 |
PDBsum entry 3kv8

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural basis of the activity and substrate specificity of the fluoroacetyl-coa thioesterase flk - wild type flk in complex with fluoro-acetate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Fluoroacetyl-coa thioesterase flk. Chain: a, b. Fragment: flk. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Streptomyces cattleya. Organism_taxid: 29303. Gene: flk, fluoroacetyl-coa thioesterase flk. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.85Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.172
|
R-free:
|
0.228
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.V.B.Dias,F.Huang,D.Y.Chirgadze,M.Tosin,D.Spiteller,E.F.Valentine, P.F.Leadlay,J.B.Spencer,T.L.Blundell
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.V.Dias
et al.
(2010).
Structural basis for the activity and substrate specificity of fluoroacetyl-CoA thioesterase FlK.
J Biol Chem,
285,
22495-22504.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Nov-09
|
Release date:
|
21-Apr-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q1EMV2
(FLK_STRCT) -
Fluoroacetyl-CoA thioesterase from Streptantibioticus cattleyicolor
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
139 a.a.
133 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.2.29
- fluoroacetyl-CoA thioesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
fluoroacetyl-CoA + H2O = fluoroacetate + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
fluoroacetyl-CoA
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
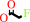 fluoroacetate
fluoroacetate
|
+
|
CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
285:22495-22504
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for the activity and substrate specificity of fluoroacetyl-CoA thioesterase FlK.
|
|
M.V.Dias,
F.Huang,
D.Y.Chirgadze,
M.Tosin,
D.Spiteller,
E.F.Dry,
P.F.Leadlay,
J.B.Spencer,
T.L.Blundell.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The thioesterase FlK from the fluoroacetate-producing Streptomyces cattleya
catalyzes the hydrolysis of fluoroacetyl-coenzyme A. This provides an effective
self-defence mechanism, preventing any fluoroacetyl-coenzyme A formed from being
further metabolized to 4-hydroxy-trans-aconitate, a lethal inhibitor of the
tricarboxylic acid cycle. Remarkably FlK does not accept acetyl-coenzyme A as a
substrate. Crystal structure analysis shows that FlK forms a dimer, in which
each subunit adopts a hot-dog fold as observed for type II thioesterases. Unlike
other type II thioesterases, which invariably utilize either an aspartate or a
glutamate as catalytic base, we show by site-directed mutagenesis and
crystallography that FlK employs a catalytic triad composed of Thr42, His76 and
a water molecule, analogous to the Ser/Cys-His-acid triad of type I
thioesterases. Structural comparison of FlK complexed with various substrate
analogues suggests that the interaction between the fluorine of the substrate
and the side chain of Arg120 located opposite to the catalytic triad is
essential for correct coordination of the substrate at the active site and
therefore accounts for the substrate specificity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

