 |
PDBsum entry 1kp2

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.4.5
- argininosuccinate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Urea Cycle and Arginine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-citrulline + L-aspartate + ATP = 2-(N(omega)-L-arginino)succinate + AMP + diphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-citrulline
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
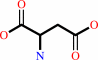 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
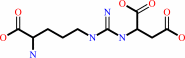 2-(N(omega)-L-arginino)succinate
2-(N(omega)-L-arginino)succinate
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
277:13074-13081
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Substrate induced conformational changes in argininosuccinate synthetase.
|
|
C.T.Lemke,
P.L.Howell.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Argininosuccinate synthetase (AS) is the rate-limiting enzyme of both the urea
and arginine-citrulline cycles. In mammals, deficiency of AS leads to
citrullinemia, a debilitating and often fatal autosomal recessive urea cycle
disorder, whereas its overexpression for sustained nitric oxide production via
the arginine-citrulline cycle leads to the potentially fatal hypotension
associated with septic and cytokine-induced circulatory shock. The crystal
structures of Escherichia coli argininosuccinate synthetase (EAS) in complex
with ATP and with ATP and citrulline have been determined at 2.0-A resolution.
These are the first EAS structures to be solved in the presence of a nucleotide
substrate and clearly identify the residues that interact with both ATP and
citrulline. Two distinct conformations are revealed for ATP, both of which are
believed to be catalytically relevant. In addition, comparisons of these EAS
structures with those of the apoenzyme and EAS complexed with aspartate and
citrulline (Lemke, C. T., and Howell, P. L. (2001) Structure (Lond.) 9,
1153-1164) provide structural evidence of ATP-induced conformational changes in
the nucleotide binding domain. Combined, these structures also provide
structural explanations of some of the observed kinetic properties of the enzyme
and have enabled a detailed enzymatic mechanism of AS catalysis to be proposed.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. The argininosuccinate synthetase mechanism. Step
1, activated citrulline-adenylate is formed, releasing inorganic
pyrophosphate. Step 2, nucleophilic attack by aspartate amino
group forms argininosuccinate and releases AMP.
|
 |
Figure 8.
Fig. 8. ATP conformations. The conformations of ATP
observed in lysyl tRNA synthetase (a), EAS ( b), and NAD^+
synthetase (c) are shown. The dashed lines are drawn between the
 -phosphate
of ATP and nucleophile. -phosphate
of ATP and nucleophile.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2002,
277,
13074-13081)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.R.Guerreiro,
C.Lameu,
E.F.Oliveira,
C.F.Klitzke,
R.L.Melo,
E.Linares,
O.Augusto,
J.W.Fox,
I.Lebrun,
S.M.Serrano,
and
A.C.Camargo
(2009).
Argininosuccinate synthetase is a functional target for a snake venom anti-hypertensive peptide: role in arginine and nitric oxide production.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
20022-20033.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Karlberg,
R.Collins,
S.van den Berg,
A.Flores,
M.Hammarström,
M.Högbom,
L.Holmberg Schiavone,
and
J.Uppenberg
(2008).
Structure of human argininosuccinate synthetase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
64,
279-286.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kuratani,
Y.Yoshikawa,
Y.Bessho,
K.Higashijima,
T.Ishii,
R.Shibata,
S.Takahashi,
K.Yutani,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2007).
Structural basis of the initial binding of tRNA(Ile) lysidine synthetase TilS with ATP and L-lysine.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
1642-1653.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Curis,
I.Nicolis,
C.Moinard,
S.Osowska,
N.Zerrouk,
S.Bénazeth,
and
L.Cynober
(2005).
Almost all about citrulline in mammals.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
29,
177-205.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ikeuchi,
A.Soma,
T.Ote,
J.Kato,
Y.Sekine,
and
T.Suzuki
(2005).
molecular mechanism of lysidine synthesis that determines tRNA identity and codon recognition.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
19,
235-246.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Husson,
C.Brasse-Lagnel,
A.Fairand,
S.Renouf,
and
A.Lavoinne
(2003).
Argininosuccinate synthetase from the urea cycle to the citrulline-NO cycle.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
1887-1899.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Z.Gao,
K.Kobayashi,
A.Tabata,
H.Tsuge,
M.Iijima,
T.Yasuda,
H.S.Kalkanoglu,
A.Dursun,
A.Tokatli,
T.Coskun,
F.K.Trefz,
D.Skladal,
H.Mandel,
J.Seidel,
S.Kodama,
S.Shirane,
T.Ichida,
S.Makino,
M.Yoshino,
J.H.Kang,
M.Mizuguchi,
B.A.Barshop,
S.Fuchinoue,
S.Seneca,
S.Zeesman,
I.Knerr,
M.Rodés,
P.Wasant,
I.Yoshida,
L.De Meirleir,
M.Abdul Jalil,
L.Begum,
M.Horiuchi,
N.Katunuma,
S.Nakagawa,
and
T.Saheki
(2003).
Identification of 16 novel mutations in the argininosuccinate synthetase gene and genotype-phenotype correlation in 38 classical citrullinemia patients.
|
| |
Hum Mutat,
22,
24-34.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Lemke,
G.D.Smith,
and
P.L.Howell
(2002).
S-SAD, Se-SAD and S/Se-SIRAS using Cu Kalpha radiation: why wait for synchrotron time?
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
2096-2101.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

