 |
PDBsum entry 1upc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Synthase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Carboxyethylarginine synthase from streptomyces clavuligerus
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carboxyethylarginine synthase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Streptomyces clavuligerus. Organism_taxid: 1901. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from PDB file)
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.45Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.178
|
R-free:
|
0.216
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.E.C.Caines,J.M.Elkins,K.S.Hewitson,C.J.Schofield
|
Key ref:

|
 |
M.E.Caines
et al.
(2004).
Crystal structure and mechanistic implications of N2-(2-carboxyethyl)arginine synthase, the first enzyme in the clavulanic acid biosynthesis pathway.
J Biol Chem,
279,
5685-5692.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Sep-03
|
Release date:
|
20-Nov-03
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9LCV9
(CEAS_STRCL) -
N(2)-(2-carboxyethyl)arginine synthase from Streptomyces clavuligerus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
573 a.a.
559 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.66
- N(2)-(2-carboxyethyl)arginine synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Clavulanate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + L-arginine = N2-(2-carboxyethyl)-L- arginine + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
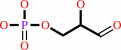 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
 L-arginine
L-arginine
|
=
|
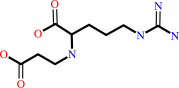 N(2)-(2-carboxyethyl)-L- arginine
N(2)-(2-carboxyethyl)-L- arginine
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
279:5685-5692
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure and mechanistic implications of N2-(2-carboxyethyl)arginine synthase, the first enzyme in the clavulanic acid biosynthesis pathway.
|
|
M.E.Caines,
J.M.Elkins,
K.S.Hewitson,
C.J.Schofield.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The initial step in the biosynthesis of the clinically important beta-lactamase
inhibitor clavulanic acid involves condensation of two primary metabolites,
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and L-arginine, to give
N2-(2-carboxyethyl)arginine, a beta-amino acid. This unusual N-C bond forming
reaction is catalyzed by the thiamin diphosphate (ThP2)-dependent enzyme
N2-(2-carboxyethyl)arginine synthase. Here we report the crystal structure of
N2-(2-carboxyethyl)arginine synthase, complexed with ThP2 and Mg2+, to 2.35-A
resolution. The structure was solved in two space groups, P2(1)2(1)2(1) and
P2(1)2(1)2. In both, the enzyme is observed in a tetrameric form, composed of a
dimer of two more tightly associated dimers, consistent with both mass
spectrometric and gel filtration chromatography studies. Both ThP2 and Mg2+
cofactors are present at the active site, with ThP2 in a "V" conformation as in
related enzymes. A sulfate anion is observed in the active site of the enzyme in
a location proposed as a binding site for the phosphate group of the
d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate substrate. The mechanistic implications of the
active site arrangement are discussed, including the potential role of the
aminopyrimidine ring of the ThP2. The structure will form a basis for future
mechanistic and structural studies, as well as engineering aimed at production
of alternative beta-amino acids.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIG. 1. Biosynthetic pathway leading to clavulanic acid.
BLS,  -lactam synthetase; PAH,
proclavaminate amidino hydrolase; CAS, clavaminic synthase; CAD,
clavaldehyde dehydrogenase; 2-OG, 2-oxoglutarate. -lactam synthetase; PAH,
proclavaminate amidino hydrolase; CAS, clavaminic synthase; CAD,
clavaldehyde dehydrogenase; 2-OG, 2-oxoglutarate.
|
 |
Figure 2.
FIG. 2. Structure of the CEAS tetramer. The ThP[2]
molecules are shown as a ball-and-stick representation.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2004,
279,
5685-5692)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Dawson,
M.Chen,
P.K.Fyfe,
Z.Guo,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2010).
Structure and reactivity of Bacillus subtilis MenD catalyzing the first committed step in menaquinone biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
401,
253-264.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Song,
S.E.Jensen,
and
K.J.Lee
(2010).
Clavulanic acid biosynthesis and genetic manipulation for its overproduction.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
88,
659-669.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Shaanan,
and
D.M.Chipman
(2009).
Reaction mechanisms of thiamin diphosphate enzymes: new insights into the role of a conserved glutamate residue.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
2447-2453.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Juan,
M.M.Hoque,
M.T.Hossain,
T.Yamamoto,
S.Imamura,
K.Suzuki,
T.Sekiguchi,
and
A.Takénaka
(2007).
The structures of pyruvate oxidase from Aerococcus viridans with cofactors and with a reaction intermediate reveal the flexibility of the active-site tunnel for catalysis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
900-907.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.McCourt,
and
R.G.Duggleby
(2006).
Acetohydroxyacid synthase and its role in the biosynthetic pathway for branched-chain amino acids.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
31,
173-210.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.J.Kershaw,
M.E.Caines,
M.C.Sleeman,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2005).
The enzymology of clavam and carbapenem biosynthesis.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
4251-4263.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.G.Mosbacher,
M.Mueller,
and
G.E.Schulz
(2005).
Structure and mechanism of the ThDP-dependent benzaldehyde lyase from Pseudomonas fluorescens.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
6067-6076.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Tahlan,
C.Anders,
and
S.E.Jensen
(2004).
The paralogous pairs of genes involved in clavulanic acid and clavam metabolite biosynthesis are differently regulated in Streptomyces clavuligerus.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
186,
6286-6297.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

