 |
PDBsum entry 2e80

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2e80
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.7.2.2
- nitrite reductase (cytochrome; ammonia-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
6 Fe(III)-[cytochrome c] + NH4+ + 2 H2O = 6 Fe(II)-[cytochrome c] + nitrite + 8 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
6
×
Fe(III)-[cytochrome c]
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
=
|
6
×
Fe(II)-[cytochrome c]
|
+
|
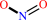 nitrite
nitrite
|
+
|
8
×
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+); Heme
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Ca(2+)
|
Heme
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
HEM)
matches with 95.45% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
124:11737-11745
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanism of the six-electron reduction of nitrite to ammonia by cytochrome c nitrite reductase.
|
|
O.Einsle,
A.Messerschmidt,
R.Huber,
P.M.Kroneck,
F.Neese.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cytochrome c nitrite reductase catalyzes the six-electron reduction of nitrite
to ammonia without the release of potential reaction intermediates, such as NO
or hydroxylamine. On the basis of the crystallographic observation of reaction
intermediates and of density functional calculations, we present a working
hypothesis for the reaction mechanism of this multiheme enzyme which carries a
novel lysine-coordinated heme group (Fe-Lys). It is proposed that nitrite
reduction starts with a heterolytic cleavage of the N-O bond which is
facilitated by a pronounced back-bonding interaction of nitrite coordinated
through nitrogen to the reduced (Fe(II)) but not the oxidized (Fe(III)) active
site iron. This step leads to the formation of an [FeNO](6) species and a water
molecule and is further facilitated by a hydrogen bonding network that induces
an electronic asymmetry in the nitrite molecule that weakens one N-O bond and
strengthens the other. Subsequently, two rapid one-electron reductions lead to
an [FeNO](8) form and, by protonation, to an Fe(II)-HNO adduct. Hereafter,
hydroxylamine will be formed by a consecutive two-electron two-proton step which
is dehydrated in the final two-electron reduction step to give ammonia and an
additional water molecule. A single electron reduction of the active site closes
the catalytic cycle.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Bykov,
and
F.Neese
(2011).
Substrate binding and activation in the active site of cytochrome c nitrite reductase: a density functional study.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
16,
417-430.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Rinaldo,
G.Giardina,
N.Castiglione,
V.Stelitano,
and
F.Cutruzzolà
(2011).
The catalytic mechanism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cd1 nitrite reductase.
|
| |
Biochem Soc Trans,
39,
195-200.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Silveira,
S.Besson,
I.Moura,
J.J.Moura,
and
M.G.Almeida
(2010).
Measuring the cytochrome C nitrite reductase activity-practical considerations on the enzyme assays.
|
| |
Bioinorg Chem Appl,
(),
0.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.L.Kemp,
T.A.Clarke,
S.J.Marritt,
C.Lockwood,
S.R.Poock,
A.M.Hemmings,
D.J.Richardson,
M.R.Cheesman,
and
J.N.Butt
(2010).
Kinetic and thermodynamic resolution of the interactions between sulfite and the pentahaem cytochrome NrfA from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochem J,
431,
73-80.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kern,
F.Eisel,
J.Scheithauer,
R.G.Kranz,
and
J.Simon
(2010).
Substrate specificity of three cytochrome c haem lyase isoenzymes from Wolinella succinogenes: unconventional haem c binding motifs are not sufficient for haem c attachment by NrfI and CcsA1.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
75,
122-137.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Yi,
J.Heinecke,
H.Tan,
P.C.Ford,
and
G.B.Richter-Addo
(2009).
The distal pocket histidine residue in horse heart myoglobin directs the O-binding mode of nitrite to the heme iron.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
18119-18128.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Gutiérrez,
G.B.Alluisetti,
C.Gaviglio,
F.Doctorovich,
J.A.Olabe,
and
V.T.Amorebieta
(2009).
Catalytic disproportionation of N-alkylhydroxylamines bound to pentacyanoferrates.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
1187-1194.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Xu,
and
G.S.Thomas
(2008).
Ambidentate H-bonding by heme-bound NO: structural and spectral effects of -O versus -N H-bonding.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
13,
613-621.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.van Wonderen,
B.Burlat,
D.J.Richardson,
M.R.Cheesman,
and
J.N.Butt
(2008).
The nitric oxide reductase activity of cytochrome c nitrite reductase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
9587-9594.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Kostera,
M.D.Youngblut,
J.M.Slosarczyk,
and
A.A.Pacheco
(2008).
Kinetic and product distribution analysis of NO* reductase activity in Nitrosomonas europaea hydroxylamine oxidoreductase.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
13,
1073-1083.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.V.Tikhonova,
E.S.Slutskaya,
A.A.Filimonenkov,
K.M.Boyko,
S.Y.Kleimenov,
P.V.Konarev,
K.M.Polyakov,
D.I.Svergun,
A.A.Trofimov,
V.G.Khomenkov,
R.A.Zvyagilskaya,
and
V.O.Popov
(2008).
Isolation and oligomeric composition of cytochrome c nitrite reductase from the haloalkaliphilic bacterium Thioalkalivibrio nitratireducens.
|
| |
Biochemistry (Mosc),
73,
164-170.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.N.Zahran,
L.Chooback,
D.M.Copeland,
A.H.West,
and
G.B.Richter-Addo
(2008).
Crystal structures of manganese- and cobalt-substituted myoglobin in complex with NO and nitrite reveal unusual ligand conformations.
|
| |
J Inorg Biochem,
102,
216-233.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Rodrigues,
T.Oliveira,
P.M.Matias,
I.C.Martins,
F.M.Valente,
I.A.Pereira,
and
M.Archer
(2006).
Crystallization and preliminary structure determination of the membrane-bound complex cytochrome c nitrite reductase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
565-568.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.G.Mowat,
and
S.K.Chapman
(2005).
Multi-heme cytochromes--new structures, new chemistry.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
3381-3389.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Allen,
P.D.Barker,
O.Daltrop,
J.M.Stevens,
E.J.Tomlinson,
N.Sinha,
Y.Sambongi,
and
S.J.Ferguson
(2005).
Why isn't 'standard' heme good enough for c-type and d1-type cytochromes?
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
3410-3418.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kura,
S.Kuwata,
and
T.Ikariya
(2005).
N-Methylhydroxylamido(1-)- and nitrosomethaneruthenium complexes derived from nitrosyl complexes: reversible N-protonation of an N-coordinated nitrosoalkane.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
44,
6406-6409.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Nasri,
M.K.Ellison,
M.Shang,
C.E.Schulz,
and
W.R.Scheidt
(2004).
Variable pi-bonding in iron(II) porphyrinates with nitrite, CO, and tert-butyl isocyanide: characterization of [Fe(TpivPP)(NO2)(CO)]-.
|
| |
Inorg Chem,
43,
2932-2942.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Cabello,
C.Pino,
M.F.Olmo-Mira,
F.Castillo,
M.D.Roldán,
and
C.Moreno-Vivián
(2004).
Hydroxylamine assimilation by Rhodobacter capsulatus E1F1. requirement of the hcp gene (hybrid cluster protein) located in the nitrate assimilation nas gene region for hydroxylamine reduction.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
45485-45494.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Clarke,
V.Dennison,
H.E.Seward,
B.Burlat,
J.A.Cole,
A.M.Hemmings,
and
D.J.Richardson
(2004).
Purification and spectropotentiometric characterization of Escherichia coli NrfB, a decaheme homodimer that transfers electrons to the decaheme periplasmic nitrite reductase complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
41333-41339.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Cunha,
S.Macieira,
J.M.Dias,
G.Almeida,
L.L.Goncalves,
C.Costa,
J.Lampreia,
R.Huber,
J.J.Moura,
I.Moura,
and
M.J.Romão
(2003).
Cytochrome c nitrite reductase from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans ATCC 27774. The relevance of the two calcium sites in the structure of the catalytic subunit (NrfA).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
17455-17465.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

