 |
PDBsum entry 2j4l

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|





 (+ 2 more)
214 a.a.
(+ 2 more)
214 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|


 198 a.a.
198 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 171 a.a.
171 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of uridylate kinase from sulfolobus solfataricus in complex with utp to 2.8 angstrom resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Uridylate kinase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l. Fragment: residues 2-227. Synonym: uk, uridine monophosphate kinase, ump kinase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sulfolobus solfataricus. Organism_taxid: 2287. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.246
|
R-free:
|
0.278
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.S.Jensen,E.Johansson,K.F.Jensen
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.S.Jensen
et al.
(2007).
Structural and enzymatic investigation of the Sulfolobus solfataricus uridylate kinase shows competitive UTP inhibition and the lack of GTP stimulation.
Biochemistry,
46,
2745-2757.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
01-Sep-06
|
Release date:
|
27-Feb-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q97ZE2
(PYRH_SULSO) -
Uridylate kinase from Saccharolobus solfataricus (strain ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
227 a.a.
214 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L:
E.C.2.7.4.22
- Ump kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
UMP + ATP = UDP + ADP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
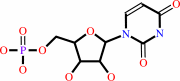 UMP
UMP
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
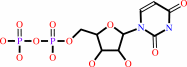 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 86.21% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
46:2745-2757
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and enzymatic investigation of the Sulfolobus solfataricus uridylate kinase shows competitive UTP inhibition and the lack of GTP stimulation.
|
|
K.S.Jensen,
E.Johansson,
K.F.Jensen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The pyrH gene encoding uridylate kinase (UMPK) from the extreme
thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus was cloned and expressed in
Escherichia coli, and the enzyme (SsUMPK) was purified. Size exclusion
chromatography and sedimentation experiments showed that the oligomeric state in
solution is hexameric. SsUMPK shows maximum catalytic rate at pH 7.0, and
variation of pH only influences the turnover number. Catalysis proceeds by a
sequential reaction mechanism of random order and depends on a divalent cation.
The enzyme exhibits high substrate specificity toward UMP and ATP and is
inhibited by UTP, whereas CTP and GTP do not influence activity. UTP binds to
the enzyme with a sigmoid binding curve, whereas GTP does not bind. The crystal
structure of SsUMPK was determined for three different complexes, a ternary
complex with UMP and the nonhydrolyzable ATP analogue beta,gamma-methylene-ATP,
a complex with UMP, and a complex with UTP to 2.1, 2.2, and 2.8 A resolution,
respectively. One UTP molecule was bound in the acceptor site per subunit,
leading to the exclusion of both substrates from the active site. In all cases,
SsUMPK crystallized as a hexamer with the main fold shared with other
prokaryotic UMPKs. Similar to UMPK from Pyrococcus furiosus, SsUMPK has an
active site enclosing loop. This loop was only ordered in one subunit in the
ternary complex, which also contained an unusual arrangement of ligands
(possibly a dinucleotide) in the active site and an altered orientation of the
catalytic residue Arg48 relative to the other five subunits of the hexamer.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Labesse,
K.Benkali,
I.Salard-Arnaud,
A.M.Gilles,
and
H.Munier-Lehmann
(2011).
Structural and functional characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis uridine monophosphate kinase: insights into the allosteric regulation.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
39,
3458-3472.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yan,
K.Li,
H.Ding,
C.Liao,
X.Li,
L.Yuan,
and
C.Li
(2011).
Root morphological and proteomic responses to growth restriction in maize plants supplied with sufficient N.
|
| |
J Plant Physiol,
168,
1067-1075.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Dellas,
and
J.P.Noel
(2010).
Mutation of archaeal isopentenyl phosphate kinase highlights mechanism and guides phosphorylation of additional isoprenoid monophosphates.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
5,
589-601.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Meyer,
C.Evrin,
P.Briozzo,
N.Joly,
O.Bârzu,
and
A.M.Gilles
(2008).
Structural and Functional Characterization of Escherichia coli UMP Kinase in Complex with Its Allosteric Regulator GTP.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
36011-36018.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Pakhomova,
S.G.Bartlett,
A.Augustus,
T.Kuzuyama,
and
M.E.Newcomer
(2008).
Crystal Structure of Fosfomycin Resistance Kinase FomA from Streptomyces wedmorensis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
28518-28526.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
| |

