 |
PDBsum entry 6tqn

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transcription
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6tqn
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 255 a.a.
255 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 495 a.a.
495 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 134 a.a.
134 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 98 a.a.
98 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 178 a.a.
178 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 322 a.a.
322 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 222 a.a.
222 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 90 a.a.
90 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 1342 a.a.
1342 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 1337 a.a.
1337 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transcription
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Rrn anti-termination complex without s4
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Inositol monophosphatase. Chain: t. Engineered: yes. Inositol-1-monophosphatase. Chain: s. Synonym: inositol-1-phosphatase. Engineered: yes. Transcription termination/antitermination protein nusa. Chain: a.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: b9s25_006930. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Gene: suhb, ssya, b2533, jw2517. Gene: nusa, ccu01_003250. Gene: nusb, ccu01_023355. Gene: rpsj, ad31_3986.
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.H.Huang,M.C.Wahl,B.Loll,T.Hilal,N.Said
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Y.H.Huang
et al.
(2020).
Structure-Based Mechanisms of a Molecular RNA Polymerase/Chaperone Machine Required for Ribosome Biosynthesis.
Mol Cell,
79,
1024.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Dec-19
|
Release date:
|
05-Aug-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0ADG4
(SUHB_ECOLI) -
Nus factor SuhB from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
267 a.a.
255 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P0AFF6
(NUSA_ECOLI) -
Transcription termination/antitermination protein NusA from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
495 a.a.
495 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P0A780
(NUSB_ECOLI) -
Transcription antitermination protein NusB from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
139 a.a.
134 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P0A7R5
(RS10_ECOLI) -
Small ribosomal subunit protein uS10 from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
103 a.a.
98 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P0AFG0
(NUSG_ECOLI) -
Transcription termination/antitermination protein NusG from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
181 a.a.
178 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P0A7Z4
(RPOA_ECOLI) -
DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit alpha from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
329 a.a.
322 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P0A7Z4
(RPOA_ECOLI) -
DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit alpha from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
329 a.a.
222 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P0A800
(RPOZ_ECOLI) -
DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit omega from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
91 a.a.
90 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains T, S:
E.C.3.1.3.25
- inositol-phosphate phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
myo-Inositol Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a myo-inositol phosphate + H2O = myo-inositol + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
myo-inositol phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
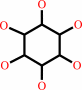 myo-inositol
myo-inositol
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains U, V, W, X, Y:
E.C.2.7.7.6
- DNA-directed Rna polymerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
RNA(n) + a ribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate = RNA(n+1) + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 RNA(n)
RNA(n)
|
+
|
ribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate
|
=
|
RNA(n+1)
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Mol Cell
79:1024
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure-Based Mechanisms of a Molecular RNA Polymerase/Chaperone Machine Required for Ribosome Biosynthesis.
|
|
Y.H.Huang,
T.Hilal,
B.Loll,
J.Bürger,
T.Mielke,
C.Böttcher,
N.Said,
M.C.Wahl.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Bacterial ribosomal RNAs are synthesized by a dedicated, conserved
transcription-elongation complex that transcribes at high rates, shields RNA
polymerase from premature termination, and supports co-transcriptional RNA
folding, modification, processing, and ribosomal subunit assembly by presently
unknown mechanisms. We have determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of
complete Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA transcription elongation complexes,
comprising RNA polymerase; DNA; RNA bearing an N-utilization-site-like
anti-termination element; Nus factors A, B, E, and G; inositol mono-phosphatase
SuhB; and ribosomal protein S4. Our structures and structure-informed functional
analyses show that fast transcription and anti-termination involve suppression
of NusA-stabilized pausing, enhancement of NusG-mediated anti-backtracking,
sequestration of the NusG C-terminal domain from termination factor ρ, and the
ρ blockade. Strikingly, the factors form a composite RNA chaperone around the
RNA polymerase RNA-exit tunnel, which supports co-transcriptional RNA folding
and annealing of distal RNA regions. Our work reveals a polymerase/chaperone
machine required for biosynthesis of functional ribosomes.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| | |

