 |
PDBsum entry 1jdv

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase complexed with adenosine and sulfate ion
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: mta phosphorylase. Mtap. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sulfolobus solfataricus. Organism_taxid: 2287. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Hexamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.218
|
R-free:
|
0.246
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.C.Appleby,I.I.Mathews,M.Porcelli,G.Cacciapuoti,S.E.Ealick
|
Key ref:

|
 |
T.C.Appleby
et al.
(2001).
Three-dimensional structure of a hyperthermophilic 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase from Sulfolobus solfataricus.
J Biol Chem,
276,
39232-39242.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
15-Jun-01
|
Release date:
|
26-Oct-01
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P50389
(PNPH_SULSO) -
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Saccharolobus solfataricus (strain ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
236 a.a.
227 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.1
- purine-nucleoside phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a purine D-ribonucleoside + phosphate = a purine nucleobase + alpha- D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
2.
|
a purine 2'-deoxy-D-ribonucleoside + phosphate = a purine nucleobase + 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
purine D-ribonucleoside
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
purine nucleobase
|
+
|
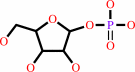 alpha- D-ribose 1-phosphate
alpha- D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
purine 2'-deoxy-D-ribonucleoside
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
purine nucleobase
|
+
|
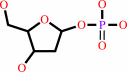 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.28
- S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine + phosphate = 5-(methylsulfanyl)-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate + adenine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
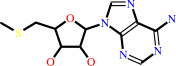 S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine
S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 85.71% similarity
|
=
|
5-(methylsulfanyl)-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
+
|
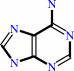 adenine
adenine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
276:39232-39242
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Three-dimensional structure of a hyperthermophilic 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase from Sulfolobus solfataricus.
|
|
T.C.Appleby,
I.I.Mathews,
M.Porcelli,
G.Cacciapuoti,
S.E.Ealick.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase from Sulfolobus
solfataricus (SsMTAP) has been determined alone, as ternary complexes with
sulfate plus substrates 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine, adenosine, or
guanosine, or with the noncleavable substrate analog Formycin B and as binary
complexes with phosphate or sulfate alone. The structure of unliganded SsMTAP
was refined at 2.5-A resolution and the structures of the complexes were refined
at resolutions ranging from 1.6 to 2.0 A. SsMTAP is unusual both for its broad
substrate specificity and for its extreme thermal stability. The hexameric
structure of SsMTAP is similar to that of purine-nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP)
from Escherichia coli, however, only SsMTAP accepts
5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine as a substrate. The active site of SsMTAP is
similar to that of E. coli PNP with 13 of 18 nearest residues being identical.
The main differences are at Thr(89), which corresponds to serine in E. coli PNP,
and Glu(163), which corresponds to proline in E. coli PNP. In addition, a water
molecule is found near the purine N-7 position in the guanosine complex of
SsMTAP. Thr(89) is near the 5'-position of the nucleoside and may account for
the ability of SsMTAP to accept either hydrophobic or hydrophilic substituents
in that position. Unlike E. coli PNP, the structures of SsMTAP reveal a
substrate-induced conformational change involving Glu(163). This residue is
located at the interface between subunits and swings in toward the active site
upon nucleoside binding. The high-resolution structures of SsMTAP suggest that
the transition state is stabilized in different ways for 6-amino versus 6-oxo
substrates. SsMTAP has optimal activity at 120 degrees C and retains full
activity after 2 h at 100 degrees C. Examination of the three-dimensional
structure of SsMTAP suggests that unlike most thermophilic enzymes, disulfide
linkages play a key in role in its thermal stability.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 5.
Fig. 5. Active site drawing of the phosphate-binding
site. a, interaction observed when sulfate occupies the site. b,
interactions observed when phosphate occupies the binding site.
The molecule of Tris is observed only with phosphate. Hydrogen
bonds are shown as dashed lines with the corresponding
donor-acceptor distance labeled. Residues belongs to the
neighboring subunit are designated with an asterisk (*).
|
 |
Figure 8.
Fig. 8. Active site drawing of the SsMTAP FMB-sulfate
complex. a, the binding geometry for FMB. b, the binding
geometry for the E. coli PNP-FMB complex for comparison. The
coordinates were taken from PDB entry code 1A69 (14). Hydrogen
bonds are shown as dashed lines with the corresponding
donor-acceptor distance labeled. Residues belongs to the
neighboring subunit are designated with an asterisk (*).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2001,
276,
39232-39242)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.Parveen,
and
K.A.Cornell
(2011).
Methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase, a critical enzyme for bacterial metabolism.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
79,
7.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.N.Kang,
Y.Zhang,
P.W.Allan,
W.B.Parker,
J.W.Ting,
C.Y.Chang,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2010).
Structure of grouper iridovirus purine nucleoside phosphorylase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
155-162.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Cacciapuoti,
I.Peluso,
F.Fuccio,
and
M.Porcelli
(2009).
Purine nucleoside phosphorylases from hyperthermophilic Archaea require a CXC motif for stability and folding.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
5799-5805.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.K.Siu,
J.E.Lee,
J.R.Sufrin,
B.A.Moffatt,
M.McMillan,
K.A.Cornell,
C.Isom,
and
P.L.Howell
(2008).
Molecular determinants of substrate specificity in plant 5'-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
378,
112-128.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Grillo,
and
S.Colombatto
(2008).
S-adenosylmethionine and its products.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
34,
187-193.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Porcelli,
L.Concilio,
I.Peluso,
A.Marabotti,
A.Facchiano,
and
G.Cacciapuoti
(2008).
Pyrimidine-specific ribonucleoside hydrolase from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus--biochemical characterization and homology modeling.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
1900-1914.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Li,
X.Jiang,
H.Li,
and
D.Ren
(2008).
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Pseudoalteromonas sp. Bsi590: molecular cloning, gene expression and characterization of the recombinant protein.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
12,
325-333.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.H.Yeang,
and
D.Haussler
(2007).
Detecting coevolution in and among protein domains.
|
| |
PLoS Comput Biol,
3,
e211.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Schnick,
M.A.Robien,
A.M.Brzozowski,
E.J.Dodson,
G.N.Murshudov,
L.Anderson,
J.R.Luft,
C.Mehlin,
W.G.Hol,
J.A.Brannigan,
and
A.J.Wilkinson
(2005).
Structures of Plasmodium falciparum purine nucleoside phosphorylase complexed with sulfate and its natural substrate inosine.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1245-1254.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Cacciapuoti,
S.Forte,
M.A.Moretti,
A.Brio,
V.Zappia,
and
M.Porcelli
(2005).
A novel hyperthermostable 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
1886-1899.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Eichler,
and
M.W.Adams
(2005).
Posttranslational protein modification in Archaea.
|
| |
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,
69,
393-425.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Usui,
S.Katayama,
M.Kanamori-Katayama,
C.Ogawa,
C.Kai,
M.Okada,
J.Kawai,
T.Arakawa,
P.Carninci,
M.Itoh,
K.Takio,
M.Miyano,
S.Kidoaki,
T.Matsuda,
Y.Hayashizaki,
and
H.Suzuki
(2005).
Protein-protein interactions of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
6,
R98.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Beeby,
B.D.O'Connor,
C.Ryttersgaard,
D.R.Boutz,
L.J.Perry,
and
T.O.Yeates
(2005).
The genomics of disulfide bonding and protein stabilization in thermophiles.
|
| |
PLoS Biol,
3,
e309.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.B.Bertin,
S.P.Lozzi,
J.K.Howell,
G.Restrepo-Cadavid,
D.Neves,
A.R.Teixeira,
M.V.de Sousa,
S.J.Norris,
and
J.M.Santana
(2005).
The thermophilic, homohexameric aminopeptidase of Borrelia burgdorferi is a member of the M29 family of metallopeptidases.
|
| |
Infect Immun,
73,
2253-2261.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Bu,
E.C.Settembre,
M.H.el Kouni,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2005).
Structural basis for inhibition of Escherichia coli uridine phosphorylase by 5-substituted acyclouridines.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
863-872.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Cacciapuoti,
M.A.Moretti,
S.Forte,
A.Brio,
L.Camardella,
V.Zappia,
and
M.Porcelli
(2004).
Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. Mechanism of the reaction and assignment of disulfide bonds.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
4834-4844.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Roovers,
J.Wouters,
J.M.Bujnicki,
C.Tricot,
V.Stalon,
H.Grosjean,
and
L.Droogmans
(2004).
A primordial RNA modification enzyme: the case of tRNA (m1A) methyltransferase.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
32,
465-476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
S.E.Cottet,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2004).
Structure of Escherichia coli AMP nucleosidase reveals similarity to nucleoside phosphorylases.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
1383-1394.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

