 |
PDBsum entry 3jsx

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3jsx
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
X-ray crystal structure of NAD(p)h: quinone oxidoreductase-1 (nqo1) bound to the coumarin-based inhibitor as1
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
NAD(p)h dehydrogenase [quinone] 1. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Synonym: quinone reductase 1, NAD(p)h:quinone oxidoreductase 1, qr1, dt-diaphorase, dtd, azoreductase, phylloquinone reductase, menadione reductase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: dia4, nmor1, nqo1, nqo1 cdna. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.45Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.210
|
R-free:
|
0.269
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.S.Dunstan,C.Levy,D.Leys
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.A.Nolan
et al.
(2009).
Synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin-based inhibitors of NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1).
J Med Chem,
52,
7142-7156.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
11-Sep-09
|
Release date:
|
12-Jan-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P15559
(NQO1_HUMAN) -
NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
274 a.a.
270 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.6.5.2
- NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a quinone + NADH + H+ = a quinol + NAD+
|
|
2.
|
a quinone + NADPH + H+ = a quinol + NADP+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
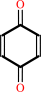 quinone
quinone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
quinol
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 quinone
quinone
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
quinol
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Med Chem
52:7142-7156
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin-based inhibitors of NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1).
|
|
K.A.Nolan,
J.R.Doncaster,
M.S.Dunstan,
K.A.Scott,
A.D.Frenkel,
D.Siegel,
D.Ross,
J.Barnes,
C.Levy,
D.Leys,
R.C.Whitehead,
I.J.Stratford,
R.A.Bryce.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The synthesis is reported here of two novel series of inhibitors of human
NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1), an enzyme overexpressed in several
types of tumor cell. The first series comprises substituted symmetric dicoumarol
analogues; the second series contains hybrid compounds where one
4-hydroxycoumarin system is replaced by a different aromatic moiety. Several
compounds show equivalent or improved NQO1 inhibition over dicoumarol, both in
the presence and in the absence of added protein. Further, correlation is
demonstrated between the ability of these agents to inhibit NQO1 and computed
binding affinity. We have solved the crystal structure of NQO1 complexed to a
hybrid compound and find good agreement with the in silico model. For both MIA
PaCa-2 pancreatic tumor cells and HCT116 colon cancer cells, dicoumarol shows
the greatest toxicity of all compounds. Thus, we provide a computational,
synthetic, and biological platform to generate competitive NQO1 inhibitors with
superior pharmacological properties to dicoumarol. This will allow a more
definitive study of NQO1 activity in cells, in particular, its drug
activating/detoxifying properties and ability to modulate oncoprotein stability.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

