 |
PDBsum entry 3ae7

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3ae7
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 613 a.a.
613 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 239 a.a.
239 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 138 a.a.
138 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 102 a.a.
102 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of porcine heart mitochondrial complex ii bound with 2-iodo-n-(3-isopropoxy-phenyl)-benzamide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein subunit, mitochondrial. Chain: a. Synonym: flavoprotein subunit of complex ii, fp. Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur subunit, mitochondrial. Chain: b. Synonym: iron-sulfur subunit of complex ii, ip. Succinate dehydrogenase cytochrome b560 subunit,
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sus scrofa. Pig. Organism_taxid: 9823. Organ: heart. Tissue: muscle. Tissue: muscle
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.62Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.259
|
R-free:
|
0.305
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Harada,T.Sasaki,M.Shindo,Y.Kido,D.K.Inaoka,J.Omori,A.Osanai, K.Sakamoto,J.Mao,S.Matsuoka,M.Inoue,T.Honma,A.Tanaka,K.Kita
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
D.K.Inaoka
et al.
(2015).
Structural Insights into the Molecular Design of Flutolanil Derivatives Targeted for Fumarate Respiration of Parasite Mitochondria.
Int J Mol Sci,
16,
15287-15308.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Feb-10
|
Release date:
|
09-Feb-11
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q0QF01
(SDHA_PIG) -
Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein subunit, mitochondrial from Sus scrofa
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
664 a.a.
613 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
Q007T0
(SDHB_PIG) -
Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur subunit, mitochondrial from Sus scrofa
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
280 a.a.
239 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.1.1.5.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.1.3.5.1
- succinate dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a quinone + succinate = fumarate + a quinol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
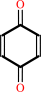 quinone
quinone
|
+
|
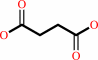 succinate
succinate
|
=
|
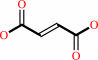 fumarate
fumarate
|
+
|
quinol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD; Iron-sulfur
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
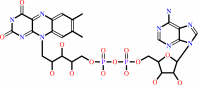 FAD
FAD
|
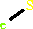 Iron-sulfur
Iron-sulfur
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Int J Mol Sci
16:15287-15308
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Insights into the Molecular Design of Flutolanil Derivatives Targeted for Fumarate Respiration of Parasite Mitochondria.
|
|
D.K.Inaoka,
T.Shiba,
D.Sato,
E.O.Balogun,
T.Sasaki,
M.Nagahama,
M.Oda,
S.Matsuoka,
J.Ohmori,
T.Honma,
M.Inoue,
K.Kita,
S.Harada.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Recent studies on the respiratory chain of Ascaris suum showed that the
mitochondrial NADH-fumarate reductase system composed of complex I, rhodoquinone
and complex II plays an important role in the anaerobic energy metabolism of
adult A. suum. The system is the major pathway of energy metabolism for
adaptation to a hypoxic environment not only in parasitic organisms, but also in
some types of human cancer cells. Thus, enzymes of the pathway are potential
targets for chemotherapy. We found that flutolanil is an excellent inhibitor for
A. suum complex II (IC50 = 0.058 μM) but less effectively inhibits homologous
porcine complex II (IC50 = 45.9 μM). In order to account for the specificity of
flutolanil to A. suum complex II from the standpoint of structural biology, we
determined the crystal structures of A. suum and porcine complex IIs binding
flutolanil and its derivative compounds. The structures clearly demonstrated key
interactions responsible for its high specificity to A. suum complex II and
enabled us to find analogue compounds, which surpass flutolanil in both potency
and specificity to A. suum complex II. Structures of complex IIs binding these
compounds will be helpful to accelerate structure-based drug design targeted for
complex IIs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| | |

