 |
PDBsum entry 2yii
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Manipulating the regioselectivity of phenylalanine aminomutase: new insights into the reaction mechanism of mio-dependent enzymes from structure-guided directed evolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: phenylalanine aminomutase. Engineered: yes. Other_details: thioester bond between the mdo prosthetic group and a molecule of beta-mercaptoethanol, disulfide bridge between residue c89 and a beta-mercaptoethanol molecule, covalent bond between mdo 175 and residue d178
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Taxus wallichiana var. Chinensis. Chinese yew. Organism_taxid: 29808. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 83333. Expression_system_variant: top10.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.18Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.181
|
R-free:
|
0.215
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
B.Wu,W.Szymanski,G.G.Wybenga,M.M.Heberling,S.Bartsch,S.Wildeman, G.J.Poelarends,B.L.Feringa,B.W.Dijkstra,D.B.Janssen
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
B.Wu
et al.
(2012).
Mechanism-inspired engineering of phenylalanine aminomutase for enhanced β-regioselective asymmetric amination of cinnamates.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
51,
482-486.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-May-11
|
Release date:
|
09-Nov-11
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q68G84
(PAM_TAXCH) -
Phenylalanine aminomutase (L-beta-phenylalanine forming) from Taxus chinensis
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
687 a.a.
644 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.1.24
- phenylalanine ammonia-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-phenylalanine = (E)-cinnamate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
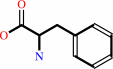 L-phenylalanine
L-phenylalanine
|
=
|
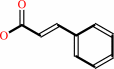 (E)-cinnamate
(E)-cinnamate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
MIO
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.3.10
- phenylalanine aminomutase (L-beta-phenylalanine forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-phenylalanine = L-beta-phenylalanine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 L-phenylalanine
L-phenylalanine
|
=
|
L-beta-phenylalanine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
MIO
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
51:482-486
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanism-inspired engineering of phenylalanine aminomutase for enhanced β-regioselective asymmetric amination of cinnamates.
|
|
B.Wu,
W.Szymański,
G.G.Wybenga,
M.M.Heberling,
S.Bartsch,
S.de Wildeman,
G.J.Poelarends,
B.L.Feringa,
B.W.Dijkstra,
D.B.Janssen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

