 |
PDBsum entry 1v3q

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of human pnp complexed with ddi
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Chain: e. Synonym: inosine phosphorylase, pnp. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pnp. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Trimer (from PDB file)
Trimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.214
|
R-free:
|
0.306
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
F.Canduri,J.H.Pereira,D.M.Dos Santos,R.G.Silva,M.S.Palma,L.A.Basso, W.F.De Azevedo Jr.,D.S.Santos
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
F.Canduri
et al.
(2004).
Structures of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase complexed with inosine and ddI.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
313,
907-914.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Nov-03
|
Release date:
|
20-Jan-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00491
(PNPH_HUMAN) -
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
289 a.a.
288 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.1
- purine-nucleoside phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a purine D-ribonucleoside + phosphate = a purine nucleobase + alpha- D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
2.
|
a purine 2'-deoxy-D-ribonucleoside + phosphate = a purine nucleobase + 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
purine D-ribonucleoside
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
purine nucleobase
|
+
|
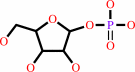 alpha- D-ribose 1-phosphate
alpha- D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
purine 2'-deoxy-D-ribonucleoside
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
purine nucleobase
|
+
|
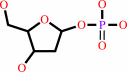 2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
2-deoxy-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochem Biophys Res Commun
313:907-914
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase complexed with inosine and ddI.
|
|
F.Canduri,
D.M.dos Santos,
R.G.Silva,
M.A.Mendes,
L.A.Basso,
M.S.Palma,
W.F.de Azevedo,
D.S.Santos.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Human purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) is a ubiquitous enzyme which plays a
key role in the purine salvage pathway, and PNP deficiency in humans leads to an
impairment of T-cell function, usually with no apparent effect on B-cell
function. PNP is highly specific for 6-oxopurine nucleosides and exhibits
negligible activity for 6-aminopurine nucleosides. The catalytic efficiency for
inosine is 350,000-fold greater than for adenosine. Adenine nucleosides and
nucleotides are deaminated by adenosine deaminase and AMP deaminase to their
corresponding inosine derivatives which, in turn, may be further degraded. Here
we report the crystal structures of human PNP in complex with inosine and
2('),3(')-dideoxyinosine, refined to 2.8A resolution using synchrotron
radiation. The present structures provide explanation for ligand binding, refine
the purine-binding site, and can be used for future inhibitor design.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.D'Muniz Pereira,
G.Oliva,
and
R.C.Garratt
(2011).
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Schistosoma mansoni in complex with ribose-1-phosphate.
|
| |
J Synchrotron Radiat,
18,
62-65.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Nannemann,
K.W.Kaufmann,
J.Meiler,
and
B.O.Bachmann
(2010).
Design and directed evolution of a dideoxy purine nucleoside phosphorylase.
|
| |
Protein Eng Des Sel,
23,
607-616.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.B.Zanchi,
R.A.Caceres,
R.G.Stabeli,
and
W.F.de Azevedo
(2010).
Molecular dynamics studies of a hexameric purine nucleoside phosphorylase.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
16,
543-550.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Bellows,
and
C.A.Floudas
(2010).
Computational methods for de novo protein design and its applications to the human immunodeficiency virus 1, purine nucleoside phosphorylase, ubiquitin specific protease 7, and histone demethylases.
|
| |
Curr Drug Targets,
11,
264-278.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Pauli,
L.F.Timmers,
R.A.Caceres,
L.A.Basso,
D.S.Santos,
and
W.F.de Azevedo
(2009).
Molecular modeling and dynamics studies of purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Bacteroides fragilis.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
15,
913-922.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Modrak-Wójcik,
A.Kirilenko,
D.Shugar,
and
B.Kierdaszuk
(2008).
Role of ionization of the phosphate cosubstrate on phosphorolysis by purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) of bacterial (E. coli) and mammalian (human) origin.
|
| |
Eur Biophys J,
37,
153-164.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Murkin,
M.R.Birck,
A.Rinaldo-Matthis,
W.Shi,
E.A.Taylor,
S.C.Almo,
and
V.L.Schramm
(2007).
Neighboring group participation in the transition state of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
5038-5049.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Canduri,
R.G.Silva,
D.M.dos Santos,
M.S.Palma,
L.A.Basso,
D.S.Santos,
and
W.F.de Azevedo
(2005).
Structure of human PNP complexed with ligands.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
856-862.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

