 |
PDBsum entry 7d1h
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.2.5
- glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-terminal L-glutaminyl-[peptide] = N-terminal 5-oxo-L-prolyl-[peptide] + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
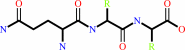 L-glutaminyl-peptide
L-glutaminyl-peptide
|
=
|
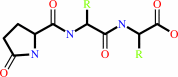 5-oxoprolyl-peptide
5-oxoprolyl-peptide
|
+
|
NH(3)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
433:166960
(2021)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A Unique Carboxylic-Acid Hydrogen-Bond Network (CAHBN) Confers Glutaminyl Cyclase Activity on M28 Family Enzymes.
|
|
K.F.Huang,
J.S.Huang,
M.L.Wu,
W.L.Hsieh,
K.C.Hsu,
H.L.Hsu,
T.P.Ko,
A.H.Wang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Proteins with sequence or structure similar to those of di-Zn exopeptidases are
usually classified as the M28-family enzymes, including the mammalian-type
glutaminyl cyclases (QCs). QC catalyzes protein N-terminal pyroglutamate
formation, a posttranslational modification important under many physiological
and pathological conditions, and is a drug target for treating neurodegenerative
diseases, cancers and inflammatory disorders. Without functional
characterization, mammalian QCs and their orthologs remain indistinguishable at
the sequence and structure levels from other M28-family proteins, leading to few
reported QCs. Here, we show that a low-barrier carboxylic-acid hydrogen-bond
network (CAHBN) is required for QC activity and discriminates QCs from
M28-family peptidases. We demonstrate that the CAHBN-containing M28 peptidases
deposited in the PDB are indeed QCs. Our analyses identify several thousands of
QCs from the three domains of life, and we enzymatically and structurally
characterize several. For the first time, the interplay between a CAHBN and the
binuclear metal-binding center of mammalian QCs is made clear. We found that the
presence or absence of CAHBN is a key discriminator for the formation of either
the mono-Zn QCs or the di-Zn exopeptidases. Our study helps explain the possible
roles of QCs in life.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

