 |
PDBsum entry 4x4l

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4x4l
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of human aldh1a1 with inhibitor cm037
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Retinal dehydrogenase 1. Chain: a. Synonym: raldh1,aldh-e1,alhdii,aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member a1,aldehyde dehydrogenase,cytosolic. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: aldh1a1, aldc, aldh1, pumb1. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.85Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.204
|
R-free:
|
0.233
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.A.Morgan,T.D.Hurley
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.A.Morgan
and
T.D.Hurley
(2015).
Characterization of two distinct structural classes of selective aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 inhibitors.
J Med Chem,
58,
1964-1975.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
03-Dec-14
|
Release date:
|
11-Feb-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00352
(AL1A1_HUMAN) -
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
501 a.a.
493 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.19
- aminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
4-aminobutanal + NAD+ + H2O = 4-aminobutanoate + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
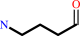 4-aminobutanal
4-aminobutanal
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
 4-aminobutanoate
4-aminobutanoate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.28
- benzaldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
benzaldehyde + NAD+ + H2O = benzoate + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
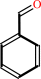 benzaldehyde
benzaldehyde
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
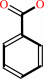 benzoate
benzoate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.3
- aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an aldehyde + NAD+ + H2O = a carboxylate + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
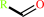 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
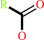 carboxylate
carboxylate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.36
- retinal dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
retinal + NAD+ + H2O = retinoate + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
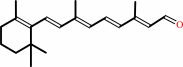 retinal
retinal
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
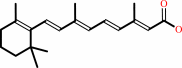 retinoate
retinoate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
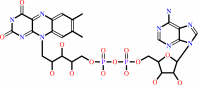 FAD
FAD
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
58:1964-1975
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Characterization of two distinct structural classes of selective aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 inhibitors.
|
|
C.A.Morgan,
T.D.Hurley.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDH) catalyze the irreversible oxidation of aldehydes
to their corresponding carboxylic acid. Alterations in ALDH1A1 activity are
associated with such diverse diseases as cancer, Parkinson's disease, obesity,
and cataracts. Inhibitors of ALDH1A1 could aid in illuminating the role of this
enzyme in disease processes. However, there are no commercially available
selective inhibitors for ALDH1A1. Here we characterize two distinct chemical
classes of inhibitors that are selective for human ALDH1A1 compared to eight
other ALDH isoenzymes. The prototypical members of each structural class, CM026
and CM037, exhibit submicromolar inhibition constants but have different
mechanisms of inhibition. The crystal structures of these compounds bound to
ALDH1A1 demonstrate that they bind within the aldehyde binding pocket of ALDH1A1
and exploit the presence of a unique glycine residue to achieve their
selectivity. These two novel and selective ALDH1A1 inhibitors may serve as
chemical tools to better understand the contributions of ALDH1A1 to normal
biology and to disease states.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

