 |
PDBsum entry 5eqe

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5eqe
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of choline kinase alpha-1 bound by [4-[(4-methyl-1, 4-diazepan-1-yl)methyl]phenyl]methanamine (compound 11)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Choline kinase alpha. Chain: a, b. Fragment: unp residues 75-457. Synonym: ck,chetk-alpha,ethanolamine kinase,ek. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: chka, chk, cki. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.225
|
R-free:
|
0.263
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.Zhou,X.Zhu,D.C.Dalgarno
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.G.Zech
et al.
(2016).
Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors of Choline Kinase Identified by Fragment-Based Drug Discovery.
J Med Chem,
59,
671-686.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
12-Nov-15
|
Release date:
|
06-Jan-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P35790
(CHKA_HUMAN) -
Choline kinase alpha from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
457 a.a.
353 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.32
- choline kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
choline + ATP = phosphocholine + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
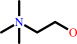 choline
choline
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
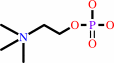 phosphocholine
phosphocholine
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.82
- ethanolamine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ethanolamine + ATP = phosphoethanolamine + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
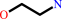 ethanolamine
ethanolamine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
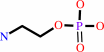 phosphoethanolamine
phosphoethanolamine
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
59:671-686
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Novel Small Molecule Inhibitors of Choline Kinase Identified by Fragment-Based Drug Discovery.
|
|
S.G.Zech,
A.Kohlmann,
T.Zhou,
F.Li,
R.M.Squillace,
L.E.Parillon,
M.T.Greenfield,
D.P.Miller,
J.Qi,
R.M.Thomas,
Y.Wang,
Y.Xu,
J.J.Miret,
W.C.Shakespeare,
X.Zhu,
D.C.Dalgarno.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Choline kinase α (ChoKα) is an enzyme involved in the synthesis of
phospholipids and thereby plays key roles in regulation of cell proliferation,
oncogenic transformation, and human carcinogenesis. Since several inhibitors of
ChoKα display antiproliferative activity in both cellular and animal models,
this novel oncogene has recently gained interest as a promising small molecule
target for cancer therapy. Here we summarize our efforts to further validate
ChoKα as an oncogenic target and explore the activity of novel small molecule
inhibitors of ChoKα. Starting from weakly binding fragments, we describe a
structure based lead discovery approach, which resulted in novel highly potent
inhibitors of ChoKα. In cancer cell lines, our lead compounds exhibit a
dose-dependent decrease of phosphocholine, inhibition of cell growth, and
induction of apoptosis at low micromolar concentrations. The druglike lead
series presented here is optimizable for improvements in cellular potency, drug
target residence time, and pharmacokinetic parameters. These inhibitors may be
utilized not only to further validate ChoKα as antioncogenic target but also as
novel chemical matter that may lead to antitumor agents that specifically
interfere with cancer cell metabolism.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

