 |
PDBsum entry 2evb

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lipid binding protein,transferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2evb
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.3.1
- methylmalonyl-CoA carboxytransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-methylmalonyl-CoA + pyruvate = propanoyl-CoA + oxaloacetate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
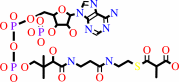 (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA
(S)-methylmalonyl-CoA
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
=
|
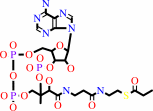 propanoyl-CoA
propanoyl-CoA
|
+
|
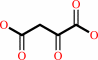 oxaloacetate
oxaloacetate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Biotin; Cobalt cation; Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
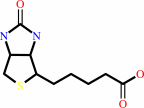 Biotin
Biotin
|
Cobalt cation
|
Zn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
283:14739-14750
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Protein biotinylation visualized by a complex structure of biotin protein ligase with a substrate.
|
|
B.Bagautdinov,
Y.Matsuura,
S.Bagautdinova,
N.Kunishima.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Biotin protein ligase (BPL) catalyzes the biotinylation of the biotin carboxyl
carrier protein (BCCP) only at a special lysine residue. Here we report the
first structure of BPL.BCCP complex crystals, which are prepared using two BPL
mutants: R48A and R48A/K111A. From a detailed structural characterization, it is
likely that the mutants retain functionality as enzymes but have a reduced
activity to produce the reaction intermediate biotinyl-5'-AMP. The observed
biotin and partly disordered ATP in the mutant structures may act as a
non-reactive analog of the substrates or biotinyl-5'-AMP, thereby providing the
complex crystals. The four crystallographically independent BPL.BCCP complexes
obtained can be classified structurally into three groups: the formation stages
1 and 2 with apo-BCCP and the product stage with biotinylated holo-BCCP.
Residues responsible for the complex formation as well as for the biotinylation
reaction have been identified. The C-terminal domain of BPL shows especially
large conformational changes to accommodate BCCP, suggesting its functional
importance. The formation stage 1 complex shows the closest distance between the
carboxyl carbon of biotin and the special lysine of BCCP, suggesting its
relevance to the unobserved reaction stage. Interestingly, bound ATP and biotin
are also seen in the product stage, indicating that the substrates may be
recruited into the product stage complex before the release of holo-BCCP,
probably for the next reaction cycle. The existence of formation and product
stages before and after the reaction stage would be favorable to ensure both the
reaction efficiency and the extreme substrate specificity of the biotinylation
reaction.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
FIGURE 3. Interface charge distribution in the double
mutant complex. The formation stage 1 complex observed in the B
and D subunits is presented. Electrostatic potential surface
representation for PhBPL (blue and red colors correspond to
positive and negative potentials, respectively) and ribbon
representation for PhBCCP are used. The buried residues of
PhBCCP at the protein·protein interface are shown as
stick models.
|
 |
Figure 5.
FIGURE 5. Enlarged stereo representation showing
intermolecular interactions in the double mutant complex.
Residues involved in the intermolecular direct hydrogen bonds
(2.2-3.5 Å) are shown in stick models and labeled. The
hydrogen bonds are indicated by red dotted lines. A, subunits B
and D in the formation stage 1; B, subunits A and C in the
product stage.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2008,
283,
14739-14750)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.V.Demirev,
A.Khanal,
B.R.Sedai,
S.K.Lim,
M.K.Na,
and
D.H.Nam
(2010).
The role of acyl-coenzyme A carboxylase complex in lipstatin biosynthesis of Streptomyces toxytricini.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
87,
1129-1139.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Solbiati,
and
J.E.Cronan
(2010).
The switch regulating transcription of the Escherichia coli biotin operon does not require extensive protein-protein interactions.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
17,
11-17.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Gupta,
R.K.Gupta,
G.Khare,
D.M.Salunke,
A.Surolia,
and
A.K.Tyagi
(2010).
Structural ordering of disordered ligand-binding loops of biotin protein ligase into active conformations as a consequence of dehydration.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
e9222.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.I.Hassan,
H.Moriyama,
and
J.Zempleni
(2010).
The polypeptide Syn67 interacts physically with human holocarboxylase synthetase, but is not a target for biotinylation.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
495,
35-41.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Beckett
(2009).
Biotin sensing at the molecular level.
|
| |
J Nutr,
139,
167-170.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Healy,
T.D.Heightman,
L.Hohmann,
D.Schriemer,
and
R.A.Gravel
(2009).
Nonenzymatic biotinylation of histone H2A.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
314-328.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Puthenveetil,
D.S.Liu,
K.A.White,
S.Thompson,
and
A.Y.Ting
(2009).
Yeast display evolution of a kinetically efficient 13-amino acid substrate for lipoic acid ligase.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
16430-16438.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.I.Hassan,
H.Moriyama,
L.J.Olsen,
X.Bi,
and
J.Zempleni
(2009).
N- and C-terminal domains in human holocarboxylase synthetase participate in substrate recognition.
|
| |
Mol Genet Metab,
96,
183-188.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

