 |
PDBsum entry 3r8h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3r8h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Akr1c3 complex with zomepirac
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member c3. Chain: a. Synonym: 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5, 17-beta-hsd 5, 3-alpha-hsd type ii, brain, 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2, 3-alpha-hsd type 2, chlordecone reductase homolog hakrb, dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 3, dd-3, dd3, dihydrodiol dehydrogenase type i, ha1753, indanol dehydrogenase, prostaglandin f synthase, pgfs, testosterone 17-beta-dehydrogenase 5, trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene- 1,2-diol dehydrogenase.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: akr1c3, ddh1, hsd17b5, kiaa0119, pgfs. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.90Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.166
|
R-free:
|
0.204
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Yosaatmadja,R.M.Teague,J.U.Flanagan,C.J.Squire
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.U.Flanagan
et al.
(2012).
Crystal structures of three classes of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in complex with aldo-keto reductase 1C3.
Plos One,
7,
e43965.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Mar-11
|
Release date:
|
02-May-12
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P42330
(AK1C3_HUMAN) -
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
323 a.a.
303 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.188
- prostaglandin-F synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
prostaglandin F2alpha + NADP+ = prostaglandin D2 + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
prostaglandin F2alpha
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
=
|
 prostaglandin D2
prostaglandin D2
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.210
- 3beta-(or 20alpha)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol + NADP+ = 17beta-hydroxy-5alpha- androstan-3-one + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
17beta-hydroxy-5alpha- androstan-3-one
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 57.69% similarity
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.239
- 3alpha-(17beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
testosterone + NAD+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
testosterone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 57.69% similarity
|
=
|
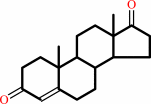 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.357
- 3alpha-hydroxysteroid 3-dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a 3alpha-hydroxysteroid + NADP+ = a 3-oxosteroid + NADPH + H+
|
|
2.
|
a 3alpha-hydroxysteroid + NAD+ = a 3-oxosteroid + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3alpha-hydroxysteroid
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
 3-oxosteroid
3-oxosteroid
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3alpha-hydroxysteroid
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
 3-oxosteroid
3-oxosteroid
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.53
- 3alpha(or 20beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol + NAD+ = 17beta-hydroxyandrostanone + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 57.69% similarity
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
17beta-hydroxyandrostanone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 6:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.62
- 17beta-estradiol 17-dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
17beta-estradiol + NAD+ = estrone + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
17beta-estradiol + NADP+ = estrone + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
estrone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
estrone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 7:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.64
- testosterone 17beta-dehydrogenase (NADP(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
testosterone + NADP+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
testosterone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 57.69% similarity
|
=
|
 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Plos One
7:e43965
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of three classes of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in complex with aldo-keto reductase 1C3.
|
|
J.U.Flanagan,
Y.Yosaatmadja,
R.M.Teague,
M.Z.Chai,
A.P.Turnbull,
C.J.Squire.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) catalyses the NADPH dependent reduction of
carbonyl groups in a number of important steroid and prostanoid molecules. The
enzyme is also over-expressed in prostate and breast cancer and its expression
is correlated with the aggressiveness of the disease. The steroid products of
AKR1C3 catalysis are important in proliferative signalling of hormone-responsive
cells, while the prostanoid products promote prostaglandin-dependent
proliferative pathways. In these ways, AKR1C3 contributes to tumour development
and maintenance, and suggest that inhibition of AKR1C3 activity is an attractive
target for the development of new anti-cancer therapies. Non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are one well-known class of compounds that
inhibits AKR1C3, yet crystal structures have only been determined for this
enzyme with flufenamic acid, indomethacin, and closely related analogues bound.
While the flufenamic acid and indomethacin structures have been used to design
novel inhibitors, they provide only limited coverage of the NSAIDs that inhibit
AKR1C3 and that may be used for the development of new AKR1C3 targeted drugs. To
understand how other NSAIDs bind to AKR1C3, we have determined ten crystal
structures of AKR1C3 complexes that cover three different classes of NSAID,
N-phenylanthranilic acids (meclofenamic acid, mefenamic acid), arylpropionic
acids (flurbiprofen, ibuprofen, naproxen), and indomethacin analogues
(indomethacin, sulindac, zomepirac). The N-phenylanthranilic and arylpropionic
acids bind to common sites including the enzyme catalytic centre and a
constitutive active site pocket, with the arylpropionic acids probing the
constitutive pocket more effectively. By contrast, indomethacin and the
indomethacin analogues sulindac and zomepirac, display three distinctly
different binding modes that explain their relative inhibition of the AKR1C
family members. This new data from ten crystal structures greatly broadens the
base of structures available for future structure-guided drug discovery efforts.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

