 |
PDBsum entry 2f3m

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of human glutathione s-transferase m1a-1a complexed with 1- (s-(glutathionyl)-2,4,6-trinitrocyclohexadienate anion
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glutathione s-transferase mu 1. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: gstm1-1, gst class-mu 1, gstm1a-1a, gstm1b-1b, hb subunit 4, gth4. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: gstm1, gst1. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from
)
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.234
|
R-free:
|
0.264
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Patskovsky,L.Patskovska,S.C.Almo,I.Listowsky
|
Key ref:

|
 |
Y.Patskovsky
et al.
(2006).
Transition state model and mechanism of nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions catalyzed by human glutathione S-transferase M1a-1a.
Biochemistry,
45,
3852-3862.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Nov-05
|
Release date:
|
25-Apr-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P09488
(GSTM1_HUMAN) -
Glutathione S-transferase Mu 1 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
218 a.a.
218 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.18
- glutathione transferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
RX + glutathione = an S-substituted glutathione + a halide anion + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
RX
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 57.14% similarity
|
+
|
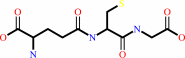 glutathione
glutathione
|
=
|
S-substituted glutathione
|
+
|
halide anion
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
45:3852-3862
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Transition state model and mechanism of nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions catalyzed by human glutathione S-transferase M1a-1a.
|
|
Y.Patskovsky,
L.Patskovska,
S.C.Almo,
I.Listowsky.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
An active site His107 residue distinguishes human glutathione S-transferase
hGSTM1-1 from other mammalian Mu-class GSTs. The crystal structure of hGSTM1a-1a
with bound glutathione (GSH) was solved to 1.9 A resolution, and site-directed
mutagenesis supports the conclusion that a proton transfer occurs in which bound
water at the catalytic site acts as a primary proton acceptor from the GSH thiol
group to transfer the proton to His107. The structure of the second
substrate-binding site (H-site) was determined from hGSTM1a-1a complexed with
1-glutathionyl-2,4-dinitrobenzene (GS-DNB) formed by a reaction in the crystal
between GSH and 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB). In that structure, the
GSH-binding site (G-site) is occupied by the GSH moiety of the product in the
same configuration as that of the enzyme-GSH complex, and the dinitrobenzene
ring is anchored between the side chains of Tyr6, Leu12, His107, Met108, and
Tyr115. This orientation suggested a distinct transition state that was
substantiated from the structure of hGSTM1a-1a complexed with transition state
analogue 1-S-(glutathionyl)-2,4,6-trinitrocyclohexadienate (Meisenheimer
complex). Kinetic data for GSTM1a-1a indicate that kcat(CDNB) for the reaction
is more than 3 times greater than kcat(FDNB), even though the nonenzymatic
second-order rate constant is more than 50-fold greater for
1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (FDNB), and the product is the same for both
substrates. In addition, Km(FDNB) is about 20 times less than Km(CDNB). The
results are consistent with a mechanism in which the formation of the transition
state is rate-limiting in the nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Data
obtained with active-site mutants support transition states in which Tyr115,
Tyr6, and His107 side chains are involved in the stabilization of the
Meisenheimer complex via interactions with the ortho nitro group of CDNB or FDNB
and provide insight into the means by which GSTs adapt to accommodate different
substrates.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Salazar-Medina,
L.García-Rico,
K.D.García-Orozco,
E.Valenzuela-Soto,
C.A.Contreras-Vergara,
R.Arreola,
A.Arvizu-Flores,
and
R.R.Sotelo-Mundo
(2010).
Inhibition by Cu2+ and Cd2+ of a mu-class glutathione S-transferase from shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei.
|
| |
J Biochem Mol Toxicol,
24,
218-222.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

