 |
PDBsum entry 1u3p

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Ispf native
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2-c-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase. Chain: a. Synonym: mecps, mecdp-synthase, ispf. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: ispf, mecs. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Trimer (from PDB file)
Trimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.85Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.226
|
R-free:
|
0.237
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Steinbacher,J.Kaiser,J.Wungsintaweekul,S.Hecht,W.Eisenreich, S.Gerhardt,A.Bacher,F.Rohdich
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Steinbacher
et al.
(2002).
Structure of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase involved in mevalonate-independent biosynthesis of isoprenoids.
J Mol Biol,
316,
79-88.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Jul-04
|
Release date:
|
31-Aug-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P62617
(ISPF_ECOLI) -
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
159 a.a.
155 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.6.1.12
- 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
4-CDP-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2-phosphate = 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4- cyclic diphosphate + CMP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
4-CDP-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2-phosphate
|
=
|
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4- cyclic diphosphate
|
+
|
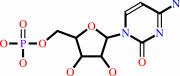 CMP
CMP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mn(2+) or Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
316:79-88
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of 2C-methyl-d-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase involved in mevalonate-independent biosynthesis of isoprenoids.
|
|
S.Steinbacher,
J.Kaiser,
J.Wungsintaweekul,
S.Hecht,
W.Eisenreich,
S.Gerhardt,
A.Bacher,
F.Rohdich.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Isoprenoids are biosynthesized from isopentenyl diphosphate and the isomeric
dimethylallyl diphosphate via the mevalonate pathway or a mevalonate-independent
pathway that was identified during the last decade. The non-mevalonate pathway
is present in many bacteria, some algae and in certain protozoa such as the
malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum and in the plastids of higher plants, but
not in mammals and archaea. Therefore, these enzymes have been recognised as
promising drug targets. We report the crystal structure of Escherichia coli 2C-
methyl-d-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (IspF), which converts
4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2-phosphate into
2C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate and CMP in a Mg-dependent reaction.
The protein forms homotrimers that tightly bind one zinc ion per subunit at the
active site, which helps to position the substrate for direct attack of the
2-phosphate group on the beta-phosphate.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Non-mevalonate pathway of isopentenyl and
dimethylallyldiphosphate biosynthesis. (a) Pyruvate and
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate are condensed to (b) 1-deoxy- Image
-xylulose 5-phosphate, which is converted into (c) 2C-methyl-
Image -erythritol 4-phosphate. Condensation with CTP yields (d)
4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl- Image -erythritol, which is
converted into (d) 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl- Image
-erythritol 2-phosphate. The last step identified so far is the
cyclisation of the latter to (f) 2C-methyl- Image -erythritol
2,4-cyclodiphosphate by IspF.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Omit electron density for bound substrate and
product molecules contoured at 2.5s (stereo view). All complexes
were prepared by soaking. (a) Product complex with bound CMP and
2C-methyl- Image -erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (data set
Prod). (b) Substrate complex with bound
4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl- Image -erythritol 2-phosphate and
zinc removed with EDTA; the green ball represents the zinc
position in the active enzyme (data set CDP-MEP). (c) Complex
with 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl- Image -erythritol (data set
CDP-ME). (d) Complex with MgCDP; the Mg ion bridges the a and
b-phosphate groups of CDP (data set MgCDP).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2002,
316,
79-88)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.Narayanasamy,
H.Eoh,
P.J.Brennan,
and
D.C.Crick
(2010).
Synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2-phosphate and kinetic studies of Mycobacterium tuberculosis IspF.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
17,
117-122.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Eoh,
P.J.Brennan,
and
D.C.Crick
(2009).
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis MEP (2C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate) pathway as a new drug target.
|
| |
Tuberculosis (Edinb),
89,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Chen,
Y.Xiao,
P.Di,
X.Yu,
W.Chen,
and
L.Zhang
(2009).
Molecular cloning and characterization of a 2C-methyl-D: -erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase gene from Cephalotaxus harringtonia.
|
| |
Mol Biol Rep,
36,
1749-1756.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.L.Ramsden,
L.Buetow,
A.Dawson,
L.A.Kemp,
V.Ulaganathan,
R.Brenk,
G.Klebe,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2009).
A structure-based approach to ligand discovery for 2C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase: a target for antimicrobial therapy.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
52,
2531-2542.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.M.Calisto,
J.Perez-Gil,
M.Bergua,
J.Querol-Audi,
I.Fita,
and
S.Imperial
(2007).
Biosynthesis of isoprenoids in plants: structure of the 2C-methyl-D-erithrytol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Comparison with the bacterial enzymes.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
16,
2082-2088.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Buetow,
A.C.Brown,
T.Parish,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2007).
The structure of Mycobacteria 2C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase, an essential enzyme, provides a platform for drug discovery.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
7,
68.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.N.Hunter
(2007).
The non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
21573-21577.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Crane,
J.Kaiser,
N.L.Ramsden,
S.Lauw,
F.Rohdich,
W.Eisenreich,
W.N.Hunter,
A.Bacher,
and
F.Diederich
(2006).
Fluorescent inhibitors for IspF, an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis and a potential target for antimalarial therapy.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
45,
1069-1074.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.H.Hsieh,
and
H.M.Goodman
(2006).
Functional evidence for the involvement of Arabidopsis IspF homolog in the nonmevalonate pathway of plastid isoprenoid biosynthesis.
|
| |
Planta,
223,
779-784.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Cornish,
J.R.Roth,
and
C.D.Poulter
(2006).
Lethal mutations in the isoprenoid pathway of Salmonella enterica.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
1444-1450.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Kim,
T.Kuzuyama,
Y.J.Chang,
and
S.U.Kim
(2006).
Cloning and characterization of 2-C-methyl-D: -erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (MECS) gene from Ginkgo biloba.
|
| |
Plant Cell Rep,
25,
829-835.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Kemp,
M.S.Alphey,
C.S.Bond,
M.A.Ferguson,
S.Hecht,
A.Bacher,
W.Eisenreich,
F.Rohdich,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2005).
The identification of isoprenoids that bind in the intersubunit cavity of Escherichia coli 2C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase by complementary biophysical methods.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
45-52.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Sgraja,
L.E.Kemp,
N.Ramsden,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2005).
A double mutation of Escherichia coli2C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase disrupts six hydrogen bonds with, yet fails to prevent binding of, an isoprenoid diphosphate.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
625-629.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Gabrielsen,
C.S.Bond,
I.Hallyburton,
S.Hecht,
A.Bacher,
W.Eisenreich,
F.Rohdich,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2004).
Hexameric assembly of the bifunctional methylerythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase and protein-protein associations in the deoxy-xylulose-dependent pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
52753-52761.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Gabrielsen,
F.Rohdich,
W.Eisenreich,
T.Gräwert,
S.Hecht,
A.Bacher,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2004).
Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: a bifunctional IspDF enzyme from Campylobacter jejuni.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
3028-3035.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ni,
H.Robinson,
G.C.Marsing,
D.E.Bussiere,
and
M.A.Kennedy
(2004).
Structure of 2C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase from Shewanella oneidensis at 1.6 A: identification of farnesyl pyrophosphate trapped in a hydrophobic cavity.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
1949-1957.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Miallau,
M.S.Alphey,
L.E.Kemp,
G.A.Leonard,
S.M.McSweeney,
S.Hecht,
A.Bacher,
W.Eisenreich,
F.Rohdich,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2003).
Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: crystal structure of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
9173-9178.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Lehmann,
K.Lim,
J.Toedt,
W.Krajewski,
A.Howard,
E.Eisenstein,
and
O.Herzberg
(2002).
Structure of 2C-methyl-D-erythrol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase from Haemophilus influenzae: activation by conformational transition.
|
| |
Proteins,
49,
135-138.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Kemp,
C.S.Bond,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2002).
Structure of 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4- cyclodiphosphate synthase: an essential enzyme for isoprenoid biosynthesis and target for antimicrobial drug development.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
6591-6596.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

