 |
PDBsum entry 3dpy

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.5.1.58
- protein farnesyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-cysteinyl-[protein] + (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate = S-(2E,6E)- farnesyl-L-cysteinyl-[protein] + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-cysteinyl-[protein]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
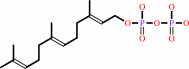 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
=
|
S-(2E,6E)- farnesyl-L-cysteinyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+); Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.5.1.59
- protein geranylgeranyltransferase type I.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
geranylgeranyl diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-[protein] = S-geranylgeranyl-L- cysteinyl-[protein] + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
geranylgeranyl diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 82.76% similarity
|
+
|
L-cysteinyl-[protein]
|
=
|
S-geranylgeranyl-L- cysteinyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Chem Biol Drug Des
72:171-181
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Caged protein prenyltransferase substrates: tools for understanding protein prenylation.
|
|
A.J.DeGraw,
M.A.Hast,
J.Xu,
D.Mullen,
L.S.Beese,
G.Barany,
M.D.Distefano.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Originally designed to block the prenylation of oncogenic Ras, inhibitors of
protein farnesyltransferase currently in preclinical and clinical trials are
showing efficacy in cancers with normal Ras. Blocking protein prenylation has
also shown promise in the treatment of malaria, Chagas disease and progeria
syndrome. A better understanding of the mechanism, targets and in vivo
consequences of protein prenylation are needed to elucidate the mode of action
of current PFTase (Protein Farnesyltransferase) inhibitors and to create more
potent and selective compounds. Caged enzyme substrates are useful tools for
understanding enzyme mechanism and biological function. Reported here is the
synthesis and characterization of caged substrates of PFTase. The caged
isoprenoid diphosphates are poor substrates prior to photolysis. The caged CAAX
peptide is a true catalytically caged substrate of PFTase in that it is to not a
substrate, yet is able to bind to the enzyme as established by inhibition
studies and X-ray crystallography. Irradiation of the caged molecules with 350
nm light readily releases their cognate substrate and their photolysis products
are benign. These properties highlight the utility of those analogs towards a
variety of in vitro and in vivo applications.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.J.DeGraw,
M.J.Keiser,
J.D.Ochocki,
B.K.Shoichet,
and
M.D.Distefano
(2010).
Prediction and evaluation of protein farnesyltransferase inhibition by commercial drugs.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
53,
2464-2471.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

