 |
PDBsum entry 4j5t
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.1.106
- mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N4-(alpha-D-Glc-(1->2)-alpha-D-Glc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Glc-(1->3)-alpha-D- Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)- alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-alpha-D-Man- (1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc)-L- asparaginyl-[protein] + H2O = N4-(alpha-D-Glc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Glc- (1->3)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D- Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]- alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-D- GlcNAc)-L-asparaginyl-[protein] + beta-D-glucose
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(4)-(alpha-D-Glc-(1->2)-alpha-D-Glc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Glc-(1->3)-alpha-D- Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)- alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-alpha-D-Man- (1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc)-L- asparaginyl-[protein]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
N(4)-(alpha-D-Glc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Glc- (1->3)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D- Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]- alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-D- GlcNAc)-L-asparaginyl-[protein]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.50% similarity
|
+
|
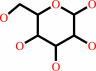 beta-D-glucose
beta-D-glucose
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
288:13563-13574
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Specificity of Processing α-glucosidase I is guided by the substrate conformation: crystallographic and in silico studies.
|
|
M.K.Barker,
D.R.Rose.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Processing α-glucosidase I (GluI) is a key member of the eukaryotic
N-glycosylation processing pathway, selectively catalyzing the first
glycoprotein trimming step in the endoplasmic reticulum. Inhibition of GluI
activity impacts the infectivity of enveloped viruses; however, despite interest
in this protein from a structural, enzymatic, and therapeutic standpoint, little
is known about its structure and enzymatic mechanism in catalysis of the unique
glycan substrate Glc3Man9GlcNAc2. The first structural model of eukaryotic GluI
is here presented at 2-Å resolution. Two catalytic residues are proposed,
mutations of which result in catalytically inactive, properly folded protein.
Using Autodocking methods with the known substrate and inhibitors as ligands,
including a novel inhibitor characterized in this work, the active site of GluI
was mapped. From these results, a model of substrate binding has been
formulated, which is most likely conserved in mammalian GluI.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

