Ornithine carbamoyltransferase
Ornithine transcarbamoylase (OTCase) catalyses the formation of citrulline from carbamoyl phosphate (CP) and L-ornithine (ORN) in the urea cycle. Deleterious mutations in the human OTCase gene are associated with clinical hyperammonemia, neurological symptoms or even death. Approximately 140 mutations that result in OTCase-linked disorders have been identified, and several mutant enzymes have been purified and characterized biochemically.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00480
 (2.1.3.3)
(2.1.3.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1oth
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN ORNITHINE TRANSCARBAMOYLASE COMPLEXED WITH N-PHOSPHONACETYL-L-ORNITHINE
(1.85 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1370
 (see all for 1oth)
(see all for 1oth)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.3.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Here, the protein active site acts to stabilise the intermediates and transition states. The ornithine substrate binds in the neutral form. The amine group initiates a nucleophilic attach on the carbonyl of the carbamoyl phosphate substrate. This forms a tetrahedral intermediate that collapses, eliminating the phosphate product with concomitant deprotonation of the L-citrulline.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1oth) | ||
| Gln171 | Gln171(138)A | Stabilises accumulation of positive charge on the N-delta of L-ornithine as this atom attacks the carbonyl of carbamoyl phosphate. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp263, Cys303 | Asp263(230)A, Cys303(270)A | Binds the ornithine substrate in the active site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His168, Arg141, Arg330 | His168(135)A, Arg141(108)A, Arg330(297)A | Stabilises accumulation of negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen of carbamoyl phosphate during nucleophilic attack by L-ornithine. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapseReferences
- McDowall S et al. (1990), Protein Eng, 4, 73-77. Site-directed mutagenesis of Arg60 and Cys271 in ornithine transcarbamylase from rat liver. DOI:10.1093/protein/4.1.73. PMID:2290837.
- Shi D et al. (2000), Proteins, 39, 271-277. Crystal structure of human ornithine transcarbamylase complexed with carbamoyl phosphate and L-norvaline at 1.9 ? resolution. DOI:10.1002/(sici)1097-0134(20000601)39:4<271::aid-prot10>3.0.co;2-e. PMID:10813810.
- Shi D et al. (1998), J Biol Chem, 273, 34247-34254. 1.85-A Resolution Crystal Structure of Human Ornithine Transcarbamoylase Complexed with N-Phosphonacetyl-L-ornithine. CATALYTIC MECHANISM AND CORRELATION WITH INHERITED DEFICIENCY. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.51.34247. PMID:9852088.
- Jin L et al. (1997), Nat Struct Biol, 4, 622-625. Crystal structure at 2.8 Å resolution of anabolic ornithine transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1038/nsb0897-622. PMID:9253409.

Step 1. The ornithine amine initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the carbamic acid phosphate ester in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys303(270)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln171(138)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Asp263(230)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg330(297)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg141(108)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His168(135)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating phosphate, which deprotonates the newly formed secondary amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys303(270)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln171(138)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp263(230)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg330(297)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg141(108)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His168(135)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, intermediate formationIntroduction
Cys 303 forms a proton relay system with Asp 263 and the alpha amino group of the ornithine. A tetrahedral intermediate is stabilised by Gln 171, which can form a hydrogen bond to the positive N-delta of ornithine, and by Arg 141, Arg 330 and His 168, which can form hydrogen bonds to the oxyanion that results from nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl. The proton attached to Cys 303 may leave the active site via a chain of ordered water molecules. PMID:9253409 pointed out a similarity between the triad of residues (E.coli numbering) His272, Cys273 and Glu299 are similar to those of the catalytic triads of thiol peptidases. However, use of the template-matching program TESS and the structural alignment program ProFit showed that the RMSD of these fits was very tenuous and the similarity is likely to be coincidental. PMID:9852088 does not believe the catalytic triad is significant. More recently, Sankaranarayanan et al. (PMID:18062991) suggest this is unlikely and that the active site is such that the ornithine binds in the neutral state (see mechanism 2).
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1oth) | ||
| His168 | His168(135)A | Stabilises accumulation of negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen of carbamoyl phosphate during nucleophilic attack by L-ornithine. May accept the proton from the N-delta of L-ornithine. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln171 | Gln171(138)A | Stabilises accumulation of positive charge on the N-delta of L-ornithine as this atom attacks the carbonyl of carbamoyl phosphate. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp263 | Asp263(230)A | Stabilises the thiolate from of the sulfhydryl group of Cys 273, enabling it to accept a proton from L-ornithine. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys303 | Cys303(270)A | Deprotonates the delta-amino group of L-ornithine to allow it to attack carbamoyl phosphate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Arg141, Arg330 | Arg141(108)A, Arg330(297)A | Stabilises accumulation of negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen of carbamoyl phosphate during nucleophilic attack by L-ornithine. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Shi D et al. (1998), J Biol Chem, 273, 34247-34254. 1.85-A Resolution Crystal Structure of Human Ornithine Transcarbamoylase Complexed with N-Phosphonacetyl-L-ornithine. CATALYTIC MECHANISM AND CORRELATION WITH INHERITED DEFICIENCY. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.51.34247. PMID:9852088.
- Shabalin IG et al. (2012), Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun, 68, 1018-1024. Structure of anabolic ornithine carbamoyltransferase fromCampylobacter jejuniat 2.7 Å resolution. DOI:10.1107/s1744309112031259. PMID:22949186.
- Shi D et al. (2000), Proteins, 39, 271-277. Crystal structure of human ornithine transcarbamylase complexed with carbamoyl phosphate and L-norvaline at 1.9 ? resolution. DOI:10.1002/(sici)1097-0134(20000601)39:4<271::aid-prot10>3.0.co;2-e. PMID:10813810.
- Jin L et al. (1997), Nat Struct Biol, 4, 622-625. Crystal structure at 2.8 Å resolution of anabolic ornithine transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1038/nsb0897-622. PMID:9253409.
- McDowall S et al. (1990), Protein Eng, 4, 73-77. Site-directed mutagenesis of Arg60 and Cys271 in ornithine transcarbamylase from rat liver. DOI:10.1093/protein/4.1.73. PMID:2290837.
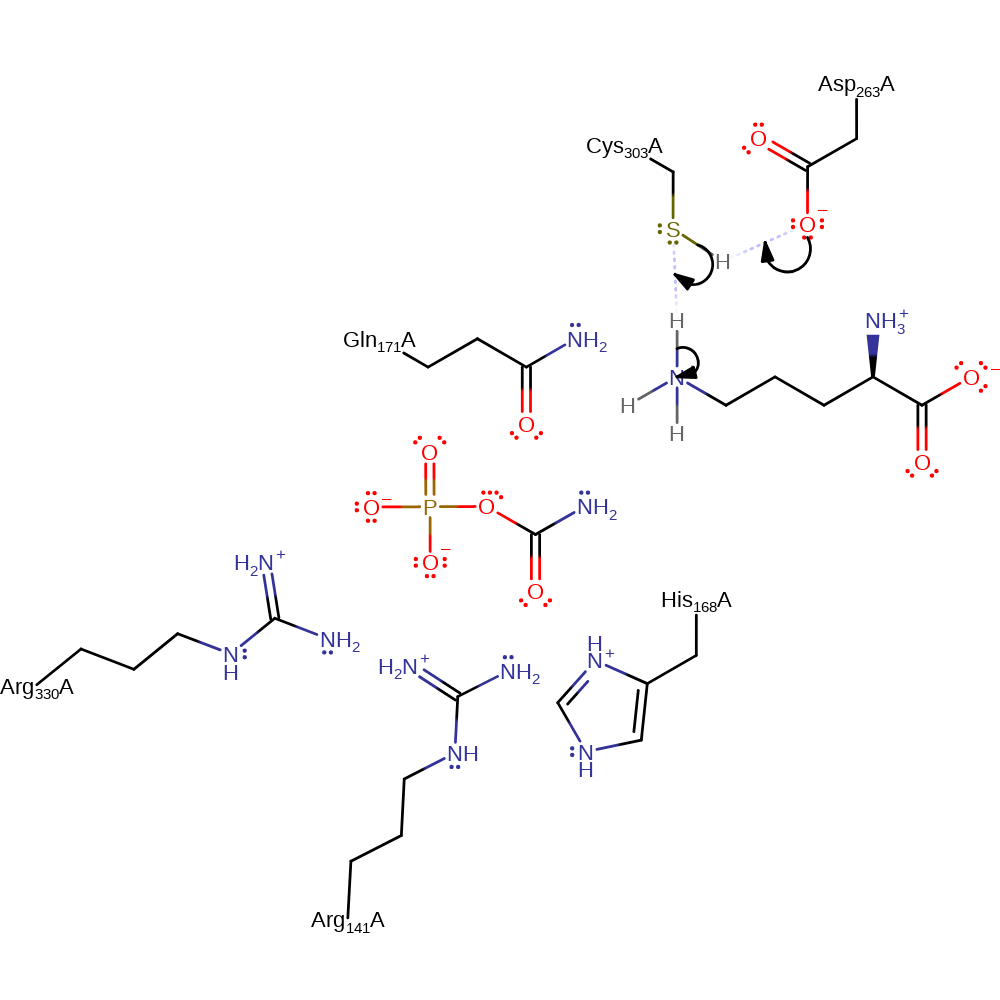
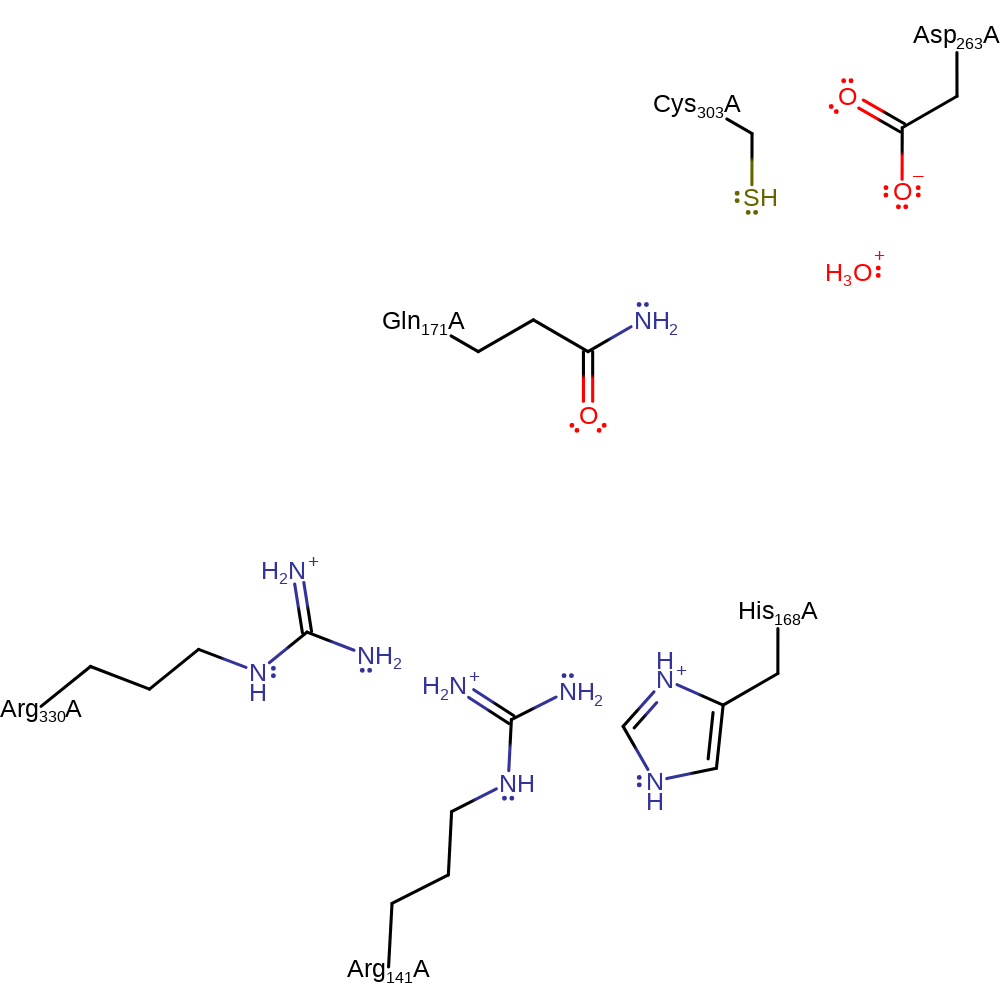
Step 1. Cys303 deprotonates the substrate, ornithine, at the terminal amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys303(270)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gln171(138)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp263(230)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg330(297)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg141(108)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His168(135)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys303(270)A | proton relay, proton donor |
| Asp263(230)A | proton acceptor |
| Cys303(270)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation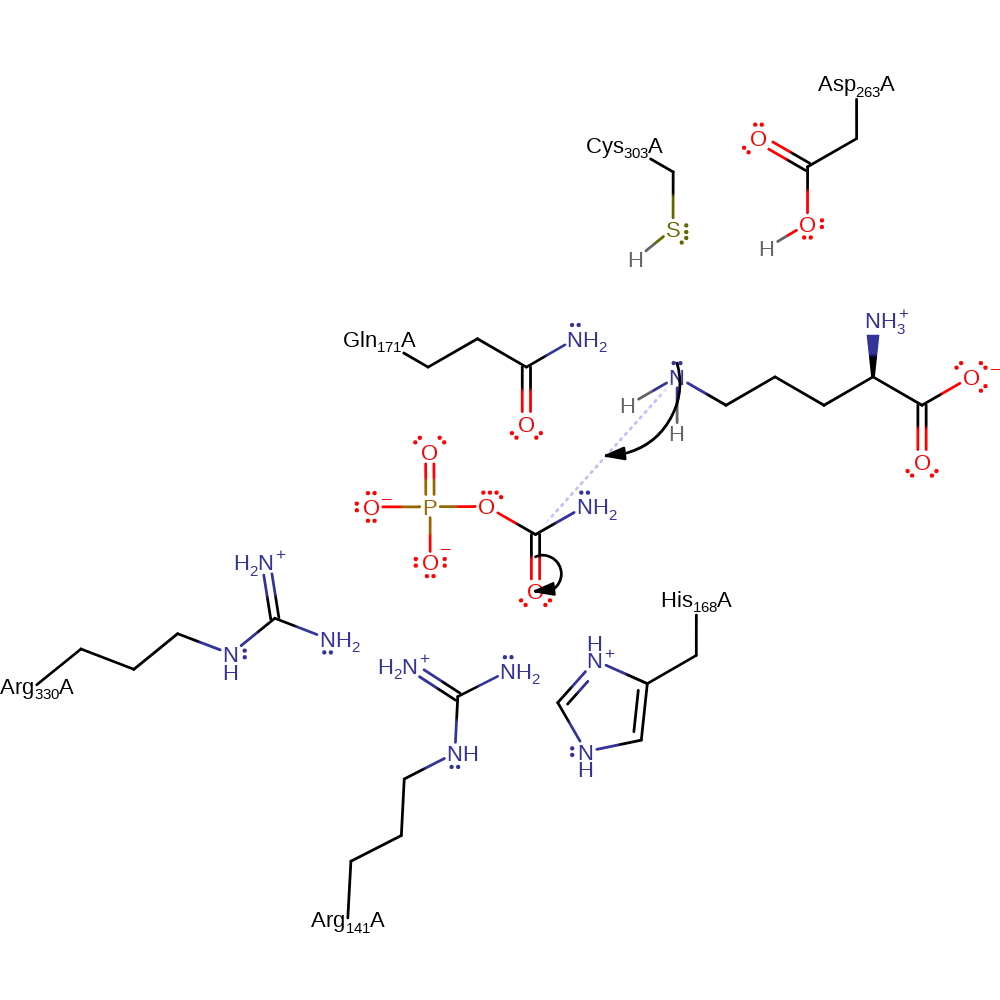
Step 2. The deprotonated amine initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the carbamic acid phosphate ester in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys303(270)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln171(138)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Asp263(230)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg330(297)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg141(108)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His168(135)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation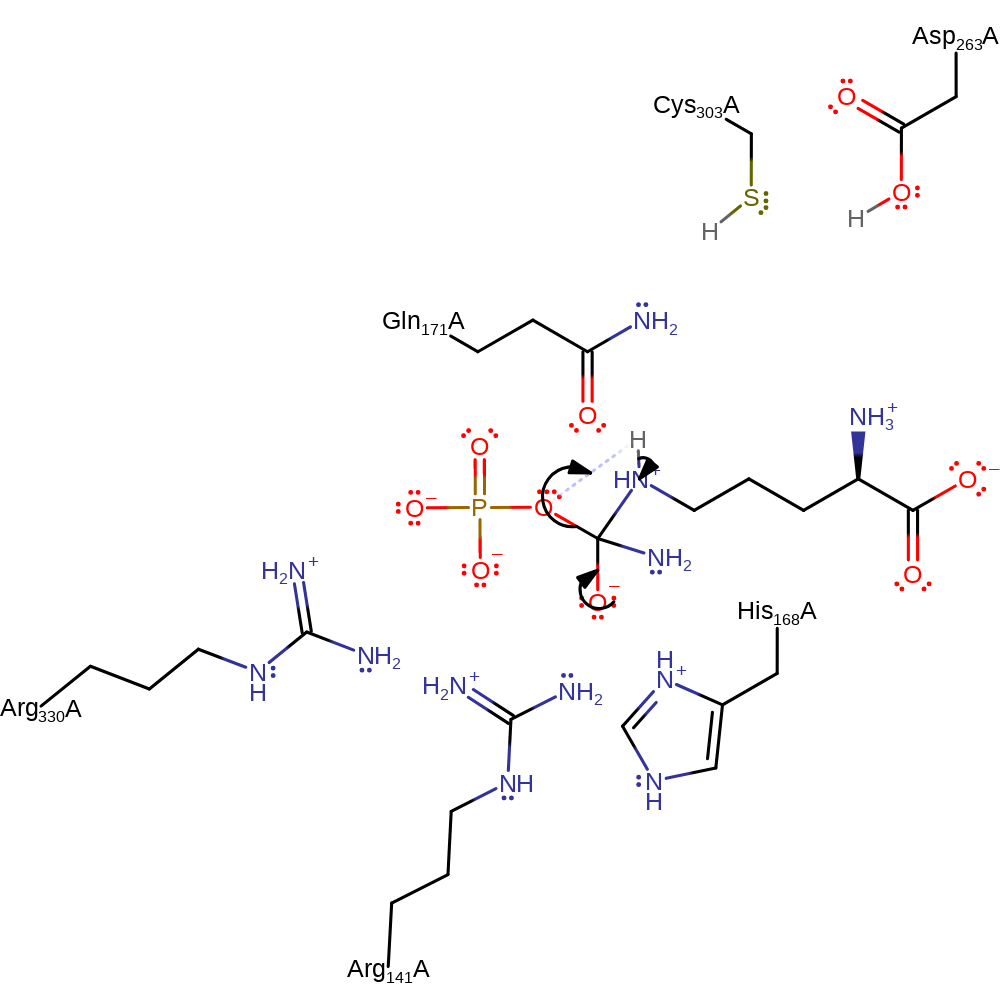
Step 3. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating phosphate, which deprotonates the newly formed secondary amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys303(270)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln171(138)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp263(230)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg330(297)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg141(108)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His168(135)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys303(270)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln171(138)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp263(230)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Arg330(297)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg141(108)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His168(135)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp263(230)A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: 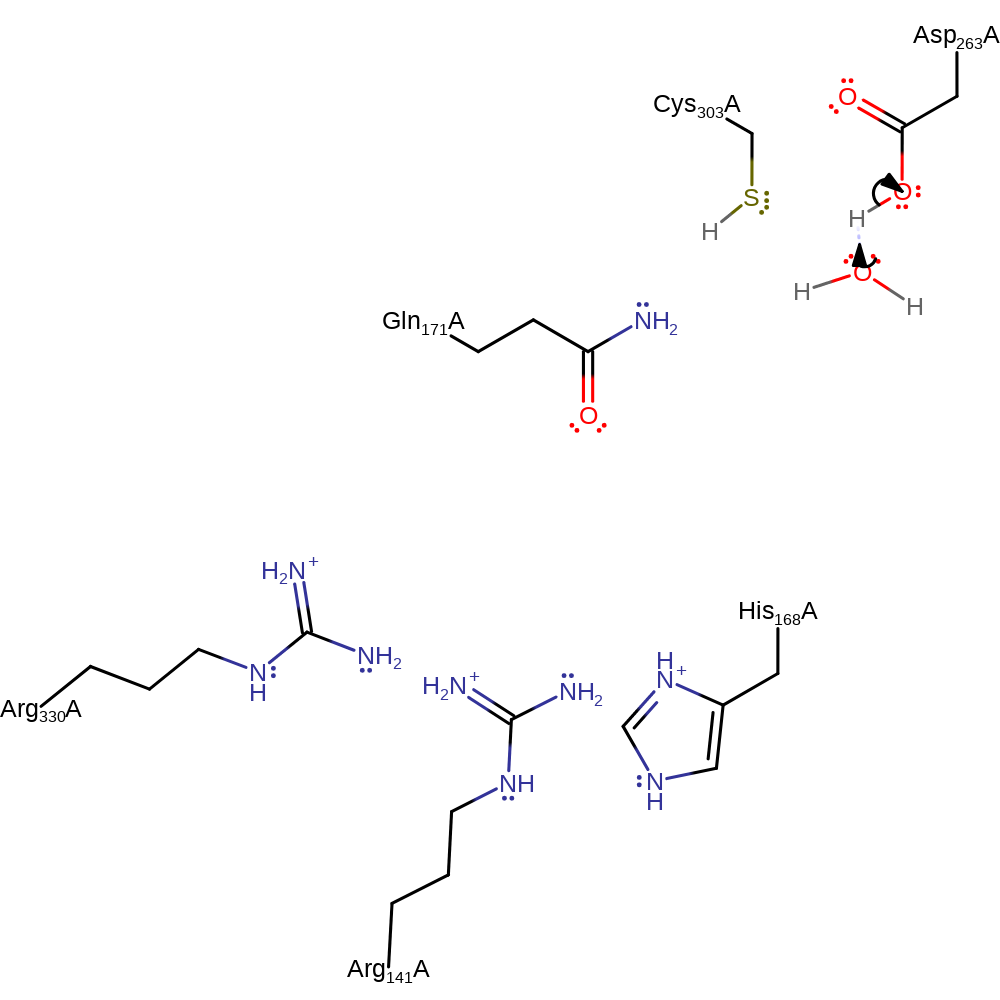
 Download:
Download: