 |
PDBsum entry 2q7d

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase (itpk1) in complex with amppnp and mn2+
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Inositol-tetrakisphosphate 1-kinase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: catalytic domain. Synonym: inositol- triphosphate 5/6-kinase, inositol 1,3,4- trisphosphate 5/6-kinase, ins1,3,4, p3, 5/6-kinase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: itpk1. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.196
|
R-free:
|
0.236
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
P.P.Chamberlain,S.A.Lesley,G.Spraggon
|
Key ref:

|
 |
P.P.Chamberlain
et al.
(2007).
Integration of inositol phosphate signaling pathways via human ITPK1.
J Biol Chem,
282,
28117-28125.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
06-Jun-07
|
Release date:
|
03-Jul-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q13572
(ITPK1_HUMAN) -
Inositol-tetrakisphosphate 1-kinase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
414 a.a.
337 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.134
- inositol-tetrakisphosphate 1-kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
myo-Inositol Phosphate Metabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
1D-myo-inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate + ATP = 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
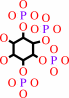 1D-myo-inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
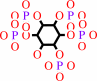 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.25% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.159
- inositol-1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate + ATP = 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5- tetrakisphosphate + ADP + H+
|
|
2.
|
1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate + ATP = 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,6- tetrakisphosphate + ADP + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
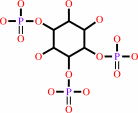 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5- tetrakisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5- tetrakisphosphate
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.25% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
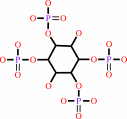 1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,6- tetrakisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,6- tetrakisphosphate
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.25% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
282:28117-28125
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Integration of inositol phosphate signaling pathways via human ITPK1.
|
|
P.P.Chamberlain,
X.Qian,
A.R.Stiles,
J.Cho,
D.H.Jones,
S.A.Lesley,
E.A.Grabau,
S.B.Shears,
G.Spraggon.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase (ITPK1) is a reversible, poly-specific
inositol phosphate kinase that has been implicated as a modifier gene in cystic
fibrosis. Upon activation of phospholipase C at the plasma membrane, inositol
1,4,5-trisphosphate enters the cytosol and is inter-converted by an array of
kinases and phosphatases into other inositol phosphates with diverse and
critical cellular activities. In mammals it has been established that inositol
1,3,4-trisphosphate, produced from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, lies in a
branch of the metabolic pathway that is separate from inositol
3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate, which inhibits plasma membrane chloride channels. We
have determined the molecular mechanism for communication between these two
pathways, showing that phosphate is transferred between inositol phosphates via
ITPK1-bound nucleotide. Intersubstrate phosphate transfer explains how competing
substrates are able to stimulate each others' catalysis by ITPK1. We further
show that these features occur in the human protein, but not in plant or
protozoan homologues. The high resolution structure of human ITPK1 identifies
novel secondary structural features able to impart substrate selectivity and
enhance nucleotide binding, thereby promoting intersubstrate phosphate transfer.
Our work describes a novel mode of substrate regulation and provides insight
into the enzyme evolution of a signaling mechanism from a metabolic role.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
FIGURE 2. Sequential intersubstrate phosphate transfer
hypotheses for hITPK1. This graphic shows hypothetical
intersubstrate phosphate transfer mechanisms by which levels of
Ins(1,3,4)P[3] could regulate the synthesis of Ins(3,4,5,6)P[4].
Panel A shows the two candidate phosphate carriers with enzyme
represented as "E" with the transferred phosphate highlighted in
red. Panel B expands the nucleotide-mediated phosphate transfer
hypothesis in which enzyme-bound nucleotide acts as the
phosphate carrier. Unliganded ITPK1 is represented by E;
phosphotransferase reactions are indicated by red graphics. The
position of the [^32P] group that is transferred between
inositol phosphates is shown in red.An asterisk indicates a
reaction for which Ins(1,3,4,5)P[4] is also produced at a
reduced rate. We do not rule out the possibility that a
phosphoenzyme intermediate might also participate in these
reactions.
|
 |
Figure 5.
FIGURE 5. Detail of the hITPK1 inositol phosphate binding
pocket. Identical projections for eITPK1 (A) and hITPK1 (B),
showing the reduction in inositol phosphate binding site volume
and ATP solvent accessibility for hITPK1. Ins(1,3,4)P[3] is
shown modeled into the hITPK1 based on structural alignment with
eITPK1 and exhibits a steric clash with His-162. A
solvent-accessible surface is shown for each molecule. The
position of the ATP  -phosphate is indicated
by " -phosphate is indicated
by "  ". Metal ions are shown
as green spheres. Panel C is a stereodiagram showing structural
superposition of hITPK1 with eITPK1. hITPK1 is shown with blue
carbons atoms, with a bound sulfate shown in gold and red.
Residues capable of carrying a phosphate that are proximal to
the ATP ". Metal ions are shown
as green spheres. Panel C is a stereodiagram showing structural
superposition of hITPK1 with eITPK1. hITPK1 is shown with blue
carbons atoms, with a bound sulfate shown in gold and red.
Residues capable of carrying a phosphate that are proximal to
the ATP  -phosphate are shown in
yellow. eITPK1 in complex with Ins(1,3,4)P[3] is shown with
orange carbon atoms for protein, magenta carbons for the
inositol. -phosphate are shown in
yellow. eITPK1 in complex with Ins(1,3,4)P[3] is shown with
orange carbon atoms for protein, magenta carbons for the
inositol.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2007,
282,
28117-28125)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.W.Majerus,
D.B.Wilson,
C.Zhang,
P.J.Nicholas,
and
M.P.Wilson
(2010).
Expression of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase (ITPK1) and its role in neural tube defects.
|
| |
Adv Enzyme Regul,
50,
365-372.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Shears
(2009).
Diphosphoinositol polyphosphates: metabolic messengers?
|
| |
Mol Pharmacol,
76,
236-252.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.R.Alcázar-Román,
and
S.R.Wente
(2008).
Inositol polyphosphates: a new frontier for regulating gene expression.
|
| |
Chromosoma,
117,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.R.Stiles,
X.Qian,
S.B.Shears,
and
E.A.Grabau
(2008).
Metabolic and signaling properties of an Itpk gene family in Glycine max.
|
| |
FEBS Lett,
582,
1853-1858.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Mitchell,
X.Wang,
G.Zhang,
M.Gentzsch,
D.J.Nelson,
and
S.B.Shears
(2008).
An expanded biological repertoire for Ins(3,4,5,6)P4 through its modulation of ClC-3 function.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
18,
1600-1605.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

