 |
PDBsum entry 3zph
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, C, D, E, F:
E.C.5.5.1.6
- chalcone isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Flavonoid Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a chalcone = a flavanone
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
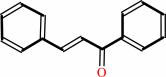 chalcone
chalcone
|
=
|
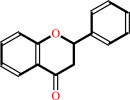 flavanone
flavanone
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
53:1439-1442
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Enzymatic conversion of flavonoids using bacterial chalcone isomerase and enoate reductase.
|
|
M.Gall,
M.Thomsen,
C.Peters,
I.V.Pavlidis,
P.Jonczyk,
P.P.Grünert,
S.Beutel,
T.Scheper,
E.Gross,
M.Backes,
T.Geissler,
J.P.Ley,
J.M.Hilmer,
G.Krammer,
G.J.Palm,
W.Hinrichs,
U.T.Bornscheuer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Flavonoids are a large group of plant secondary metabolites with a variety of
biological properties and are therefore of interest to many scientists, as they
can lead to industrially interesting intermediates. The anaerobic gut bacterium
Eubacterium ramulus can catabolize flavonoids, but until now, the pathway has
not been experimentally confirmed. In the present work, a chalcone isomerase
(CHI) and an enoate reductase (ERED) could be identified through whole genome
sequencing and gene motif search. These two enzymes were successfully cloned and
expressed in Escherichia coli in their active form, even under aerobic
conditions. The catabolic pathway of E. ramulus was confirmed by
biotransformations of flavanones into dihydrochalcones. The engineered E. coli
strain that expresses both enzymes was used for the conversion of several
flavanones, underlining the applicability of this biocatalytic cascade reaction.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

