 |
PDBsum entry 5mgb

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5mgb
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.35
- 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD+ = a 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 96.36% similarity
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
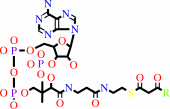 3-oxoacyl-CoA
3-oxoacyl-CoA
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.17
- enoyl-CoA hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a 4-saturated-(3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = a (3E)-enoyl-CoA + H2O
|
|
2.
|
a (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = a (2E)-enoyl-CoA + H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
4-saturated-(3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA
|
=
|
(3E)-enoyl-CoA
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 96.36% similarity
|
=
|
(2E)-enoyl-CoA
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.3.8
- Delta(3)-Delta(2)-enoyl-CoA isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a (3Z)-enoyl-CoA = a 4-saturated (2E)-enoyl-CoA
|
|
2.
|
a (3E)-enoyl-CoA = a 4-saturated (2E)-enoyl-CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
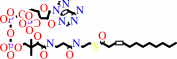 (3Z)-dodec-3-enoyl-CoA
(3Z)-dodec-3-enoyl-CoA
|
=
|
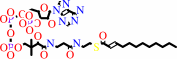 (2E)-dodec-2-enoyl-CoA
(2E)-dodec-2-enoyl-CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
FEBS Open Bio
7:1830-1842
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural enzymology comparisons of multifunctional enzyme, type-1 (MFE1): the flexibility of its dehydrogenase part.
|
|
P.Kasaragod,
G.B.Midekessa,
S.Sridhar,
W.Schmitz,
T.R.Kiema,
J.K.Hiltunen,
R.K.Wierenga.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Multifunctional enzyme, type-1 (MFE1) is a monomeric enzyme with a 2E-enoyl-CoA
hydratase and a 3S-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (HAD) active site. Enzyme
kinetic data of rat peroxisomal MFE1 show that the catalytic efficiencies for
converting the short-chain substrate 2E-butenoyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA are
much lower when compared with those of the homologous monofunctional enzymes.
The mode of binding of acetoacetyl-CoA (to the hydratase active site) and the
very similar mode of binding of NAD+and NADH (to the HAD part) are
described and compared with those of their monofunctional counterparts.
Structural comparisons suggest that the conformational flexibility of the HAD
and hydratase parts of MFE1 are correlated. The possible importance of the
conformational flexibility of MFE1 for its biocatalytic properties is discussed.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

