Adenylyl-sulfate reductase
Adenylylsulfate (adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate) reductase (APS reductase) from Archaeoglobus fulgidus catalyses the reversible reduction of APS to sulfite and AMP. This pathway provides sulfate which serves as a terminal electron acceptor of an anaerobic respiratory electron transfer chain. Electrons are also provided for anoxygenic photosynthesis and denitrification.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
O28603

O28604
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Archaeoglobus fulgidus DSM 4304 (Archaea)

- PDB
-
1jnr
- Structure of adenylylsulfate reductase from the hyperthermophilic Archaeoglobus fulgidus at 1.6 resolution
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.50.50.60
 3.30.70.20
3.30.70.20  3.90.700.10
3.90.700.10  (see all for 1jnr)
(see all for 1jnr)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1), Tetra-mu3-sulfido-tetrairon (2), Water (3) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.8.99.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The two electrons required for APS reduction are transferred from an unknown electron donor, via two [4Fe-4S] clusters from the surface of the protein to FAD. Trp 48 aids in electron transfer between cluster I and the methyl C8M group of FAD. Once the FAD has been fully oxidised, a water molecule is made more basic by the hydrogen bond network of Asn 74, Glu 141 and Asp 361. This water then accepts a proton the N5 atom of reduced FAD, acting as a general base, activating N5 for nucleophilic attack on the sulphur atom of APS. A process that is assisted by Asn 74, Trp 234 and Arg 265, which act to make the sulphur atom more electrophilic by hydrogen bonding to the sulfate oxygens of APS. The process occurs via a negatively charged, penta-coordinated intermediate which decomposes, breaking the S-O bond, forming the leaving group AMP. The resulting negative charge is then pushed onto the N5 atom of FAD, causing the N-S bond to break, releasing SO3-, which is protonated by either His 398 or a protonated water molecule as it leaves.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1jnr) | ||
| His398 | His398A | Helps to increase the electrophilicity of the sulphur atom of APS. Also protonates the sulfite leaving group. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn74 | Asn74A | Forms a hydrogen bond network with Glu 141 and Asp 361 which increases the basicity of the water molecule which deprotonates N5 of reduced FAD. Also helps to increase the electrophilicity of the sulphur atom of APS. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| Asp361 | Asp361A | Forms a hydrogen bond network with Glu 141 and Asn 74 which increases the basicity of the water molecule which deprotonates N5 of reduced FAD. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp234, Arg265 | Trp234A, Arg265A | Helps to increase the electrophilicity of the sulphur atom of APS. | increase electrophilicity, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser449 | Ser449A | Stabilises negative charge on the FAD cofactor. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp48 | Trp48B | Transfers electrons between the S3 of cluster I and the methyl group C8M of FAD. | single electron relay, van der waals interaction, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
| Glu141 | Glu141A | Forms a hydrogen bond network with Asn 74 and Asp 361 which increases the basicity of the water molecule which deprotonates N5 of reduced FAD. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate formation, electron relay, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Schiffer A et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 2960-2967. Reaction Mechanism of the Iron−Sulfur Flavoenzyme Adenosine-5‘-Phosphosulfate Reductase Based on the Structural Characterization of Different Enzymatic States†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0521689. PMID:16503650.
- Fritz G et al. (2002), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 99, 1836-1841. Structure of adenylylsulfate reductase from the hyperthermophilic Archaeoglobus fulgidus at 1.6-A resolution. DOI:10.1073/pnas.042664399. PMID:11842205.
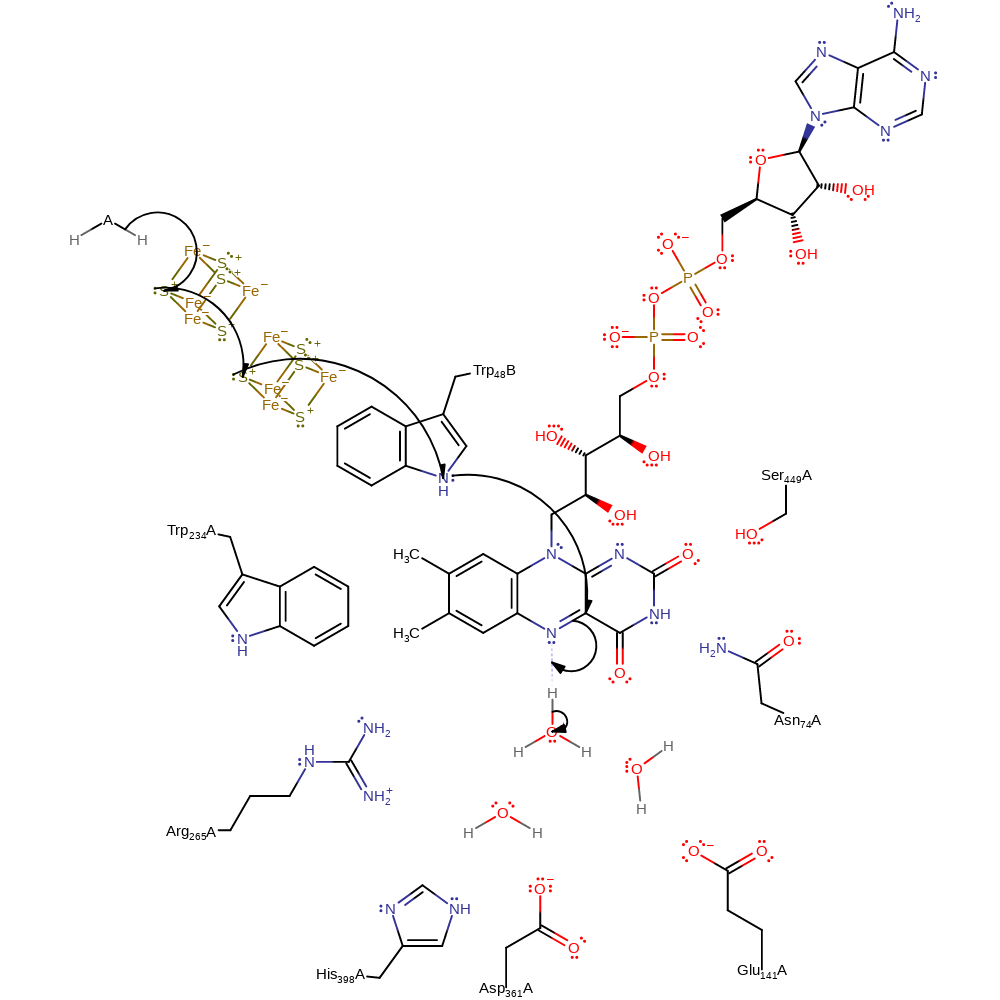
Step 1. A single electron is transferred from the donor, through two iron-sulfur clusters and Trp48B to FAD, with concomitant deprotonation of water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn74A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser449A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp48B | van der waals interaction, single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate formation, electron relay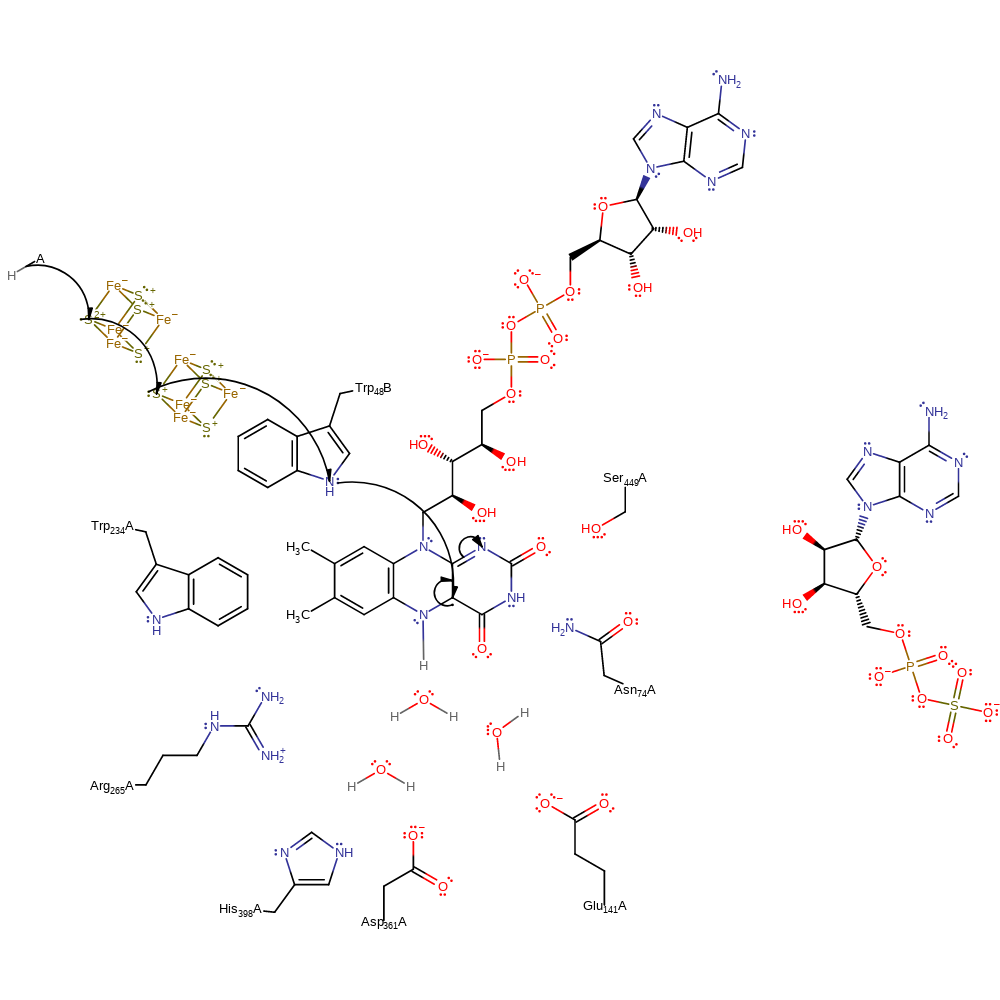
Step 2. A second single electron is transferred from the donor, through two iron-sulfur clusters and Trp48B to FAD forming the N1 anion form of reduced FAD.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn74A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser449A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp48B | van der waals interaction, single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate formation, overall product formed, electron relay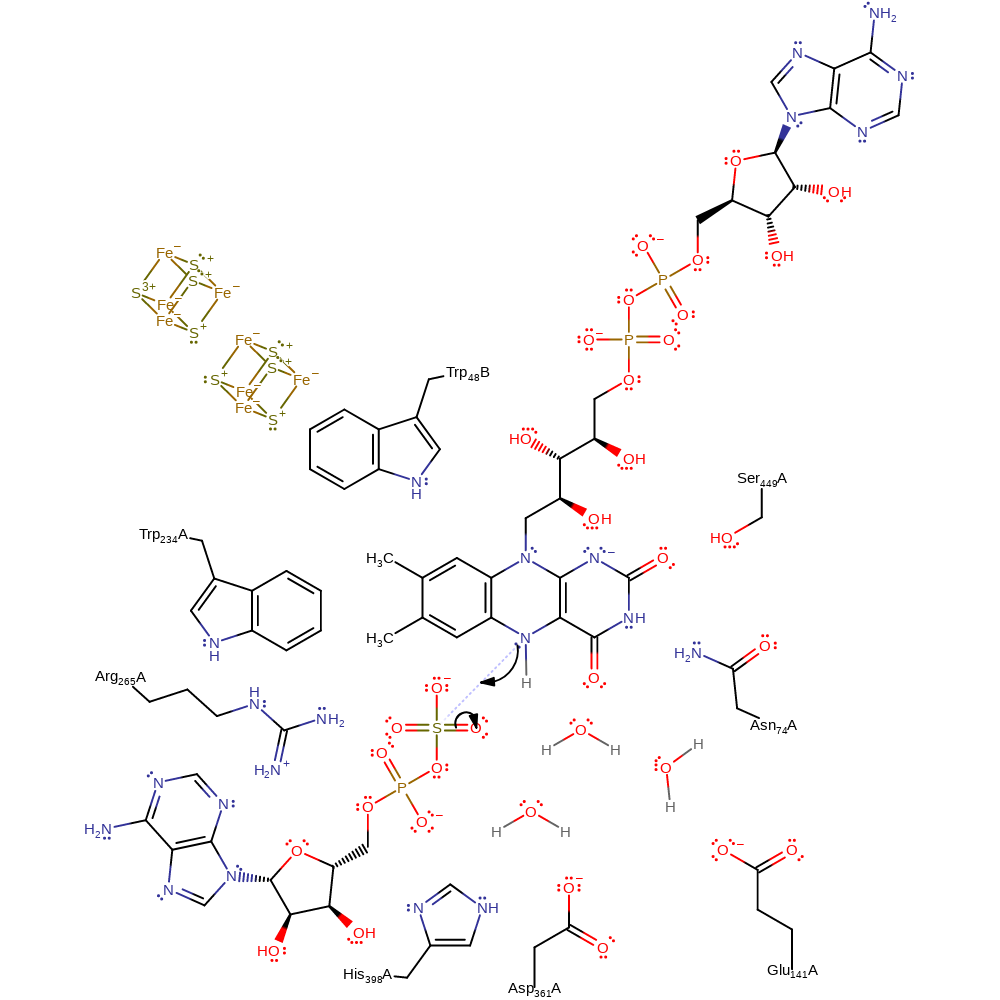
Step 3.
The N5 of FAD initiates a nucleophilic attack on the sulfur of the sulfate group in an addition reaction.
The negative charge is delocalised primarily over the N1-C=O2 group but also over the entire isoalloxazine ring including atom N5. The counter-balancing positive charge necessary to maintain the unprotonated state is provided by two hydrogen bonds donated from the polypeptide to the O2 atom of FAD and by the large dipole of the 30 Angstroms long helix that is pointing with its N-terminus directly toward the N1 atom [PMID:11842205]. By inspection of the crystal structure we attribute the stabilisation role to the main-chain amide of Asn74 and to the side-chain of Ser449. Main-chain amide of Ser449 is an hydrogen bond donor to N1 of the isoalloxazine ring. The formation of the short-lived FAD-APS transition state is most likely the rate-limiting step [PMID:16503650].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn74A | hydrogen bond donor, increase electrophilicity, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp234A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, increase electrophilicity |
| Arg265A | hydrogen bond donor, increase electrophilicity |
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser449A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp48B | van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, rate-determining step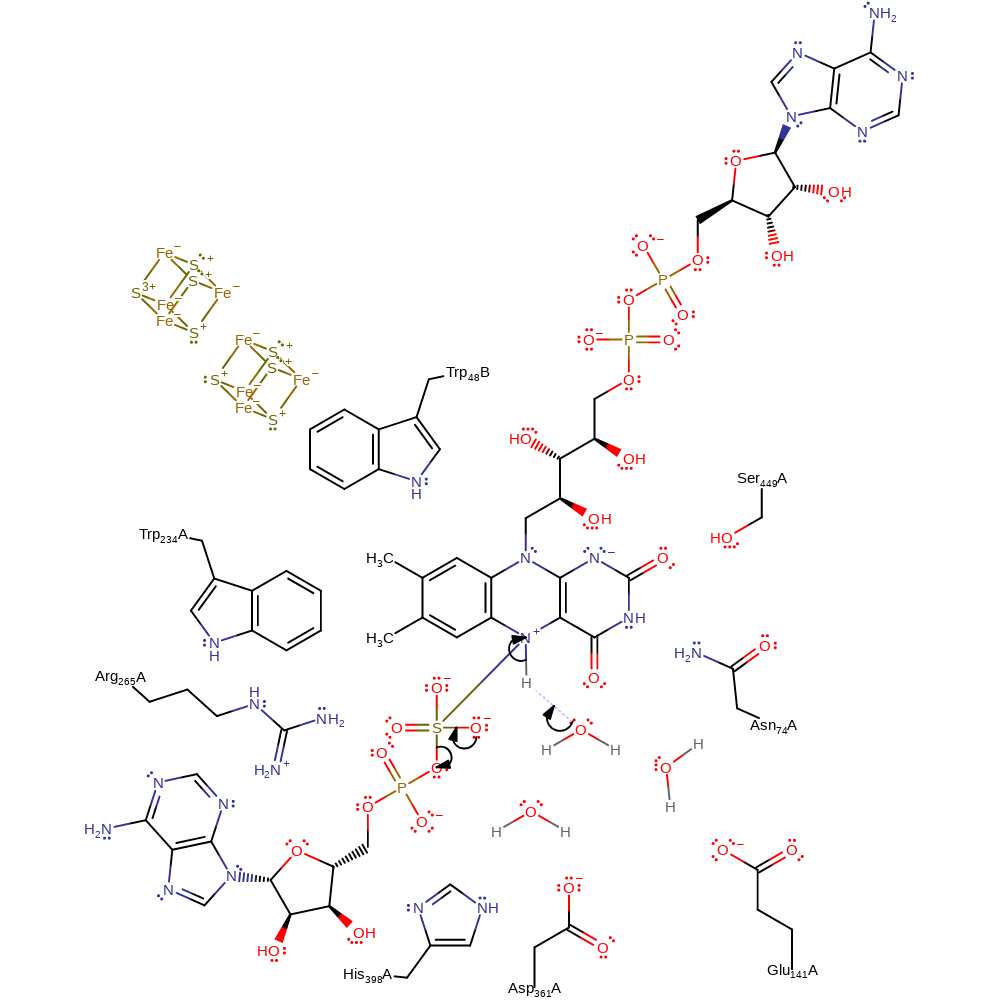
Step 4.
Water deprotonates the N5 of FAD. One of the oxygen anions of sulfate eliminates the phosphate group.
It is possible that a firmly bound water molecule located 3.8 Angstroms away from the N5 atom acts as the proton acceptor. The basicity of this water molecule is significantly increased because of the hydrogen bond network comprising the side chain amide of Asn74 and the carboxylate side chains of Glu141 and Asp361 [PMID:11842205].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn74A | hydrogen bond donor, activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu141A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Arg265A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Ser449A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp48B | van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, overall product formed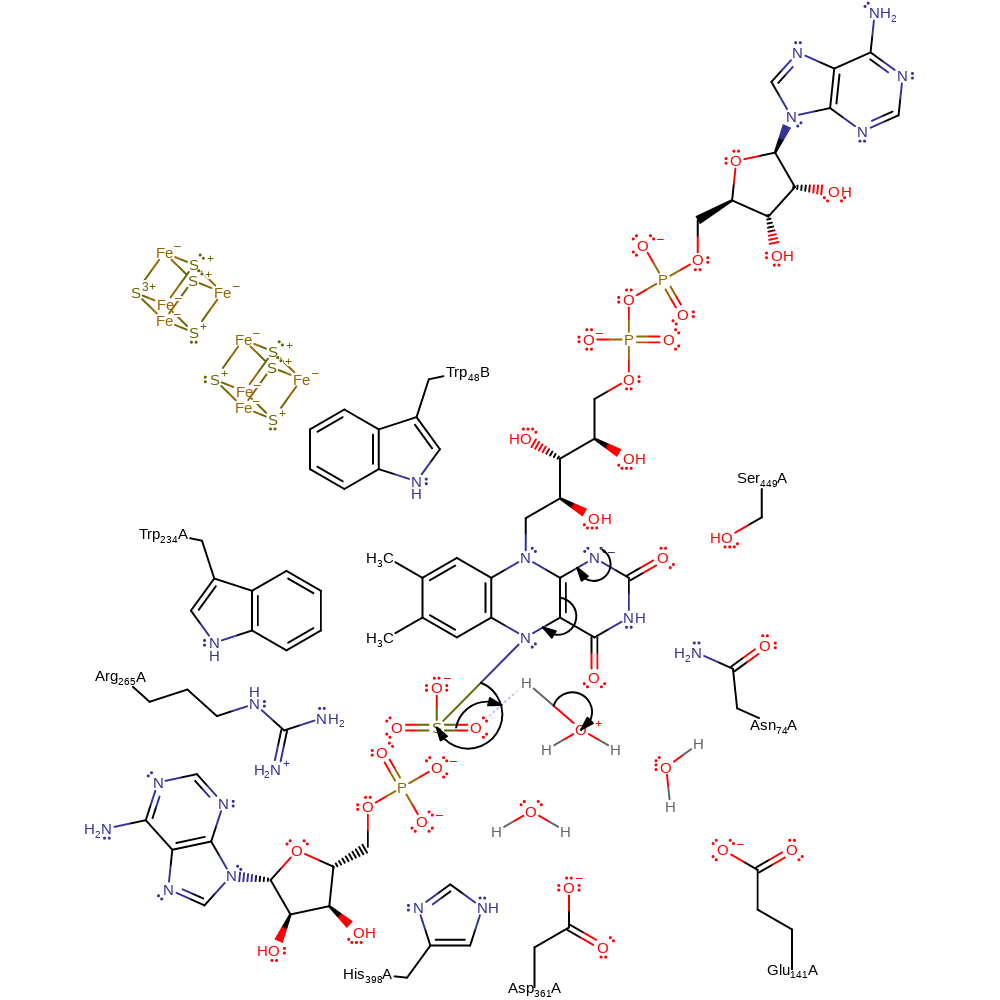
Step 5. The N5 of FAD initiates the elimination of the sulfite with concomitant deprotonation of water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn74A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp234A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg265A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp361A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His398A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser449A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp48B | van der waals interaction |






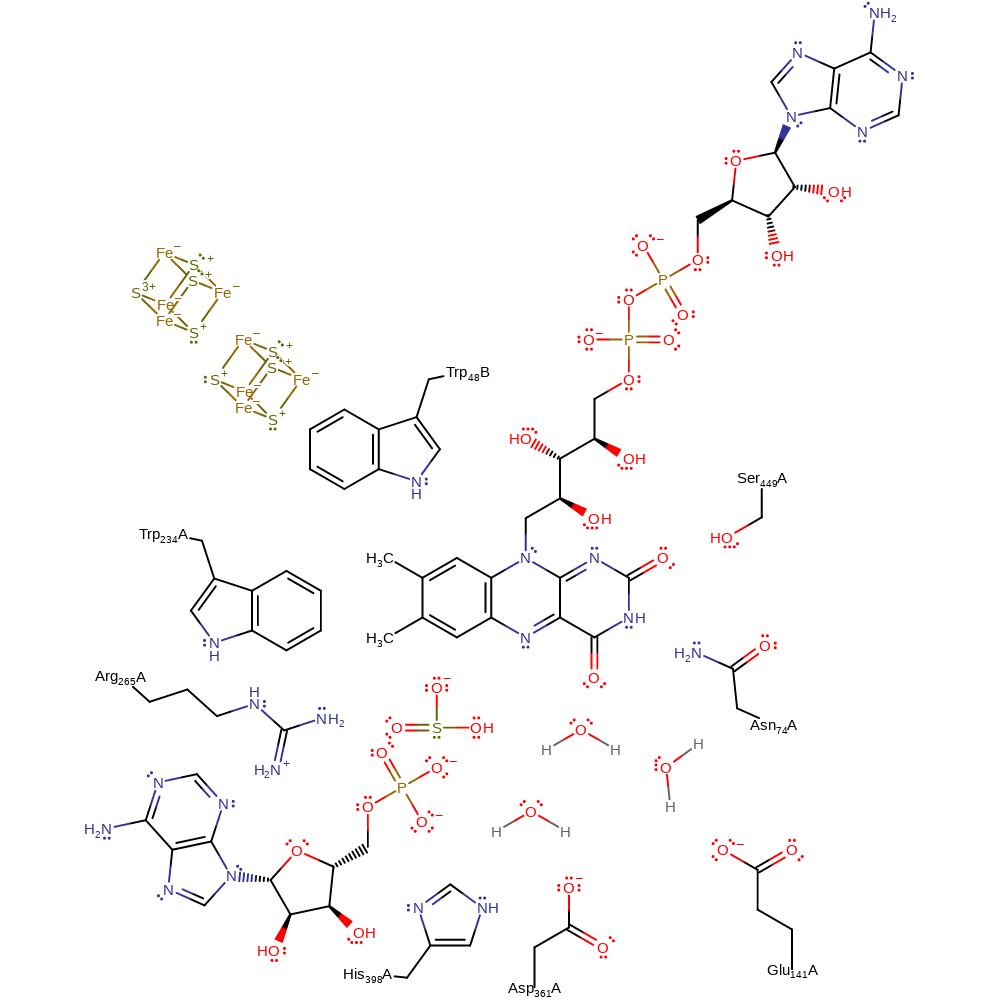 Download:
Download: