Aspartate Ammonia Lyase
Aspartate Ammonia Lyase is one of the three ammonia lyases that belong to aspartate/fumarase superfamily. It catalyses the reversible reaction of L-aspartate to make ammonia and fumarate and is important in microbial nitrogen metabolism. It is also an industrial precursor for the synthesis of food additives and artificial sweeteners.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9LCC6
 (4.3.1.1)
(4.3.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus sp. YM55-1 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
3r6v
- Crystal structure of aspartase from Bacillus sp. YM55-1 with bound L-aspartate
(2.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.275.10
 1.20.200.10
1.20.200.10  (see all for 3r6v)
(see all for 3r6v)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.3.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Aspartate ammonia lyase (Asp) catalyses the reversible reaction of L-aspartate to give fumarate and ammonia. The first and the rate limiting step is the deprotonation of L-aspartate by the catalytic base Ser318 followed by the displacement of the ammonia through the rearrangement of the double bond formed in the enediolate intermediate to form fumarate and ammonia as a product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3r6v) | ||
| His188 | His188A | Protonates the leaving ammonia. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
| Ser318 | Ser318C | Ser318 acts as the catalytic base. | proton donor |
| Thr187, Lys324, Asn142, Ser140, Thr141, Ser319, Thr101 | Thr187A, Lys324C, Asn142B, Ser140B, Thr141B, Ser319C, Thr101B | Form an extensive hydrogen bond network that stabilises the transition state and intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, proton transfer, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate baseReferences
- Zhang J et al. (2014), J Mol Graph Model, 51, 113-119. A QM/MM study of the catalytic mechanism of aspartate ammonia lyase. DOI:10.1016/j.jmgm.2014.05.003. PMID:24875395.
- de Villiers M et al. (2012), ACS Chem Biol, 7, 1618-1628. Catalytic Mechanisms and Biocatalytic Applications of Aspartate and Methylaspartate Ammonia Lyases. DOI:10.1021/cb3002792. PMID:22834890.
- Fibriansah G et al. (2011), Biochemistry, 50, 6053-6062. Structural basis for the catalytic mechanism of aspartate ammonia lyase. DOI:10.1021/bi200497y. PMID:21661762.
- Fibriansah G et al. (2011),Crystal structure of aspartase from Bacillus sp. YM55-1 with bound L-aspartate. DOI:10.2210/pdb3r6v/pdb.
- Puthan Veetil V et al. (2009), FEBS J, 276, 2994-3007. Site-directed mutagenesis, kinetic and inhibition studies of aspartate ammonia lyase from Bacillus sp. YM55-1. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07015.x. PMID:19490103.

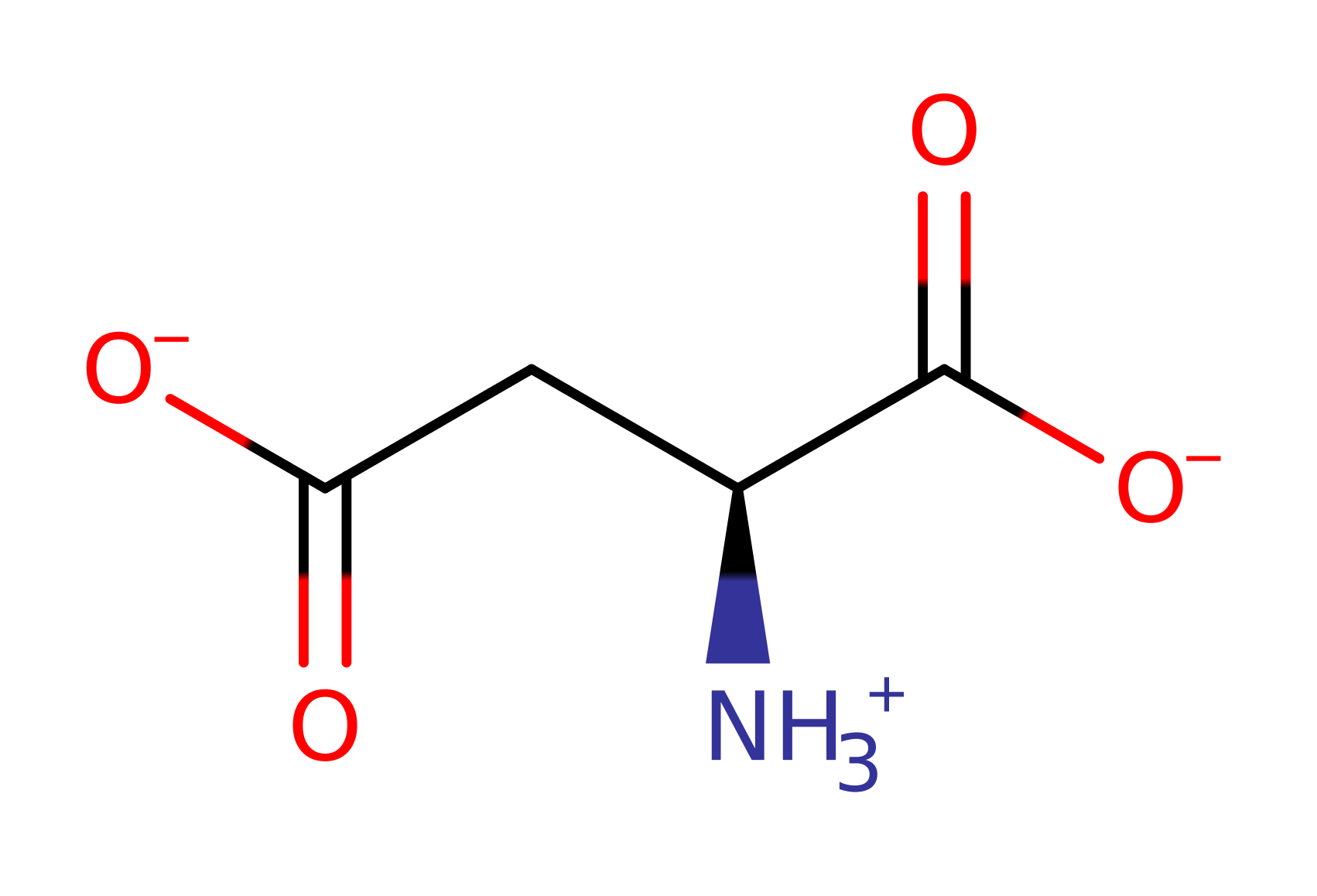
Step 1. Ser318 acts as a catalytic base and deprotonates the Cβ proton of L-aspartate substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser318C | proton donor |
| His188A | increase basicity, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr187A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn142B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr101B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys324C | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr141B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser319C | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser140B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, proton transfer
Step 2. Rearrangement of double bond displaces the NH3+. His188 loses a proton to the leaving ammonia.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His188A | proton donor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr187A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn142B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr101B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys324C | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr141B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser319C | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser140B | hydrogen bond donor |


 Download:
Download: