 |
PDBsum entry 2j6h

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.16
- glutamine--fructose-6-phosphate transaminase (isomerizing).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-fructose 6-phosphate + L-glutamine = D-glucosamine 6-phosphate + L-glutamate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
D-fructose 6-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
L-glutamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.82% similarity
|
=
|
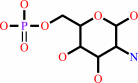 D-glucosamine 6-phosphate
D-glucosamine 6-phosphate
|
+
|
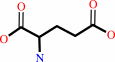 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
281:4404-4412
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Glutamine Binding Opens the Ammonia Channel and Activates Glucosamine-6P Synthase.
|
|
S.Mouilleron,
M.A.Badet-Denisot,
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glucosamine-6P synthase catalyzes the synthesis of glucosamine-6P from
fructose-6P and glutamine and uses a channel to transfer ammonia from its
glutaminase to its synthase active site. X-ray structures of glucosamine-6P
synthase have been determined at 2.05 A resolution in the presence of
fructose-6P and at 2.35 A resolution in the presence of fructose-6P and
6-diazo-5-oxo-l-norleucine, a glutamine affinity analog that covalently modifies
the N-terminal catalytic cysteine, therefore mimicking the
gamma-glutamyl-thioester intermediate formed during hydrolysis of glutamine. The
fixation of the glutamine analog activates the enzyme through several major
structural changes: 1) the closure of a loop to shield the glutaminase site
accompanied by significant domain hinging, 2) the activation of catalytic
residues involved in glutamine hydrolysis, i.e. the alpha-amino group of Cys-1
and Asn-98 that is positioned to form the oxyanion hole, and 3) a 75 degrees
rotation of the Trp-74 indole group that opens the ammonia channel.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
FIGURE 2. Comparison of the synthase sites of the
GlmS·Fru6P and GlmS·Glc6P·DON structures.
In all the figures drawn with PYMOL (www.pymol.org), the protein
in the GlmS·Fru6P structure is drawn in cyan and Fru6P in
blue, whereas the protein in the GlmS·Glc6P·DON
structure is drawn in orange, Glc6P in yellow, and DON in
off-white. F[o] - F[c] electron density maps omitting the ligand
and a 3.5 Å spherical region around it are contoured at
the level of 2.5  . Hydrogen bonds <3.3
Å are indicated as dashed lines and water molecules as red
spheres. A, GlmS·Fru6P structure. B,
GlmS·Glc6P·DON structure. C, superposition of the
synthase sites. The C . Hydrogen bonds <3.3
Å are indicated as dashed lines and water molecules as red
spheres. A, GlmS·Fru6P structure. B,
GlmS·Glc6P·DON structure. C, superposition of the
synthase sites. The C  s of the synthase
domains (residues 300–600) were superimposed on each other
(r.m.s.d., 0.48 Å). The C-tails (r.m.s.d., 1.2 Å
over 9 C s of the synthase
domains (residues 300–600) were superimposed on each other
(r.m.s.d., 0.48 Å). The C-tails (r.m.s.d., 1.2 Å
over 9 C  s) are indicated as
coils. Only the water molecules and hydrogen bonds that explain
the conformational changes occurring upon DON binding at the
glutaminase site are indicated, respectively as blue spheres and
green dashed lines for the GlmS·Fru6P structure and as
orange spheres and gray dashed lines for the
GlmS·Glc6P·DON structure. Together with the
conformational changes of Arg-26 and Trp-74 from the glutaminase
domain, the peptide bond of Lys-603 flips and the side-chains of
Ser-604 and Lys-503^* adopt different conformations in the two
structures. OH of Ser-401 is hydrogen bonded to O[2] of the
sugar only in the GlmS·Fru6P structure. s) are indicated as
coils. Only the water molecules and hydrogen bonds that explain
the conformational changes occurring upon DON binding at the
glutaminase site are indicated, respectively as blue spheres and
green dashed lines for the GlmS·Fru6P structure and as
orange spheres and gray dashed lines for the
GlmS·Glc6P·DON structure. Together with the
conformational changes of Arg-26 and Trp-74 from the glutaminase
domain, the peptide bond of Lys-603 flips and the side-chains of
Ser-604 and Lys-503^* adopt different conformations in the two
structures. OH of Ser-401 is hydrogen bonded to O[2] of the
sugar only in the GlmS·Fru6P structure.
|
 |
Figure 5.
FIGURE 5. DON binding induces a rotation of the glutaminase
domain relative to the synthase domain. The two monomers are
drawn in orange and yellow for the GlmS·DON·Glc6P
structure, and in cyan and green for the GlmS·Fru6P. The
two glutaminase domains are at top and bottom, and the two
synthase domains that form the dimeric interface in the middle.
A, the superposition of the C  s of the two synthase
domains of the two structures results in a 21° rotation
between the glutaminase domains. B, close-up view of the
interacting zone between one glutaminase domain and the synthase
domain of the neighboring monomer. The interaction between the
Q-loop and the C-terminal region of the 524^*-539^* s of the two synthase
domains of the two structures results in a 21° rotation
between the glutaminase domains. B, close-up view of the
interacting zone between one glutaminase domain and the synthase
domain of the neighboring monomer. The interaction between the
Q-loop and the C-terminal region of the 524^*-539^*  -helix
and the ionic interaction between Asp-29 and Arg-539^* that is
crucial for dimerization are conserved in the two structures. -helix
and the ionic interaction between Asp-29 and Arg-539^* that is
crucial for dimerization are conserved in the two structures.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2006,
281,
4404-4412)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Chevreux,
C.Atmanene,
P.Lopez,
J.Ouazzani,
A.Van Dorsselaer,
B.Badet,
M.A.Badet-Denisot,
and
S.Sanglier-Cianférani
(2011).
Monitoring the dynamics of monomer exchange using electrospray mass spectrometry: the case of the dimeric glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase.
|
| |
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom,
22,
431-439.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Senderek,
J.S.Müller,
M.Dusl,
T.M.Strom,
V.Guergueltcheva,
I.Diepolder,
S.H.Laval,
S.Maxwell,
J.Cossins,
S.Krause,
N.Muelas,
J.J.Vilchez,
J.Colomer,
C.J.Mallebrera,
A.Nascimento,
S.Nafissi,
A.Kariminejad,
Y.Nilipour,
B.Bozorgmehr,
H.Najmabadi,
C.Rodolico,
J.P.Sieb,
O.K.Steinlein,
B.Schlotter,
B.Schoser,
J.Kirschner,
R.Herrmann,
T.Voit,
A.Oldfors,
C.Lindbergh,
A.Urtizberea,
M.von der Hagen,
A.Hübner,
J.Palace,
K.Bushby,
V.Straub,
D.Beeson,
A.Abicht,
and
H.Lochmüller
(2011).
Hexosamine biosynthetic pathway mutations cause neuromuscular transmission defect.
|
| |
Am J Hum Genet,
88,
162-172.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Krissinel
(2010).
Crystal contacts as nature's docking solutions.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
31,
133-143.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.X.Zhou,
and
J.A.McCammon
(2010).
The gates of ion channels and enzymes.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
35,
179-185.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Lund,
Y.Fan,
Q.Shao,
Y.Q.Gao,
and
F.M.Raushel
(2010).
Carbamate transport in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: a theoretical and experimental investigation.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
132,
3870-3878.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.C.Schoenhofen,
E.Vinogradov,
D.M.Whitfield,
J.R.Brisson,
and
S.M.Logan
(2009).
The CMP-legionaminic acid pathway in Campylobacter: biosynthesis involving novel GDP-linked precursors.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
19,
715-725.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.LaRonde-LeBlanc,
M.Resto,
and
B.Gerratana
(2009).
Regulation of active site coupling in glutamine-dependent NAD(+) synthetase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
16,
421-429.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Koike,
A.Kidera,
and
M.Ota
(2009).
Alteration of oligomeric state and domain architecture is essential for functional transformation between transferase and hydrolase with the same scaffold.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
2060-2066.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Fan,
L.Lund,
Q.Shao,
Y.Q.Gao,
and
F.M.Raushel
(2009).
A combined theoretical and experimental study of the ammonia tunnel in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
10211-10219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Vanoni,
and
B.Curti
(2008).
Structure-function studies of glutamate synthases: a class of self-regulated iron-sulfur flavoenzymes essential for nitrogen assimilation.
|
| |
IUBMB Life,
60,
287-300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mouilleron,
and
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau
(2007).
Domain motions of glucosamine-6P synthase: comparison of the anisotropic displacements in the crystals and the catalytic hinge-bending rotation.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
16,
485-493.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mouilleron,
and
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau
(2007).
Conformational changes in ammonia-channeling glutamine amidotransferases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
17,
653-664.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

