Pentalenene synthase
Pentalenene synthase is structurally related to farnesyl diphosphate synthase, in accordance with the hypothesis that successive enzymes on a biosynthetic pathway are often evolutionarily related. Pentalene is a sesquiterpene that is a precursor for the pentalenolactone family of antibiotics. The sequiterpene family of secondary metabolites is a very large one, being secreted by plants, fungi and some microorganisms.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q55012
 (4.2.3.7)
(4.2.3.7)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Streptomyces exfoliatus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ps1
- PENTALENENE SYNTHASE
(2.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.600.10
 (see all for 1ps1)
(see all for 1ps1)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (3) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Originally based on QM/MM calculations, this is now the more generally accepted mechanism. In this mechanism, the initial cyclisation of FPP to the (E,E)-humulyl cation is followed by a 1,2-hydride shift, either directly or via a deprotonation–protonation sequence. The resulting protoilludyl cation then reactions in a dyotropic rearrangement. The product of this penultimate step is then deprotonated to form the final product. The general acid/base is assumed to be the pyrophosphate group.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ps1) | ||
| Ser223, Glu227, Asn219 | Ser223A, Glu227A, Asn219A | Forms part of the magnesium 3 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Trp308, His309, Phe76, Phe77 | Trp308A, His309A, Phe76A, Phe77A | F76 and F77 are well placed so as to interact with positive charge at C-1, C-2, and C-3 of the farnesyl residue and derived intermediates and act to stabilise these charges through quadrupole-charge interactions. | van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230, Arg157, Arg173, Lys226 | Arg230A, Arg157A, Arg173A, Lys226A | Stabilises the pyrophosphate leaving group. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84, Asp80 | Asp84A, Asp80A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 and 2 binding sites. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, overall reactant used, charge delocalisation, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, intramolecular electrophilic addition, cyclisation, hydride transfer, hydrogen transfer, intramolecular rearrangement, proton transfer, bimolecular eliminationReferences
- Dickschat JS (2016), Nat Prod Rep, 33, 87-110. Bacterial terpene cyclases. DOI:10.1039/c5np00102a. PMID:26563452.
- Pemberton TA et al. (2016), J Antibiot (Tokyo), 69, 486-493. General base-general acid catalysis by terpenoid cyclases. DOI:10.1038/ja.2016.39. PMID:27072285.
- Lodewyk MW et al. (2014), Org Biomol Chem, 12, 887-894. Pentalenene formation mechanisms redux. DOI:10.1039/c3ob42005a. PMID:24326700.
- Zu L et al. (2012), J Am Chem Soc, 134, 11369-11371. Effect of Isotopically Sensitive Branching on Product Distribution for Pentalenene Synthase: Support for a Mechanism Predicted by Quantum Chemistry. DOI:10.1021/ja3043245. PMID:22738258.
- Tantillo DJ (2011), Nat Prod Rep, 28, 1035-1053. Biosynthesis via carbocations: Theoretical studies on terpene formation. DOI:10.1039/c1np00006c. PMID:21541432.
- Gutta P et al. (2006), J Am Chem Soc, 128, 6172-6179. Theoretical Studies on Farnesyl Cation Cyclization: Pathways to Pentalenene. DOI:10.1021/ja058031n. PMID:16669687.
- Seemann M et al. (2002), J Am Chem Soc, 124, 7681-7689. Pentalenene synthase. Analysis of active site residues by site-directed mutagenesis. PMID:12083921.
- Lesburg CA et al. (1997), Science, 277, 1820-1824. Crystal Structure of Pentalenene Synthase: Mechanistic Insights on Terpenoid Cyclization Reactions in Biology. DOI:10.1126/science.277.5333.1820. PMID:9295272.
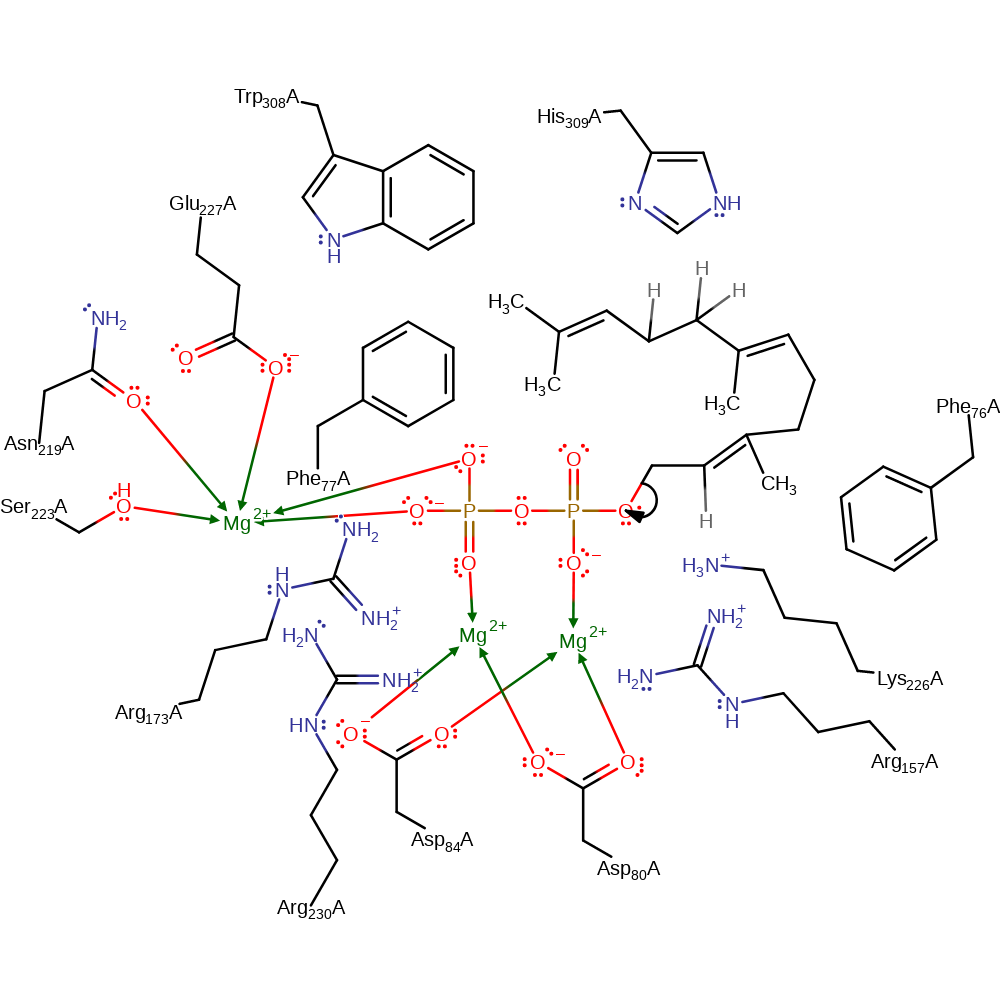
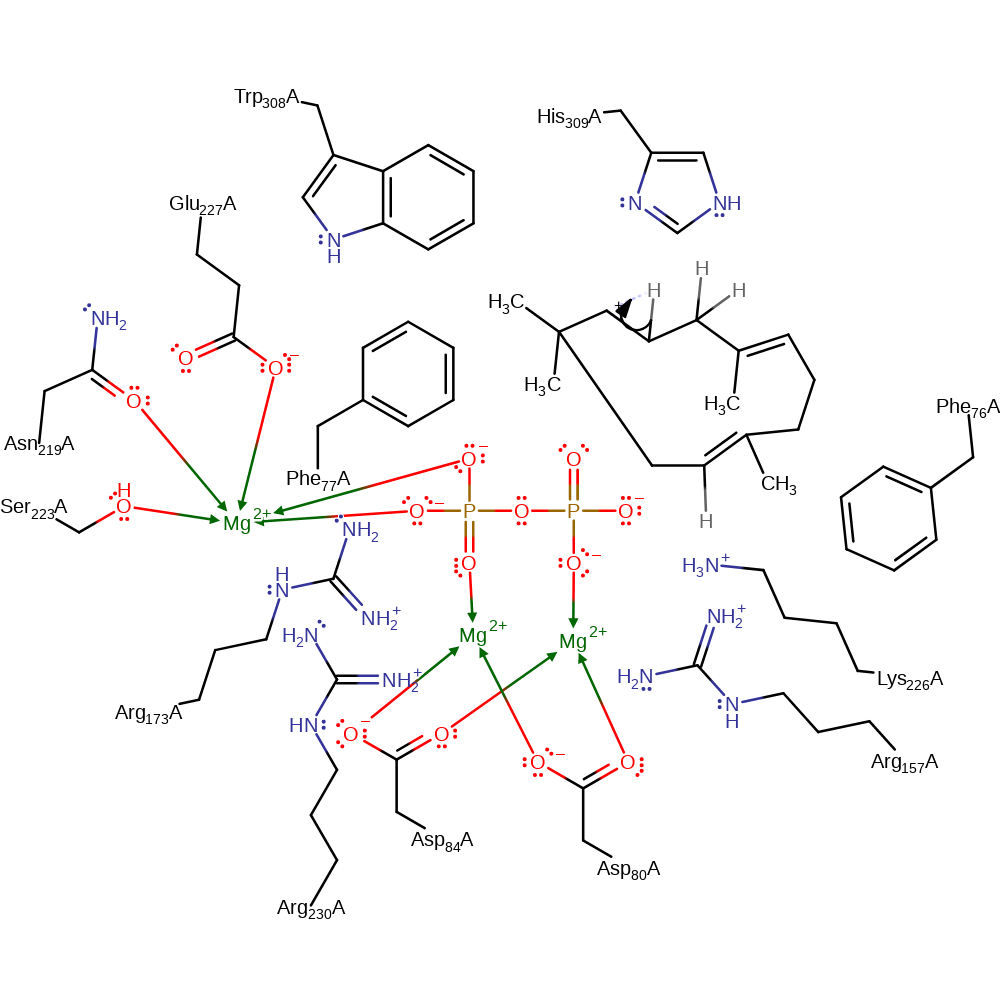
Step 1. The substrate undergoes heterolysis. The diphosphate product remains associated with the active site, and the cabocation is delocalised over the three terminal carbon atoms of the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Phe76A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe77A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Asn219A | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Trp308A | van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, overall reactant used, charge delocalisation, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation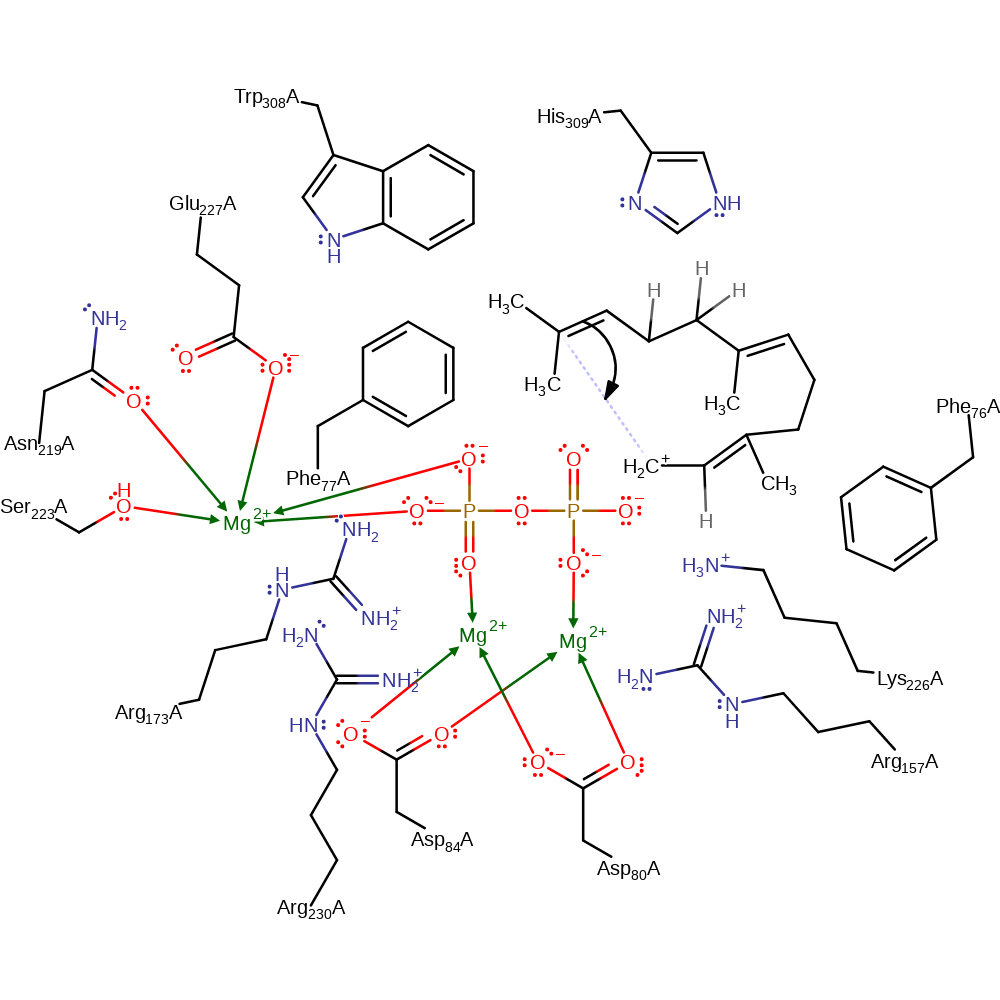
Step 2. The terminal double bond adds to the terminal carbocation in an intramolecular electrophilic addition resulting in a cyclic intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Asn219A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, cyclisation, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His309A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
hydride transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His309A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, cyclisation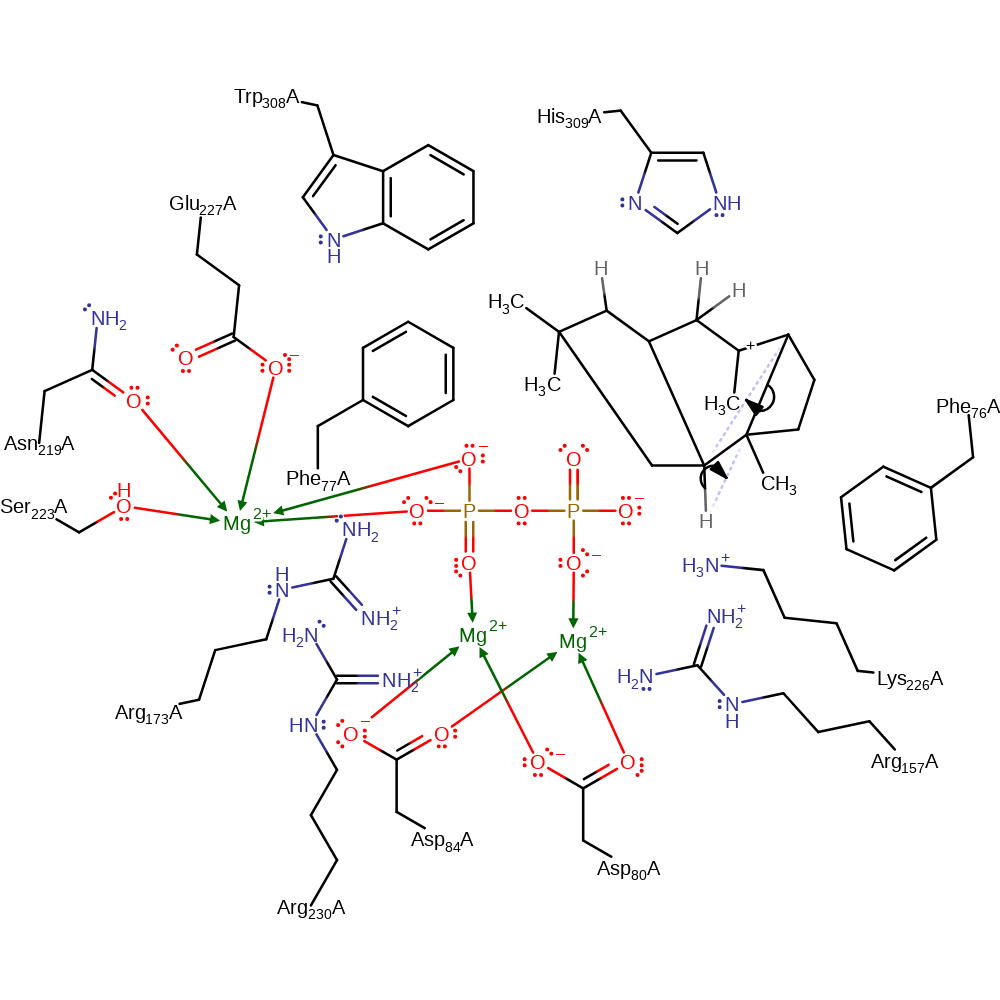
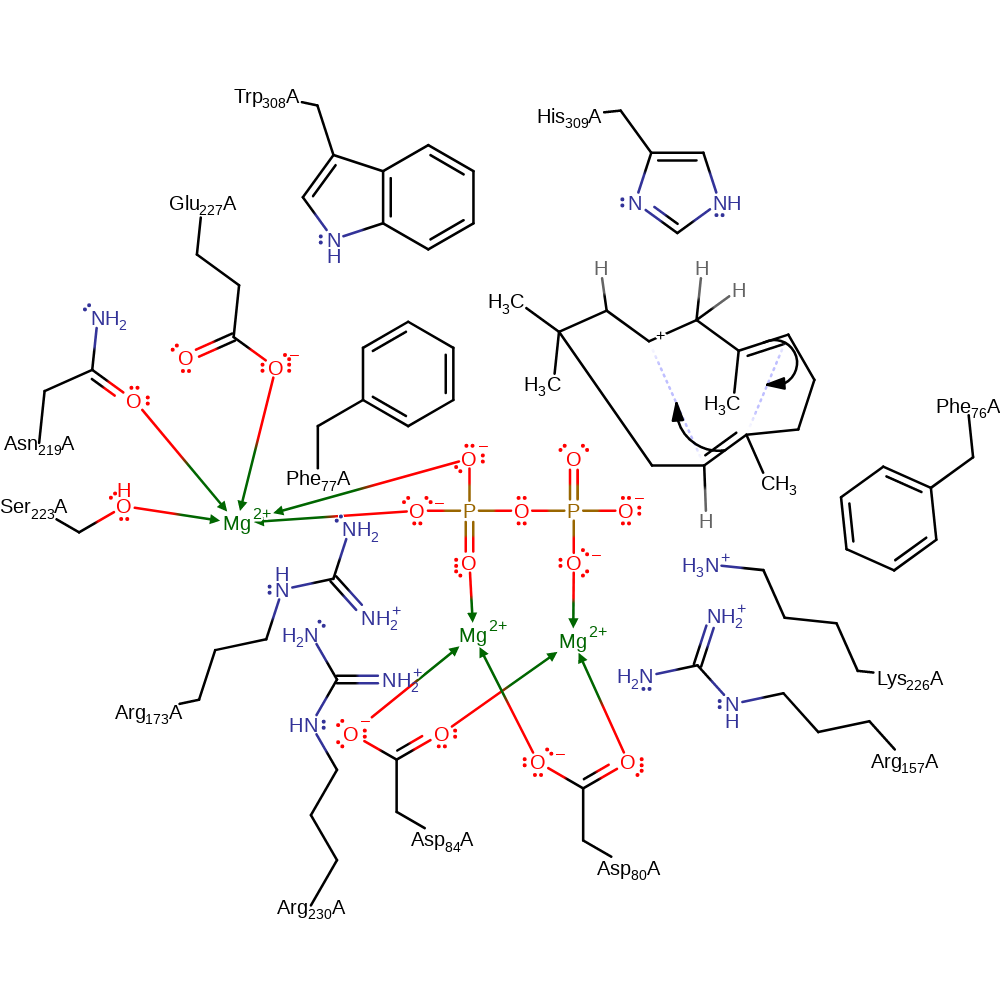
Step 5. The substrate undergoes a dyotropic rearrangement. This is an unusual elementary step in this terpene cyclisation, especially because the cationic centre seems to be not involved and rather plays a role as a spectator, but certainly the neighbouring migrating C–C-bond of the cyclobutane is substantially weakened and thus more reactive due to the presence of the cation.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn219A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His309A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, intramolecular rearrangement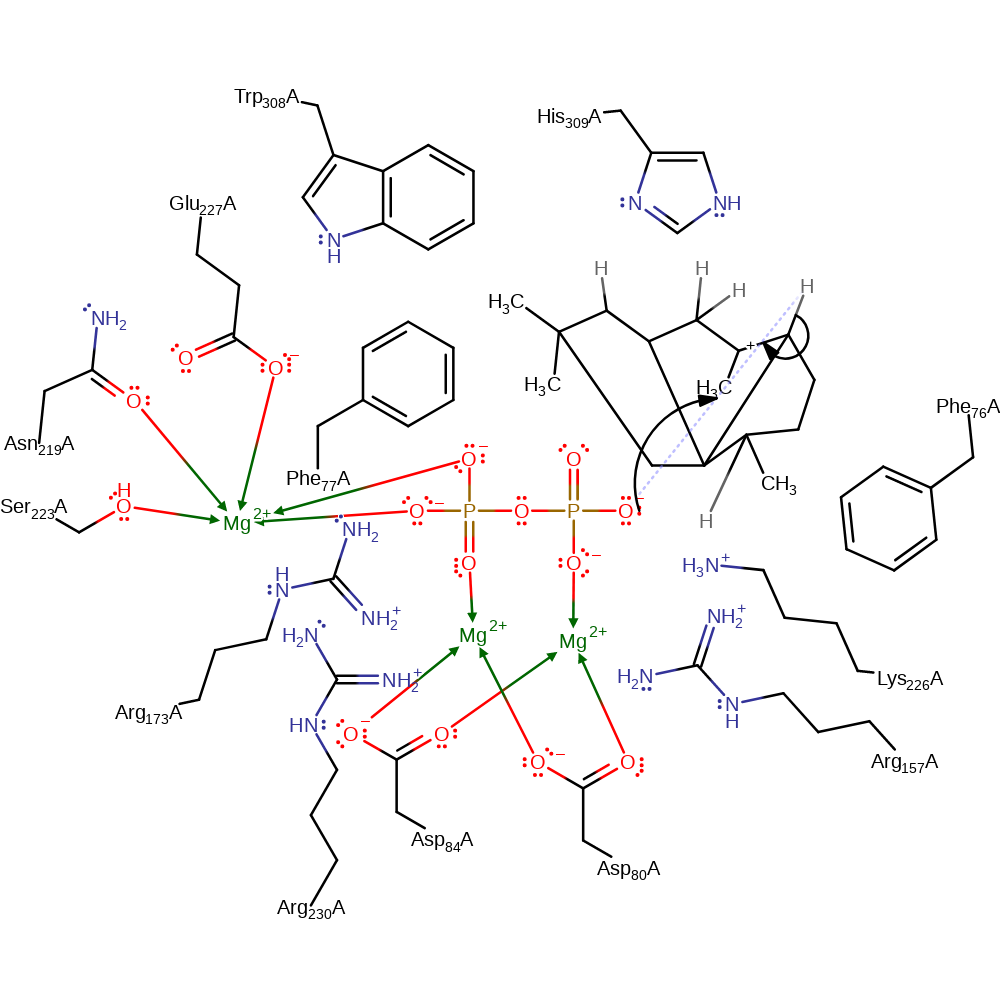
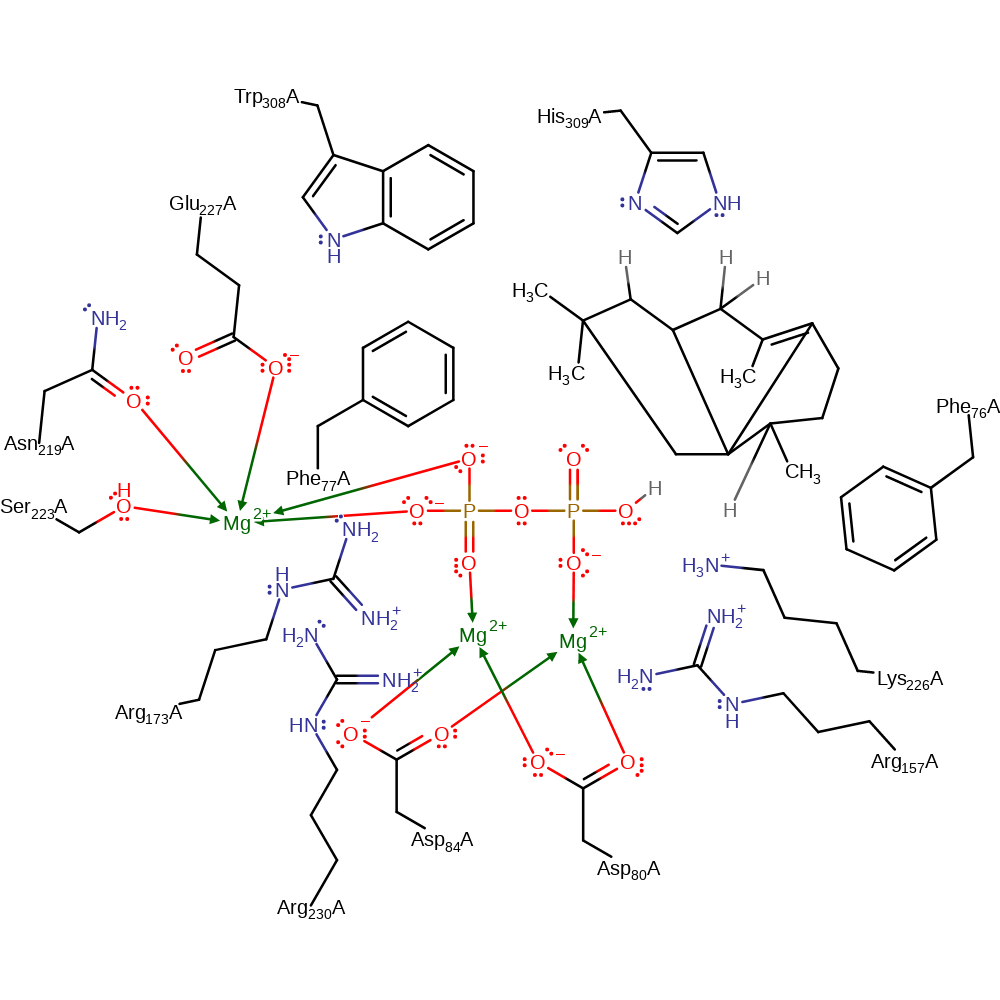
Step 6. The phosphate acts as a general acid/base, abstracting the proton from the final intermediate and generating the final product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His309A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular eliminationIntroduction
Farnesyl diphosphate is thought to undergo ionisation and electrophilic attack of the incipient allyl cation pyrophosphate pair on the distal pi bond (see PMID:9295272). Metal-triggered substrate ionisation initiates catalysis. The initial step in the reaction is likely to be a cyclisation of farnesyl diphosphate to form humulene. The most likely catalytic base is thought to be the phosphate anion.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ps1) | ||
| Ser223, Glu227, Asn219 | Ser223A, Glu227A, Asn219A | Forms part of the magnesium 3 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Trp308, His309, Phe76, Phe77 | Trp308A, His309A, Phe76A, Phe77A | F76 and F77 are well placed so as to interact with positive charge at C-1, C-2, and C-3 of the farnesyl residue and derived intermediates and act to stabilise these charges through quadrupole-charge interactions. | van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230, Arg157, Arg173, Lys226 | Arg230A, Arg157A, Arg173A, Lys226A | Stabilises the pyrophosphate leaving group. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84, Asp80 | Asp84A, Asp80A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 and 2 binding sites. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, overall reactant used, charge delocalisation, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, intramolecular electrophilic addition, cyclisation, hydride transfer, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Lesburg CA et al. (1997), Science, 277, 1820-1824. Crystal Structure of Pentalenene Synthase: Mechanistic Insights on Terpenoid Cyclization Reactions in Biology. DOI:10.1126/science.277.5333.1820. PMID:9295272.
- Pemberton TA et al. (2016), J Antibiot (Tokyo), 69, 486-493. General base-general acid catalysis by terpenoid cyclases. DOI:10.1038/ja.2016.39. PMID:27072285.
- Zu L et al. (2012), J Am Chem Soc, 134, 11369-11371. Effect of Isotopically Sensitive Branching on Product Distribution for Pentalenene Synthase: Support for a Mechanism Predicted by Quantum Chemistry. DOI:10.1021/ja3043245. PMID:22738258.
- Seemann M et al. (2002), J Am Chem Soc, 124, 7681-7689. Pentalenene synthase. Analysis of active site residues by site-directed mutagenesis. PMID:12083921.
- Seemann M et al. (1999), J Am Chem Soc, 121, 591-592. Pentalenene Synthase. Histidine-309 Is Not Required for Catalytic Activity. DOI:10.1021/ja983657h.
- Cane DE et al. (1994), Biochemistry, 33, 5846-5857. Pentalenene synthase. Purification, molecular cloning, sequencing, and high-level expression in Escherichia coli of a terpenoid cyclase from Streptomyces UC5319. PMID:8180213.
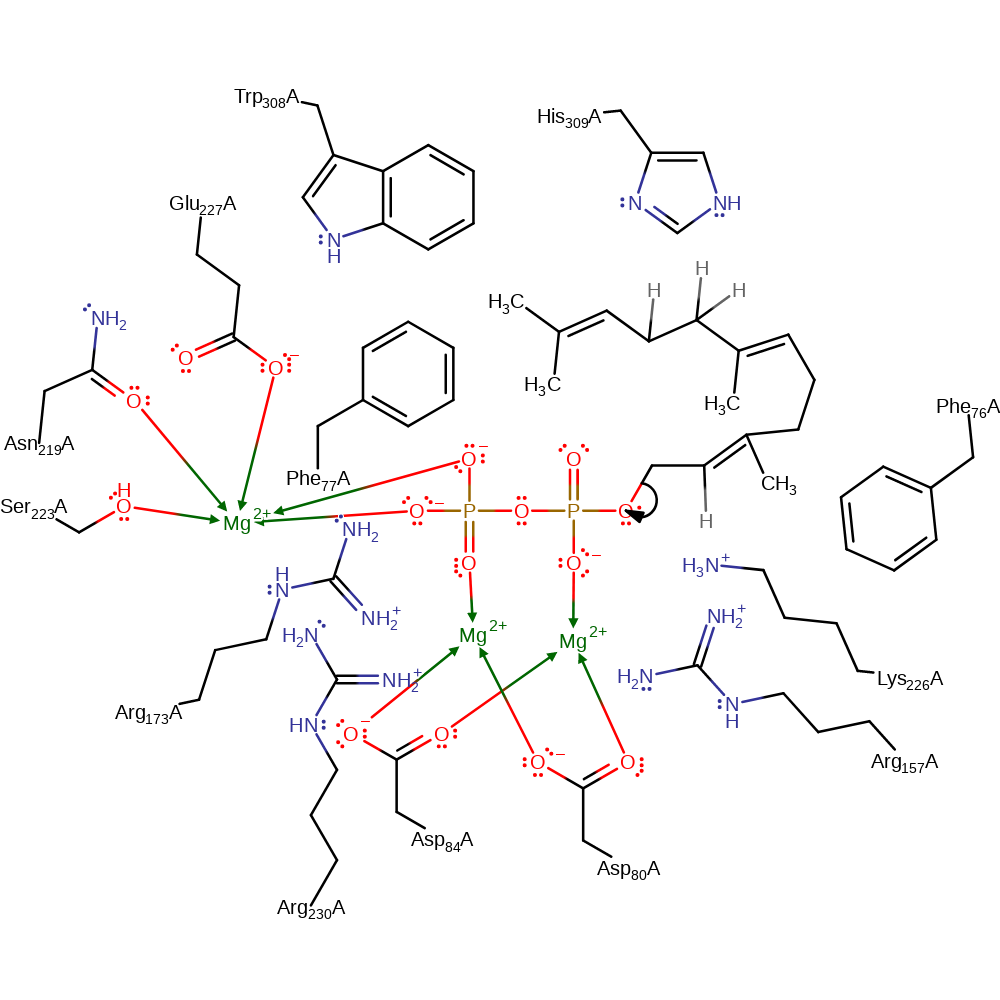
Step 1. The substrate undergoes heterolysis. The diphosphate product remains associated with the active site, and the cabocation is delocalised over the three terminal carbon atoms of the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe76A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe77A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Asn219A | steric role, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Trp308A | van der waals interaction |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, overall reactant used, charge delocalisation, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation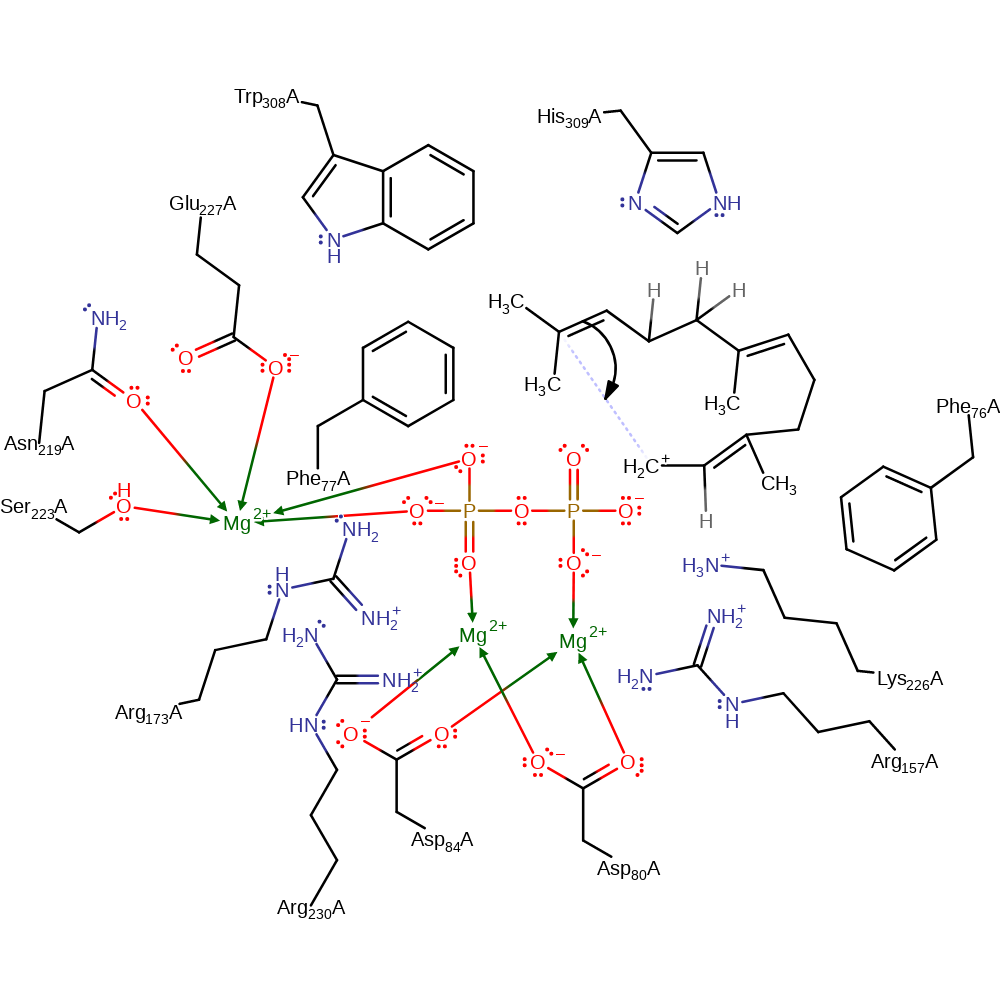
Step 2. The terminal double bond adds to the terminal carbocation in an intramolecular electrophilic addition resulting in a cyclic intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Asn219A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, cyclisation, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His309A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Asn219A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, hydride transfer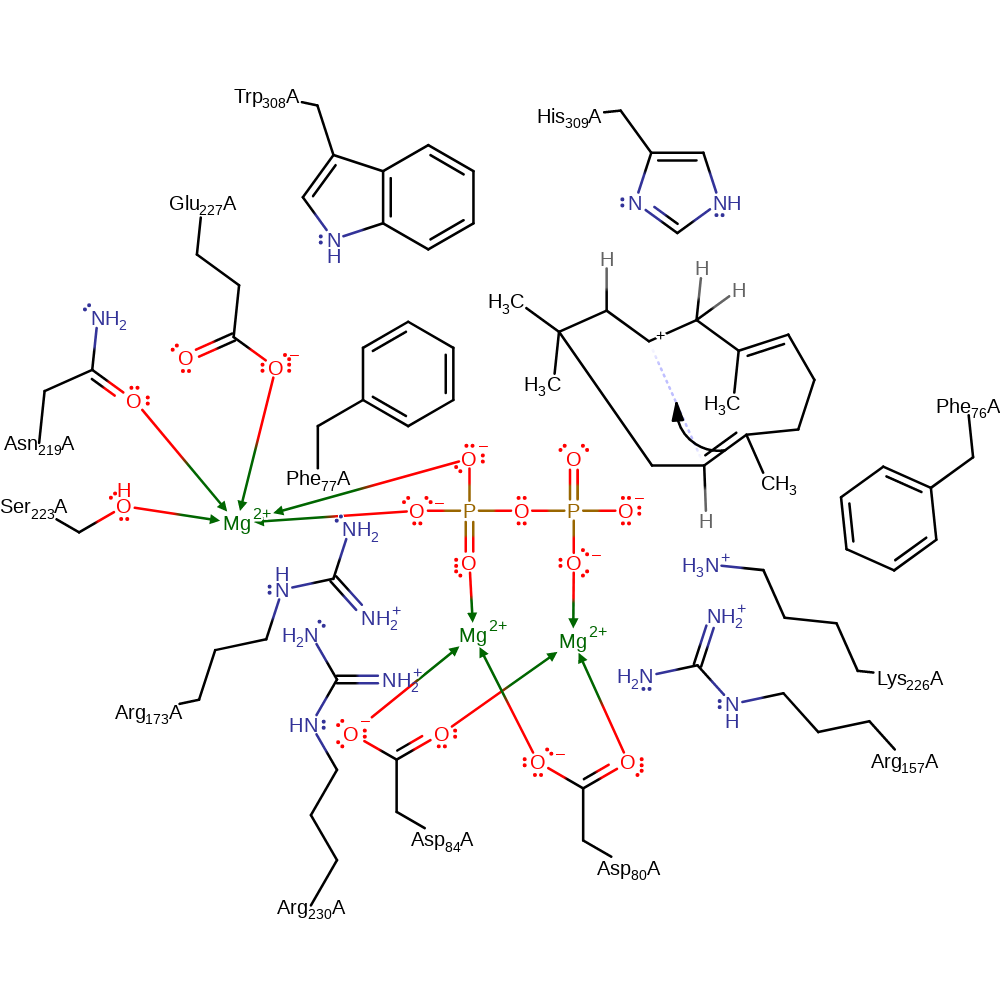
Step 4. In a second intramolecular electrophilic addition, a double bond adds across the cycle forming a five membered ring and a new carbocation.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His309A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe76A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe77A | van der waals interaction |
| Asn219A | polar/non-polar interaction |
| Trp308A | van der waals interaction |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, cyclisation, intermediate formation
Step 5. In a third intramolecular electrophilic addition, the remaining double bond adds across the cycle to form the three five membered ring motif of pentalenene, this also causes a [1,2]-hydride shift and the carbocation shifting to a different carbon atom
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Asn219A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, hydride transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic addition, cyclisation, intermediate formation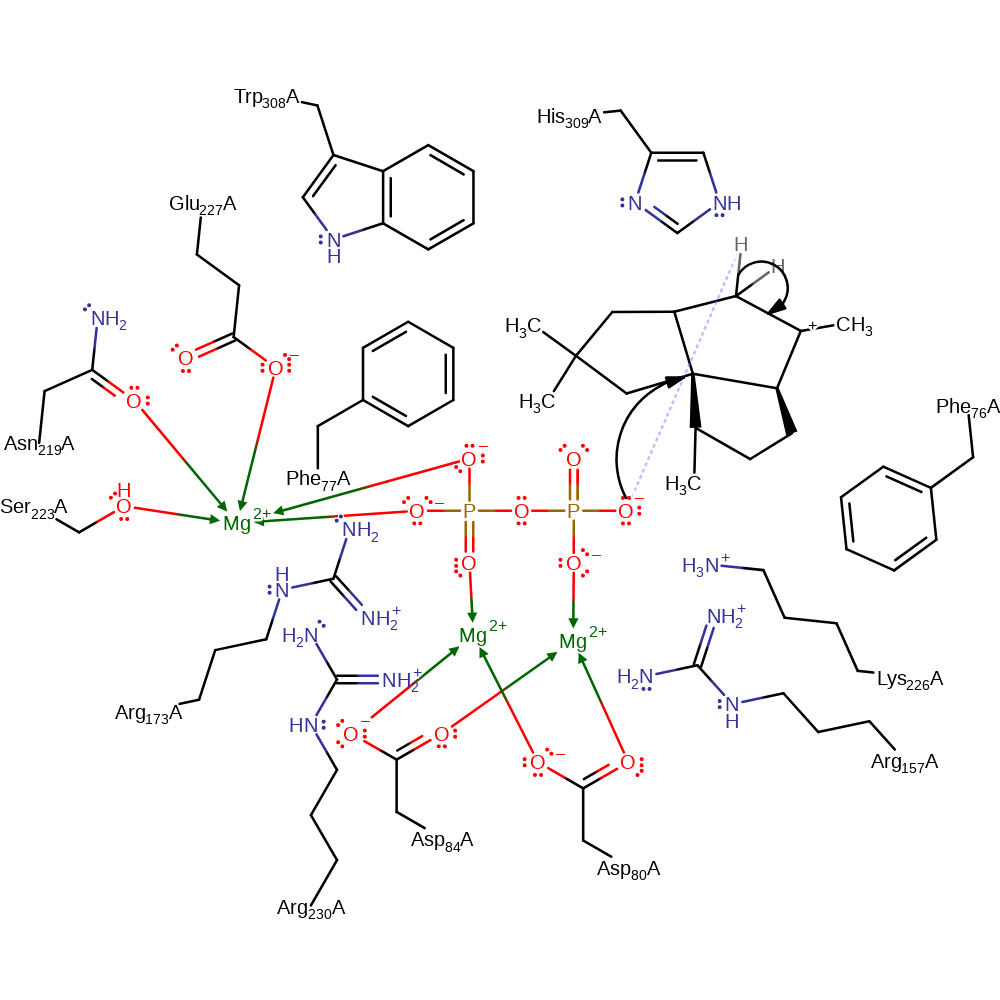
Step 6. The phosphate group deprotonates the carbon adjacent to the new carbocation, forming the final double bond of pentalenene.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His309A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Phe76A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Phe77A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Asn219A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Trp308A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Arg157A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg173A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg230A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asp80A | metal ligand |
| Glu227A | metal ligand |
| Asn219A | metal ligand |
| Ser223A | metal ligand |



 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: