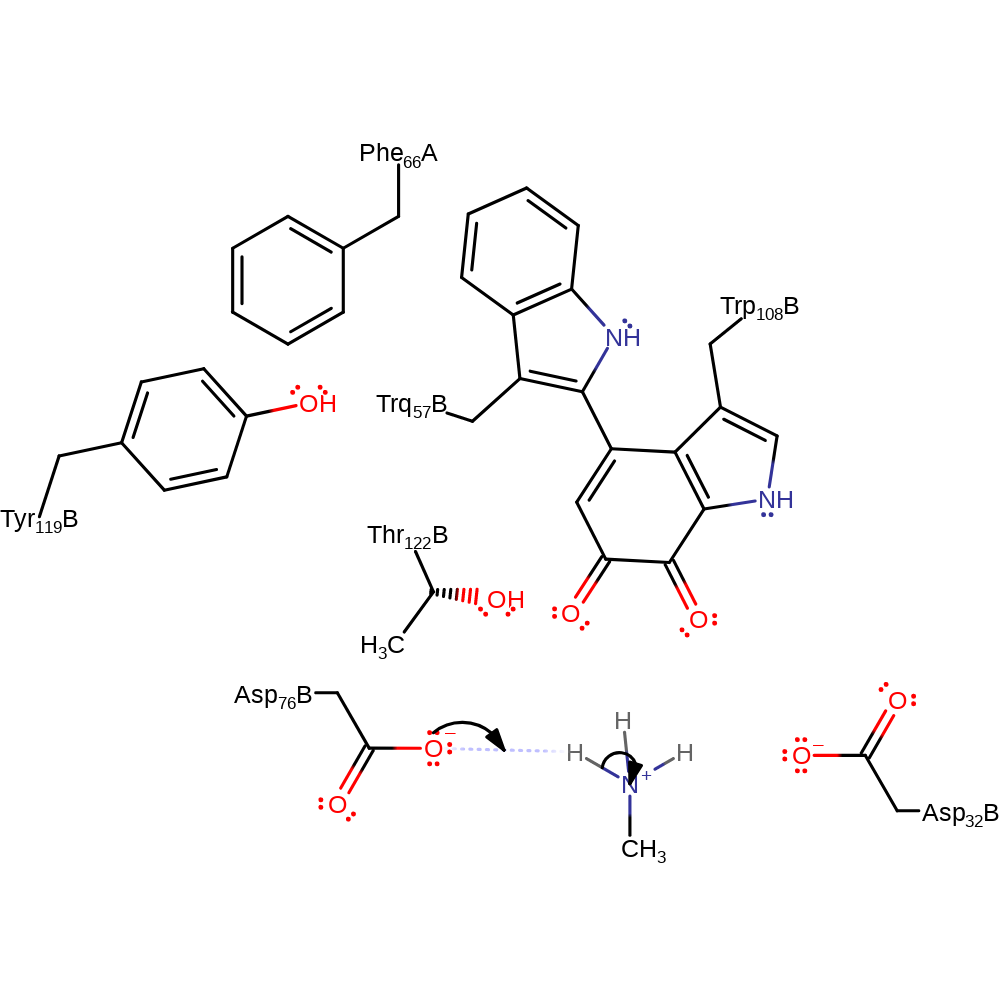
 Download:
Download: