 |
PDBsum entry 2id2

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2id2
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Gapn t244s mutant x-ray structure at 2.5 a
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
NADP-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: non-phosphorylating glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [nadp+], triosephosphate dehydrogenase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Streptococcus mutans. Organism_taxid: 1309. Strain: clarke 1924. Gene: gapn. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.176
|
R-free:
|
0.227
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Pailot,K.D'Ambrosio,C.Corbier,F.Talfournier,G.Branlant
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Pailot
et al.
(2006).
Invariant Thr244 is essential for the efficient acylation step of the non-phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus mutans.
Biochem J,
400,
521-530.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Sep-06
|
Release date:
|
18-Sep-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q59931
(GAPN_STRMU) -
NADP-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus mutans serotype c (strain ATCC 700610 / UA159)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
475 a.a.
473 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.9
- glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NADP(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + NADP+ + H2O = (2R)-3-phosphoglycerate + NADPH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
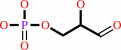 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
(2R)-3-phosphoglycerate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochem J
400:521-530
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Invariant Thr244 is essential for the efficient acylation step of the non-phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus mutans.
|
|
A.Pailot,
K.D'Ambrosio,
C.Corbier,
F.Talfournier,
G.Branlant.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
One of the most striking features of several X-ray structures of CoA-independent
ALDHs (aldehyde dehydrogenases) in complex with NAD(P) is the conformational
flexibility of the NMN moiety. However, the fact that the rate of the acylation
step is high in GAPN (non-phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase) from Streptococcus mutans implies an optimal positioning of the
nicotinamide ring relative to the hemithioacetal intermediate within the ternary
GAPN complex to allow an efficient and stereospecific hydride transfer.
Substitutions of serine for invariant Thr244 and alanine for Lys178 result in a
drastic decrease of the efficiency of hydride transfer which becomes
rate-limiting. The crystal structure of the binary complex T244S GAPN-NADP shows
that the absence of the beta-methyl group leads to a well-defined conformation
of the NMN part, including the nicotinamide ring, clearly different from that
depicted to be suitable for an efficient hydride transfer in the wild-type. The
approximately 0.6-unit increase in pK(app) of the catalytic Cys302 observed in
the ternary complex for both mutated GAPNs is likely to be due to a slight
difference in positioning of the nicotinamide ring relative to Cys302 with
respect to the wild-type ternary complex. Taken together, the data support a
critical role of the Thr244 beta-methyl group, held in position through a
hydrogen-bond interaction between the Thr244 beta-hydroxy group and the
epsilon-amino group of Lys178, in permitting the nicotinamide ring to adopt a
conformation suitable for an efficient hydride transfer during the acylation
step for all the members of the CoA-independent ALDH family.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

