 |
PDBsum entry 2f0x

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure and function of human thioesterase superfamily member 2(them2)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Thioesterase superfamily member 2. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from
)
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.216
|
R-free:
|
0.247
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Z.Cheng,F.Song,X.Shan,Y.Wang,Z.Wei,W.Gong
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Z.Cheng
et al.
(2006).
Crystal structure of human thioesterase superfamily member 2.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
349,
172-177.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Nov-05
|
Release date:
|
10-Oct-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9NPJ3
(ACO13_HUMAN) -
Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 13 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
140 a.a.
136 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.2.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.2.2
- palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hexadecanoyl-CoA + H2O = hexadecanoate + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
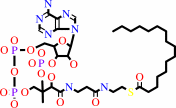 hexadecanoyl-CoA
hexadecanoyl-CoA
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
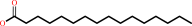 hexadecanoate
hexadecanoate
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochem Biophys Res Commun
349:172-177
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of human thioesterase superfamily member 2.
|
|
Z.Cheng,
F.Song,
X.Shan,
Z.Wei,
Y.Wang,
D.Dunaway-Mariano,
W.Gong.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Hotdog-fold has been identified in more than 1000 proteins, yet many of which in
eukaryotes are less studied. No structural or functional studies of human
thioesterase superfamily member 2 (hTHEM2) have been reported before. Since
hTHEM2 exhibits about 20% sequence identity to Escherichia coli PaaI protein, it
was proposed to be a thioesterase with a hotdog-fold. Here, we report the
crystallographic structure of recombinant hTHEM2, determined by the
single-wavelength anomalous dispersion method at 2.3A resolution. This structure
demonstrates that hTHEM2 indeed contains a hotdog-fold and forms a back-to-back
tetramer as other hotdog proteins. Based on structural and sequence
conservation, the thioesterase active site in hTHEM2 is predicted. The structure
and substrate specificity are most similar to those of the bacterial
phenylacetyl-CoA hydrolase. Asp65, located on the central alpha-helix of subunit
B, was shown by site-directed mutagenesis to be essential to catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Q.Ren,
Jing Zhou,
X.F.Zhao,
and
J.X.Wang
(2011).
Potential role of single hotdog fold thioesterase in the antiviral response of Fenneropenaeus chinensis.
|
| |
Fish Shellfish Immunol,
30,
1192-1196.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Kirkby,
N.Roman,
B.Kobe,
S.Kellie,
and
J.K.Forwood
(2010).
Functional and structural properties of mammalian acyl-coenzyme A thioesterases.
|
| |
Prog Lipid Res,
49,
366-377.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Cao,
H.Xu,
H.Zhao,
W.Gong,
and
D.Dunaway-Mariano
(2009).
The mechanisms of human hotdog-fold thioesterase 2 (hTHEM2) substrate recognition and catalysis illuminated by a structure and function based analysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
1293-1304.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wei,
H.W.Kang,
and
D.E.Cohen
(2009).
Thioesterase superfamily member 2 (Them2)/acyl-CoA thioesterase 13 (Acot13): a homotetrameric hotdog fold thioesterase with selectivity for long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs.
|
| |
Biochem J,
421,
311-322.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.S.Pidugu,
K.Maity,
K.Ramaswamy,
N.Surolia,
and
K.Suguna
(2009).
Analysis of proteins with the 'hot dog' fold: prediction of function and identification of catalytic residues of hypothetical proteins.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
37.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kotaka,
R.Kong,
I.Qureshi,
Q.S.Ho,
H.Sun,
C.W.Liew,
L.P.Goh,
P.Cheung,
Y.Mu,
J.Lescar,
and
Z.X.Liang
(2009).
Structure and catalytic mechanism of the thioesterase CalE7 in enediyne biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
15739-15749.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hosaka,
K.Murayama,
M.Kato-Murayama,
A.Urushibata,
R.Akasaka,
T.Terada,
M.Shirouzu,
S.Kuramitsu,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2009).
Structure of the putative thioesterase protein TTHA1846 from Thermus thermophilus HB8 complexed with coenzyme A and a zinc ion.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
767-776.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Angelini,
L.Cendron,
S.Goncalves,
G.Zanotti,
and
L.Terradot
(2008).
Structural and enzymatic characterization of HP0496, a YbgC thioesterase from Helicobacter pylori.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
1212-1221.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Kanno,
M.K.Wu,
D.S.Agate,
B.J.Fanelli,
N.Wagle,
E.F.Scapa,
C.Ukomadu,
and
D.E.Cohen
(2007).
Interacting proteins dictate function of the minimal START domain phosphatidylcholine transfer protein/StarD2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
30728-30736.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Smith,
and
S.C.Tsai
(2007).
The type I fatty acid and polyketide synthases: a tale of two megasynthases.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
24,
1041-1072.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

