 |
PDBsum entry 1ay0

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.2.1.1
- transketolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-sedoheptulose 7-phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate = aldehydo-D- ribose 5-phosphate + D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
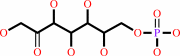 D-sedoheptulose 7-phosphate
D-sedoheptulose 7-phosphate
|
+
|
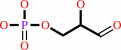 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
=
|
aldehydo-D- ribose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
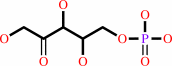 D-xylulose 5-phosphate
D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
TPP)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
36:15643-15649
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Identification of catalytically important residues in yeast transketolase.
|
|
C.Wikner,
U.Nilsson,
L.Meshalkina,
C.Udekwu,
Y.Lindqvist,
G.Schneider.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The possible roles of four histidine residues in the active site of yeast
transketolase were examined by site-directed mutagenesis. Replacement of the
invariant His69 with alanine yielded a mutant enzyme with 1.5% of the specific
activity of the wild-type enzyme and with an increased KM for the donor. This
residue is located at the bottom of the substrate cleft close to the C1 hydroxyl
group of the donor substrate, and the side chain of His69 might be required for
recognition of this hydroxyl group and possibly for maintenance of the proper
orientation of the reaction intermediate, (alpha, beta-dihydroxyethyl)thiamin
diphosphate. Amino acid replacements of His481 by alanine, serine, and glutamine
resulted in mutant enzymes with significantly increased KM values for the donor
substrate and specific activities of 4.4%, 1.9%, and 5.5% of the wild-type
enzyme. The kinetic data suggest that this residue, although close to the C2
carbonyl oxygen of the substrate, is not absolutely required for stabilization
of the negative charge that develops at this oxygen in the transition state.
This points toward the 4'-NH2 group of the pyrimidine ring of thiamin
diphosphate as the major source of charge stabilization. Mutations at positions
His30 and His263 result in mutant enzymes severely impaired in catalytic
activity (1.5% and less of the activity of wild-type transketolase). The KM
value for the donor substrate was increased for the His30Ala mutant but remained
unchanged in the His263Ala enzyme. The side chains of both residues interact
with the C3 hydroxyl group of the donor substrate, and the results indicate that
the two residues act in concert during proton abstraction of the C3 hydroxyl
proton during catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Costelloe,
J.M.Ward,
and
P.A.Dalby
(2008).
Evolutionary Analysis of the TPP-Dependent Enzyme Family.
|
| |
J Mol Evol,
66,
36-49.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Domain,
X.R.Bina,
and
S.B.Levy
(2007).
Transketolase A, an enzyme in central metabolism, derepresses the marRAB multiple antibiotic resistance operon of Escherichia coli by interaction with MarR.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
66,
383-394.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kale,
P.Arjunan,
W.Furey,
and
F.Jordan
(2007).
A dynamic loop at the active center of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E1 component modulates substrate utilization and chemical communication with the E2 component.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
28106-28116.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.A.Sevostyanova,
O.N.Solovjeva,
and
G.A.Kochetov
(2006).
Two methods for determination of transketolase activity.
|
| |
Biochemistry (Mosc),
71,
560-562.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.V.Kovina,
A.De Kok,
I.A.Sevostyanova,
L.S.Khailova,
N.V.Belkina,
and
G.A.Kochetov
(2004).
The molecular origin of the thiamine diphosphate-induced spectral bands of ThDP-dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
338-345.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mahato,
D.De,
D.Dutta,
M.Kundu,
S.Bhattacharya,
M.T.Schiavone,
and
S.K.Bhattacharya
(2004).
Potential use of sugar binding proteins in reactors for regeneration of CO2 fixation acceptor D-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate.
|
| |
Microb Cell Fact,
3,
7.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Brautaset,
Ã.˜.M.Jakobsen M,
M.C.Flickinger,
S.Valla,
and
T.E.Ellingsen
(2004).
Plasmid-dependent methylotrophy in thermotolerant Bacillus methanolicus.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
186,
1229-1238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.N.Crowell,
C.E.Packard,
C.A.Pierson,
J.L.Giner,
B.P.Downes,
and
S.N.Chary
(2003).
Identification of an allele of CLA1 associated with variegation in Arabidopsis thaliana.
|
| |
Physiol Plant,
118,
29-37.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.M.Hahn,
L.M.Eubanks,
C.A.Testa,
B.S.Blagg,
J.A.Baker,
and
C.D.Poulter
(2001).
1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase, the gene product of open reading frame (ORF) 2816 and ORF 2895 in Rhodobacter capsulatus.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
183,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.J.Baker,
J.A.Dorocke,
R.A.Harris,
and
D.E.Timm
(2001).
The crystal structure of yeast thiamin pyrophosphokinase.
|
| |
Structure,
9,
539-546.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.J.Turner
(2000).
Applications of transketolases in organic synthesis.
|
| |
Curr Opin Biotechnol,
11,
527-531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Schenk,
R.G.Duggleby,
and
P.F.Nixon
(1998).
Properties and functions of the thiamin diphosphate dependent enzyme transketolase.
|
| |
Int J Biochem Cell Biol,
30,
1297-1318.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Schneider,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(1998).
Crystallography and mutagenesis of transketolase: mechanistic implications for enzymatic thiamin catalysis.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1385,
387-398.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Hasson,
A.Muscate,
M.J.McLeish,
L.S.Polovnikova,
J.A.Gerlt,
G.L.Kenyon,
G.A.Petsko,
and
D.Ringe
(1998).
The crystal structure of benzoylformate decarboxylase at 1.6 A resolution: diversity of catalytic residues in thiamin diphosphate-dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
9918-9930.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

