 |
PDBsum entry 5dg3
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.129
- acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]--UDP-N-acetylglucosamine O-acyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP] + UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine = a UDP-3- O-[(3R)-3-hydroxyacyl]-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine + holo-[ACP]
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
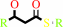 (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]
(3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]
|
+
|
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D- glucosamine
|
=
|
 [acyl-carrier-protein]
[acyl-carrier-protein]
|
+
|
UDP-3-O-(3-hydroxyacylyl)-N- acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:5937-5948
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LpxA Reveal the Basis for Its Substrate Selectivity.
|
|
E.W.Smith,
X.Zhang,
C.Behzadi,
L.D.Andrews,
F.Cohen,
Y.Chen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In Gram-negative bacteria, the first step of lipid A biosynthesis is catalyzed
by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase (LpxA) through the transfer of a
R-3-hydroxyacyl chain from the acyl carrier protein (ACP) to the 3-hydroxyl
group of UDP-GlcNAc. Previous studies suggest that LpxA is a critical
determinant of the acyl chain length found in lipid A, which varies among
species of bacteria. In Escherichia coli and Leptospira interrogans, LpxA
prefers to incorporate longer R-3-hydroxyacyl chains (C14 and C12,
respectively), whereas in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the enzyme is selective for
R-3-hydroxydecanoyl, a 10-hydrocarbon long acyl chain. We now report three P.
aeruginosa LpxA crystal structures: apo protein, substrate complex with
UDP-GlcNAc, and product complex with UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxydecanoyl)-GlcNAc. A
comparison between the apo form and complexes identifies key residues that
position UDP-GlcNAc appropriately for catalysis and supports the role of
catalytic His121 in activating the UDP-GlcNAc 3-hydroxyl group for nucleophilic
attack during the reaction. The product-complex structure, for the first time,
offers structural insights into how Met169 serves to constrain the length of the
acyl chain and thus functions as the so-called hydrocarbon ruler. Furthermore,
compared with ortholog LpxA structures, the purported oxyanion hole, formed by
the backbone amide group of Gly139, displays a different conformation in P.
aeruginosa LpxA, which suggests flexibility of this structural feature important
for catalysis and the potential need for substrate-induced conformational change
in catalysis. Taken together, the three structures provide valuable insights
into P. aeruginosa LpxA catalysis and substrate specificity as well as templates
for future inhibitor discovery.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

