 |
PDBsum entry 3glm

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.70
- Transferred entry: 7.2.4.5.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
4-carboxybut-2-enoyl-CoA = but-2-enoyl-CoA + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
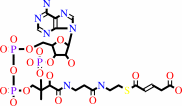 4-carboxybut-2-enoyl-CoA
4-carboxybut-2-enoyl-CoA
|
=
|
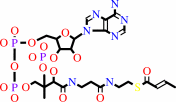 but-2-enoyl-CoA
but-2-enoyl-CoA
|
+
|
 CO(2)
CO(2)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Biotin
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
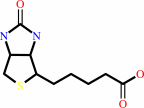 Biotin
Biotin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
284:28401-28409
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
An asymmetric model for Na+-translocating glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylases.
|
|
D.Kress,
D.Brügel,
I.Schall,
D.Linder,
W.Buckel,
L.O.Essen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase (Gcd) couples the biotin-dependent decarboxylation
of glutaconyl-CoA with the generation of an electrochemical Na(+) gradient.
Sequencing of the genes encoding all subunits of the Clostridium symbiosum
decarboxylase membrane complex revealed that it comprises two distinct biotin
carrier subunits, GcdC(1) and GcdC(2), which differ in the length of a central
alanine- and proline-rich linker domain. Co-crystallization of the decarboxylase
subunit GcdA with the substrate glutaconyl-CoA, the product crotonyl-CoA, and
the substrate analogue glutaryl-CoA, respectively, resulted in a high resolution
model for substrate binding and catalysis revealing remarkable structural
changes upon substrate binding. Unlike the GcdA structure from Acidaminococcus
fermentans, these data suggest that in intact Gcd complexes, GcdA is associated
as a tetramer crisscrossed by a network of solvent-filled tunnels.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
A, overall structure of the C. symbiosum GcdA monomer. α-
and 3[10]-helices of the N-terminal domain are colored blue, the
respective β-strands are shown in lighter blue. The secondary
structure motifs of the C-terminal domain are represented in
dark green (helices) and light green (β-strands). The bound
crotonyl-CoA is displayed as a magenta stick model and the
chloride ion bound to OAH2 is shown as a yellow sphere. Residues
missing in the electron density are indicated by broken lines.
B, GcdA dimer. N and C terminus of the symmetry-equivalent chain
B are colored dark and light gray, respectively. The
crotonyl-CoA molecules at the dimer interfaces are represented
as CPK models. The second chloride ion is displayed as a green
sphere. The positions of the active sites are highlighted by
dashed lines. C, two orthogonal orientations of the
222-symmetric GcdA tetramer deduced from the crystal packing.
Chains A to D are colored blue, green, red, and yellow,
respectively.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Stereo view of the glutaconyl binding site displayed with
amino acid residues within 4 Å of the crotonyl-CoA
product. Residues of the N- and C-terminal domains of GcdA are
colored blue and gray, respectively. Structurally equivalent
residues of A. fermentans GcdA are displayed in orange.
Non-conserved residues are marked with orange labels. The dashed
lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2009,
284,
28401-28409)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Huang,
P.Ge,
Z.H.Zhou,
and
L.Tong
(2012).
An unanticipated architecture of the 750-kDa α6β6 holoenzyme of 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase.
|
| |
Nature,
481,
219-223.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

