 |
PDBsum entry 1wpy

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.4.15
- biotin--[biotin carboxyl-carrier protein] ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
biotin + L-lysyl-[protein] + ATP = N6-biotinyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + AMP + diphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
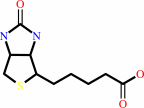 biotin
biotin
|
+
|
L-lysyl-[protein]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
N(6)-biotinyl-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
353:322-333
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of biotin protein ligase from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 and its complexes: structural basis of biotin activation.
|
|
B.Bagautdinov,
C.Kuroishi,
M.Sugahara,
N.Kunishima.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Biotin protein ligase (EC 6.3.4.15) catalyses the synthesis of an activated form
of biotin, biotinyl-5'-AMP, from substrates biotin and ATP followed by
biotinylation of the biotin carboxyl carrier protein subunit of acetyl-CoA
carboxylase. The three-dimensional structure of biotin protein ligase from
Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 has been determined by X-ray diffraction at 1.6A
resolution. The structure reveals a homodimer as the functional unit. Each
subunit contains two domains, a larger N-terminal catalytic domain and a smaller
C-terminal domain. The structural feature of the active site has been studied by
determination of the crystal structures of complexes of the enzyme with biotin,
ADP and the reaction intermediate biotinyl-5'-AMP at atomic resolution. This is
the first report of the liganded structures of biotin protein ligase with
nucleotide and biotinyl-5'-AMP. The structures of the unliganded and the
liganded forms are isomorphous except for an ordering of the active site loop
upon ligand binding. Catalytic binding sites are suitably arranged to minimize
the conformational changes required during the reaction, as the pockets for
biotin and nucleotide are located spatially adjacent to each other in a cleft of
the catalytic domain and the pocket for biotinyl-5'-AMP binding mimics the
combination of those of the substrates. The exact locations of the ligands and
the active site residues allow us to propose a general scheme for the first step
of the reaction carried out by biotin protein ligase in which the positively
charged epsilon-amino group of Lys111 facilitates the nucleophilic attack on the
ATP alpha-phosphate group by the biotin carboxyl oxygen atom and stabilizes the
negatively charged intermediates.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. Charge distribution of the molecular surface of
the biotinyl-5'-AMP liganded form. Negatively and positively
charged surfaces are coloured red and blue, respectively. The
active site architecture fits well for the ligase reaction
intermediate, biotinyl-5'-AMP, with its ureido and
tetrahydrothiophene rings of biotinyl moiety bound deep into the
cleft. The active site residues are labelled.
|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7. Hydrogen bonding interactions (within 3.5
Å) between the protein and (a) biotin, (b) ADP and (c)
biotinyl-5'-AMP, as indicated by the broken lines with distances
in Å. Relevant amino acids with hydrogen bonds are shown.
The relevant ligand atoms involved in the interactions are
labelled.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2005,
353,
322-333)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.Gupta,
R.K.Gupta,
G.Khare,
D.M.Salunke,
A.Surolia,
and
A.K.Tyagi
(2010).
Structural ordering of disordered ligand-binding loops of biotin protein ligase into active conformations as a consequence of dehydration.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
e9222.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Bagautdinov,
Y.Matsuura,
S.Bagautdinova,
and
N.Kunishima
(2008).
Protein biotinylation visualized by a complex structure of biotin protein ligase with a substrate.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
14739-14750.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sugahara,
Y.Asada,
K.Shimizu,
H.Yamamoto,
N.K.Lokanath,
H.Mizutani,
B.Bagautdinov,
Y.Matsuura,
M.Taketa,
Y.Kageyama,
N.Ono,
Y.Morikawa,
Y.Tanaka,
H.Shimada,
T.Nakamoto,
M.Sugahara,
M.Yamamoto,
and
N.Kunishima
(2008).
High-throughput crystallization-to-structure pipeline at RIKEN SPring-8 Center.
|
| |
J Struct Funct Genomics,
9,
21-28.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.R.Pendini,
S.W.Polyak,
G.W.Booker,
J.C.Wallace,
and
M.C.Wilce
(2008).
Purification, crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of biotin protein ligase from Staphylococcus aureus.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
520-523.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Purushothaman,
G.Gupta,
R.Srivastava,
V.G.Ramu,
and
A.Surolia
(2008).
Ligand specificity of group I biotin protein ligase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
3,
e2320.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
d.o. .J.Kim,
S.J.Lee,
H.S.Kim,
K.H.Kim,
H.H.Lee,
H.J.Yoon,
and
S.W.Suh
(2008).
Structural basis of octanoic acid recognition by lipoate-protein ligase B.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
1620-1625.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Bagautdinov,
Y.Matsuura,
S.Bagautdinova,
and
N.Kunishima
(2007).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of the biotin carboxyl carrier protein and biotin protein ligase complex from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
334-337.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Müller,
and
B.Kappes
(2007).
Vitamin and cofactor biosynthesis pathways in Plasmodium and other apicomplexan parasites.
|
| |
Trends Parasitol,
23,
112-121.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Naganathan,
and
D.Beckett
(2007).
Nucleation of an allosteric response via ligand-induced loop folding.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
373,
96.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Ma,
X.Zhao,
A.Nasser Eddine,
A.Geerlof,
X.Li,
J.E.Cronan,
S.H.Kaufmann,
and
M.Wilmanns
(2006).
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis LipB enzyme functions as a cysteine/lysine dyad acyltransferase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
8662-8667.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

